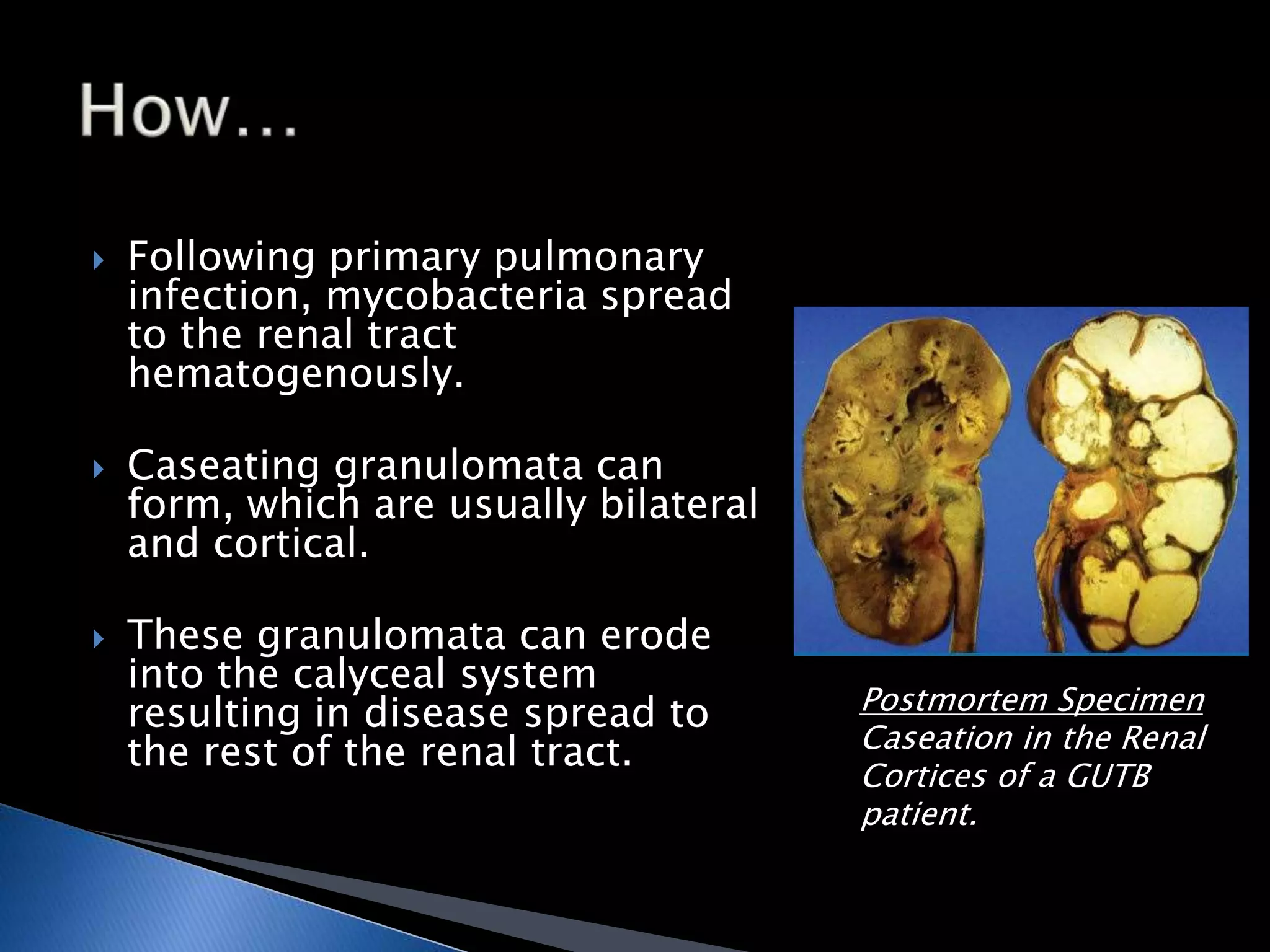
