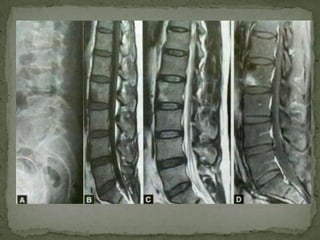
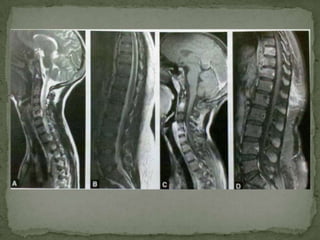
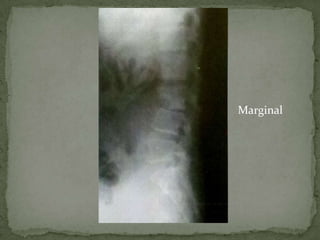
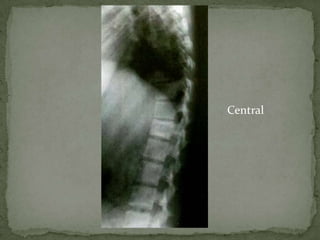
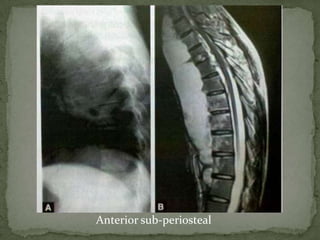
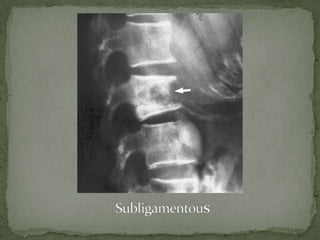
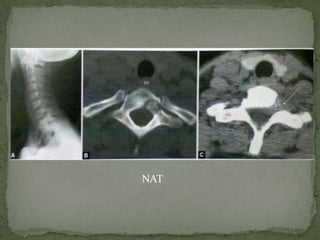
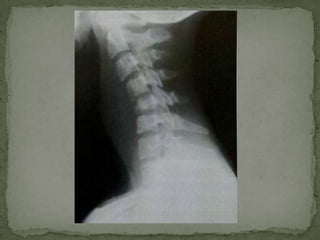
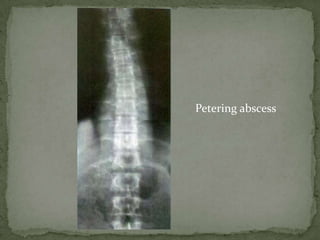
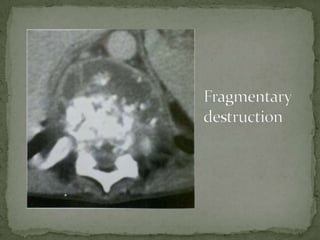
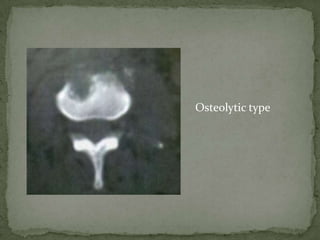
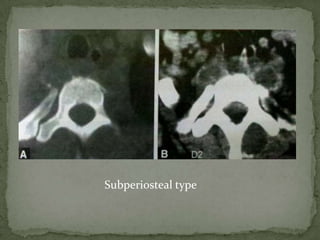
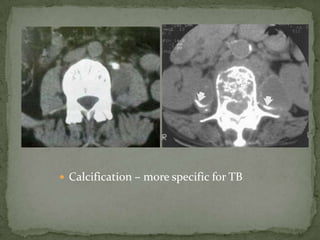
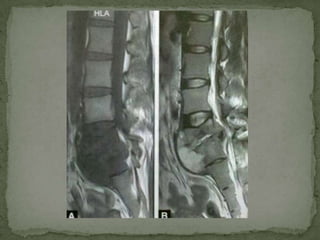
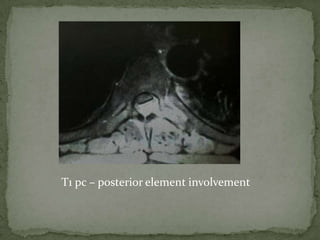
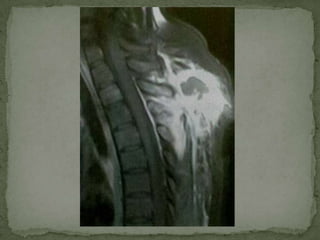
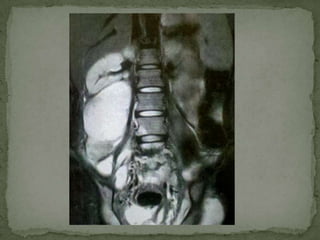
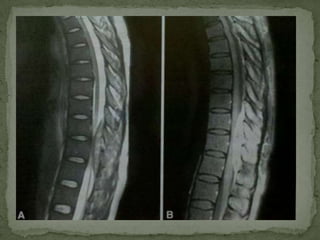
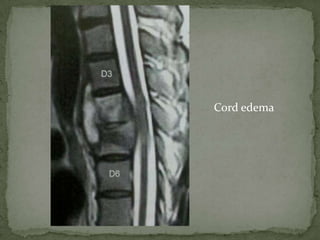
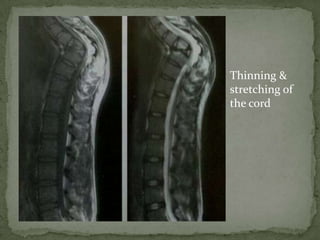
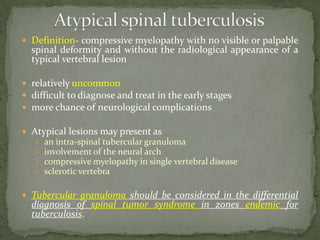
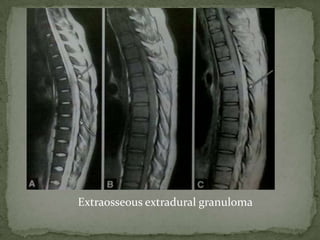
