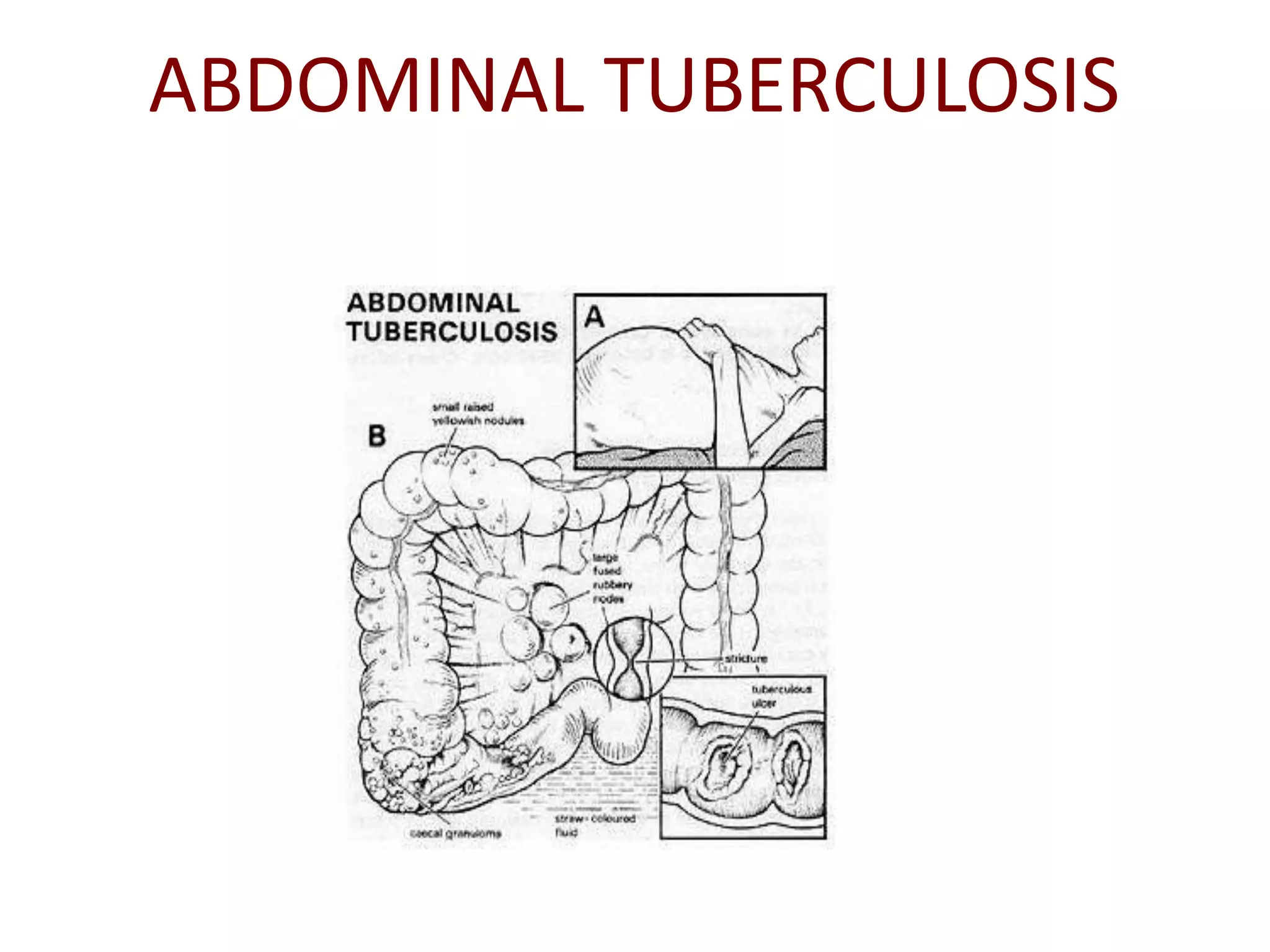
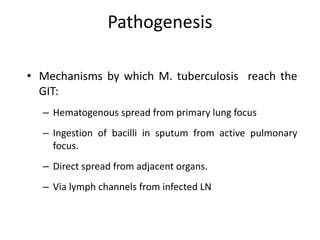
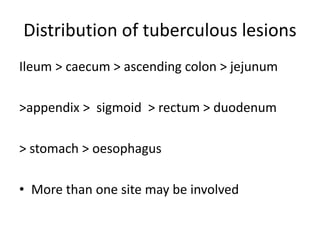
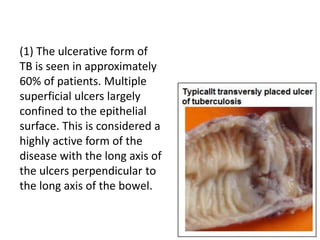
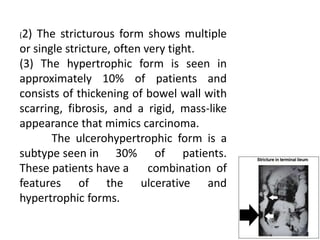
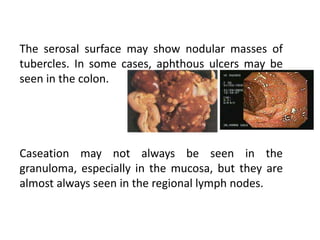
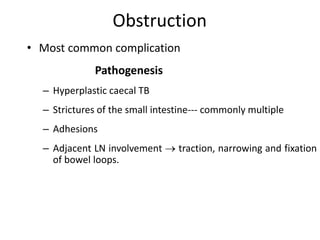
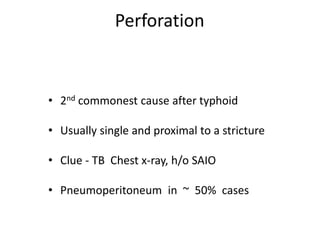
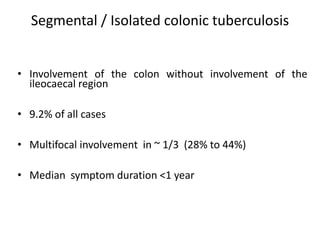
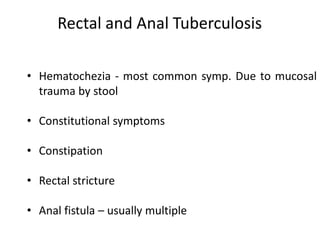
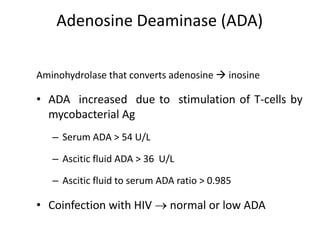
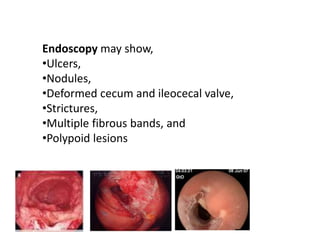
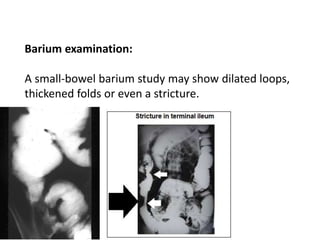
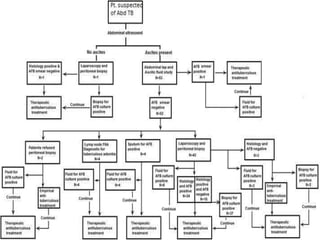
Abdominal tuberculosis can involve the gastrointestinal tract, peritoneum, and pancreatobiliary system. It most commonly involves the ileocecal region due to abundant lymphoid tissue. Patients typically present with nonspecific abdominal pain, fever, weight loss, and alteration of bowel habits. Diagnosis is challenging as findings are nonspecific but may include ascites, lymphadenopathy, bowel wall thickening on imaging. Definitive diagnosis requires biopsy and culture of tissue, with ascitic fluid analysis also useful. Treatment involves a combination of antibiotics administered for at least 6 months. Surgery may be needed for complications like obstruction or fistulae.