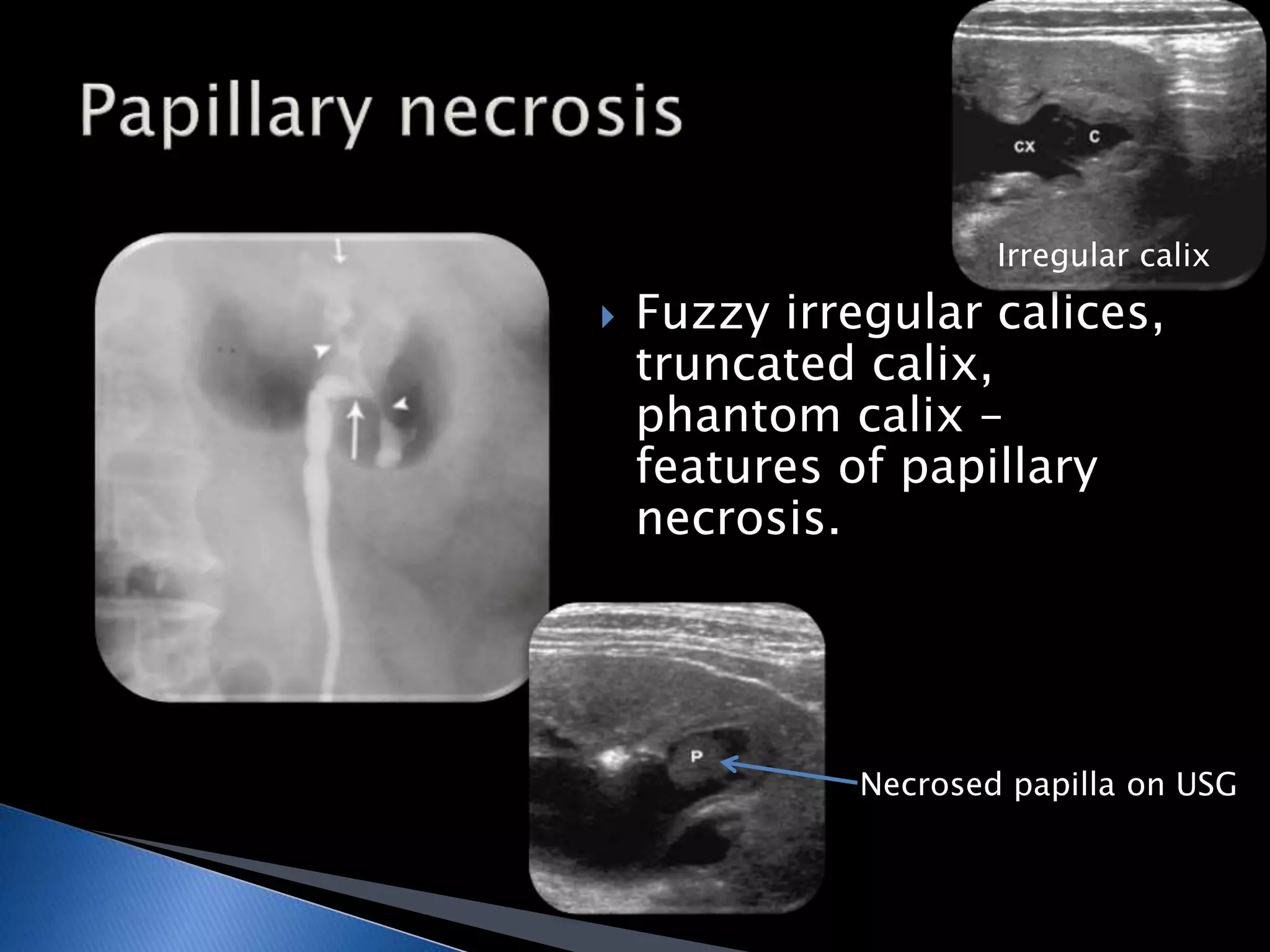