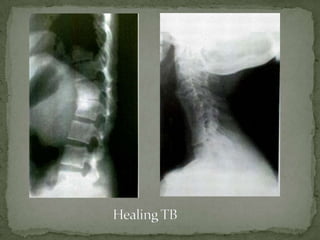
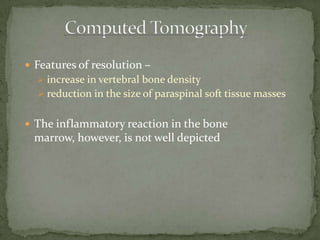
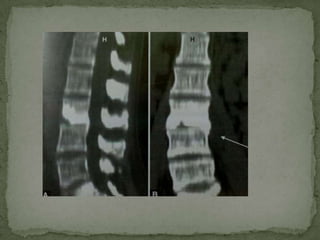
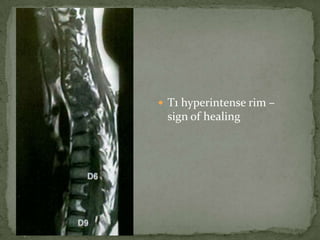
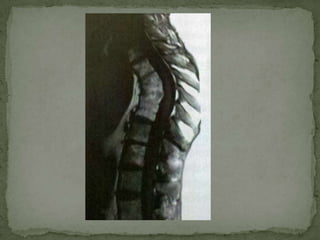
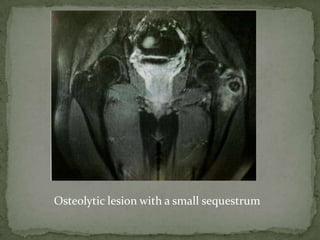
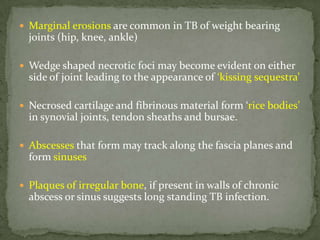
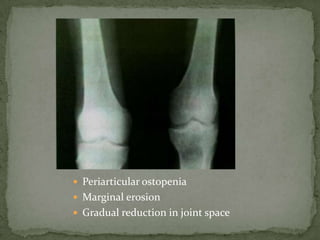
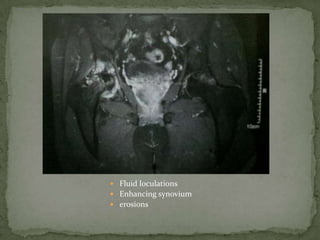
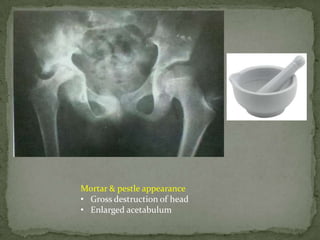
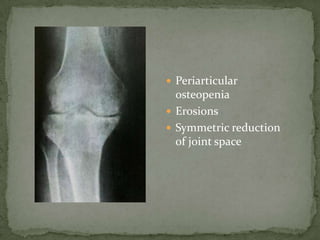
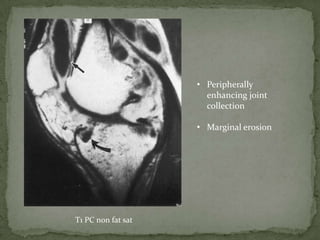
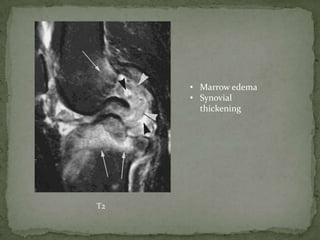
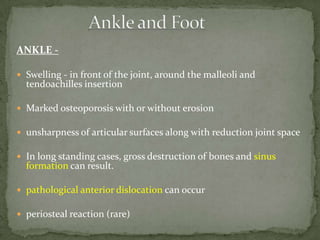
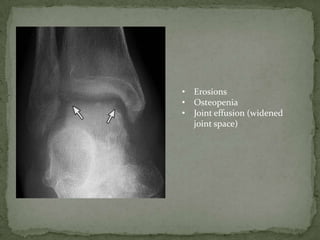
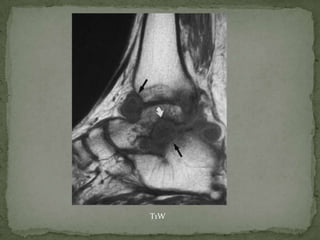
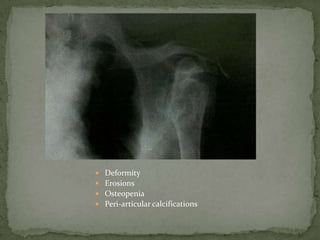
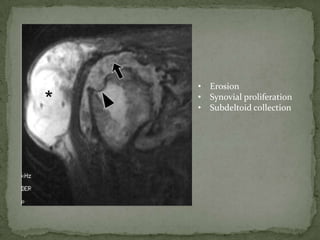
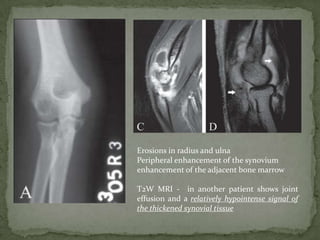
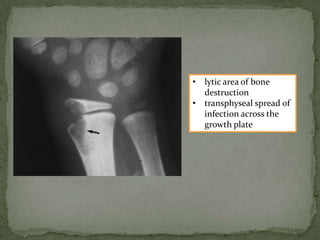
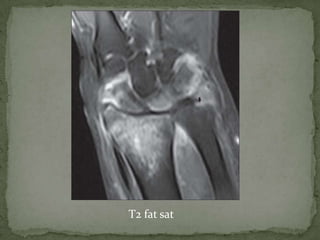
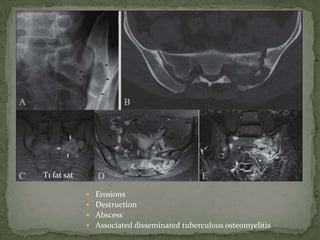