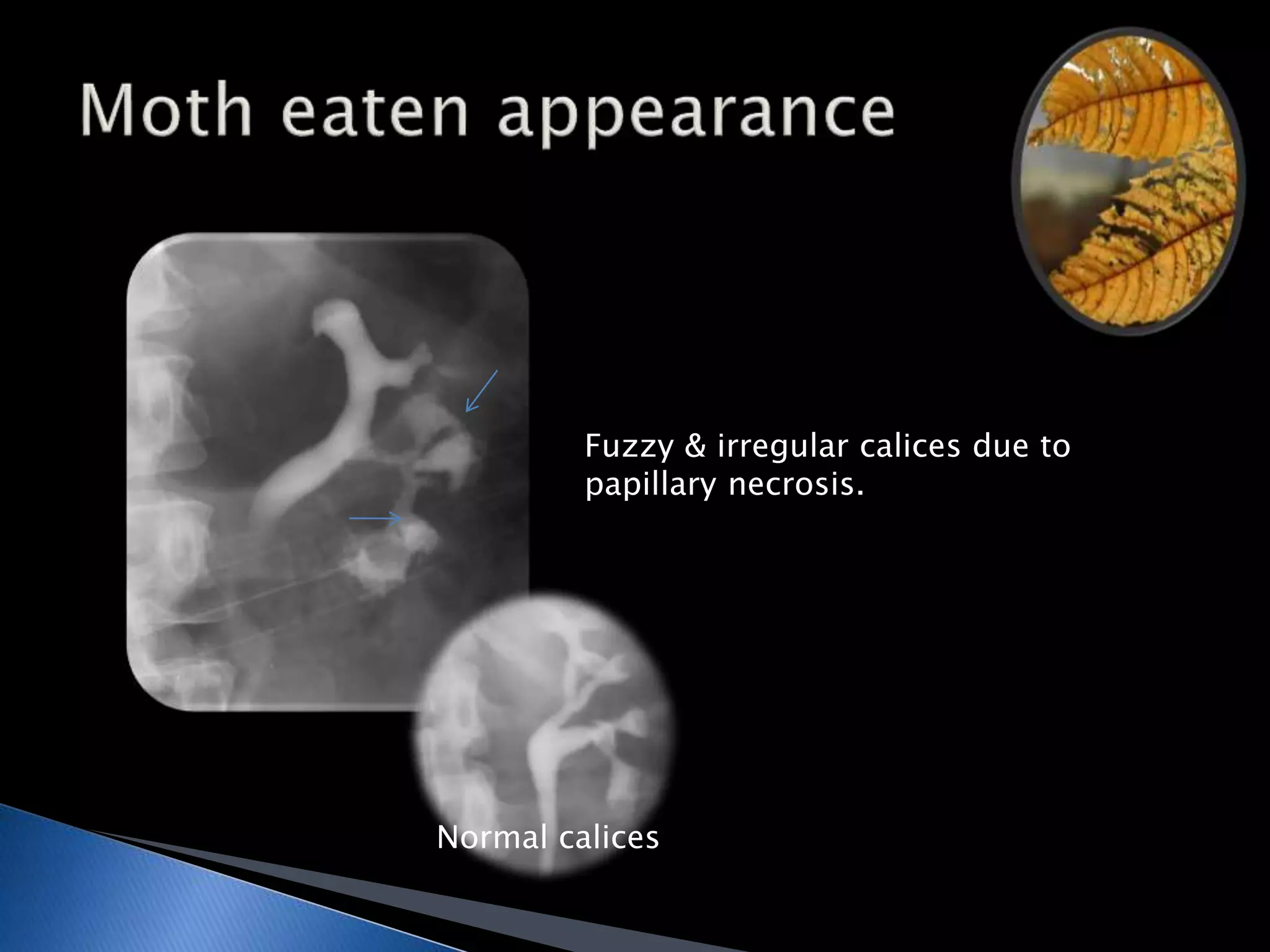