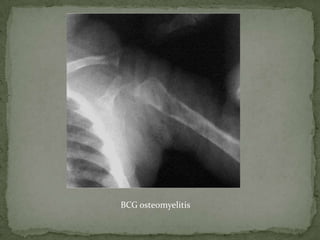
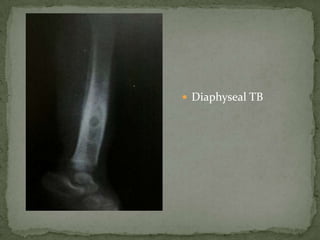
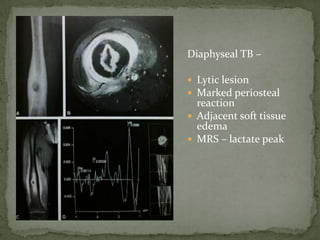
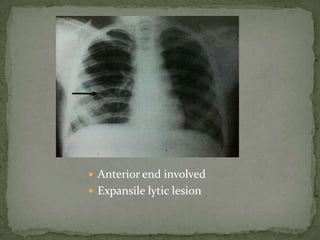
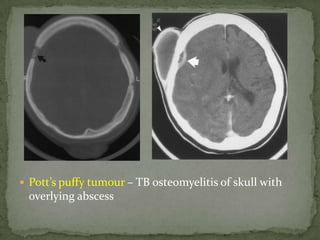
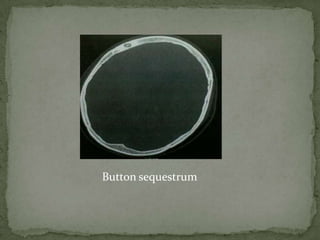
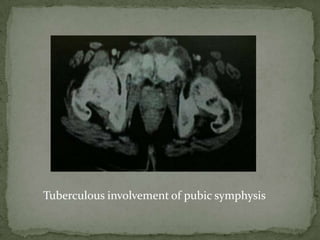
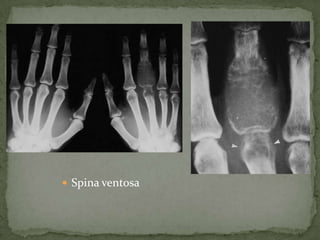
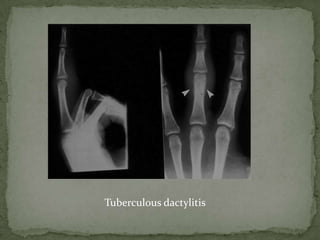
This document discusses tuberculosis of the spine (Pott's disease). It notes that the spine is the most common site of bone involvement by tuberculosis, with the lower thoracic and lumbar vertebrae most often affected. Tuberculosis of the spine typically begins in the cancellous bone and spreads to adjacent vertebrae and discs. This can lead to abscesses that track through soft tissues, potentially causing epidural abscesses and spinal cord compression. Imaging plays an important role in evaluating the extent of bone and soft tissue involvement.