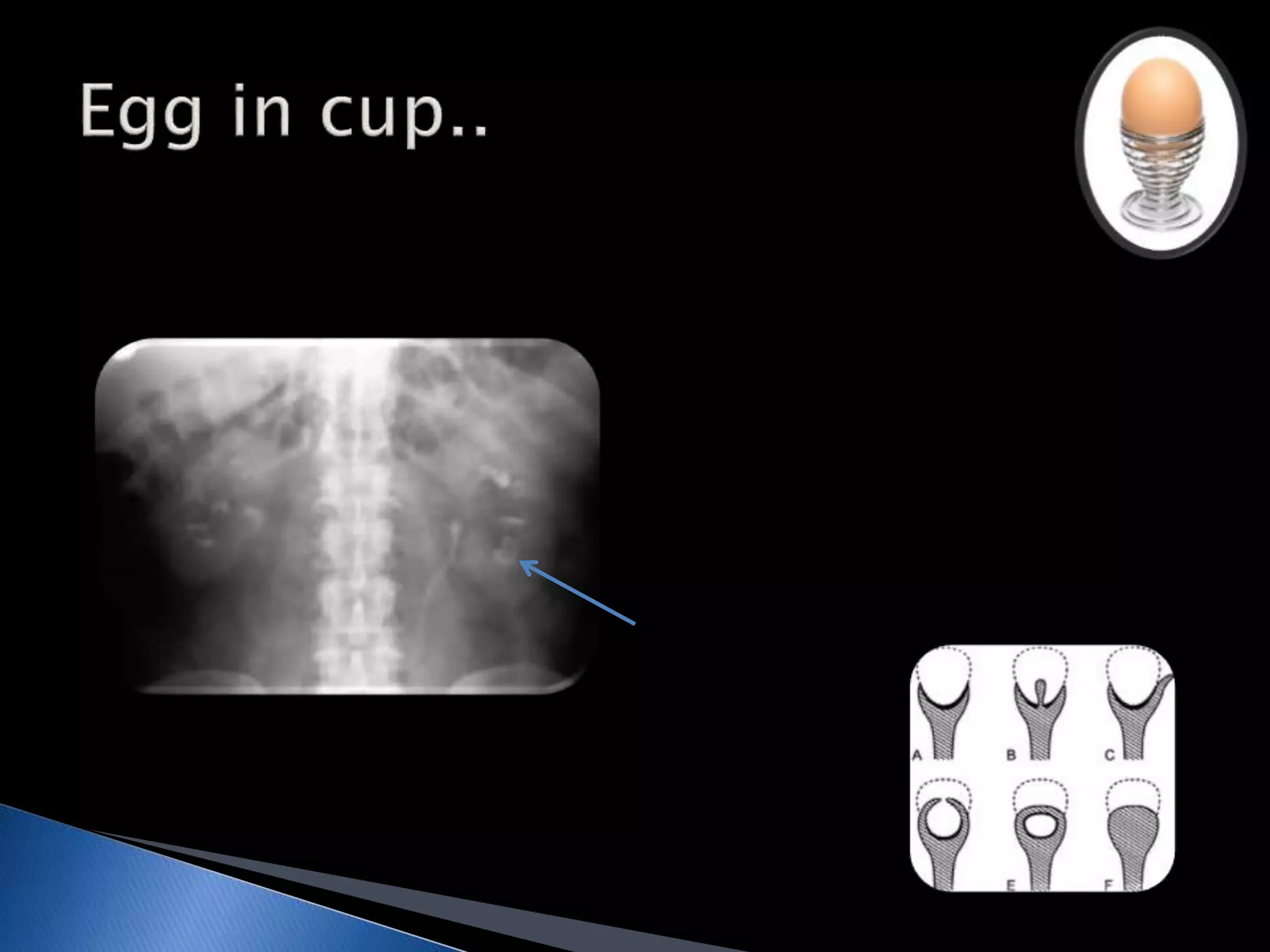
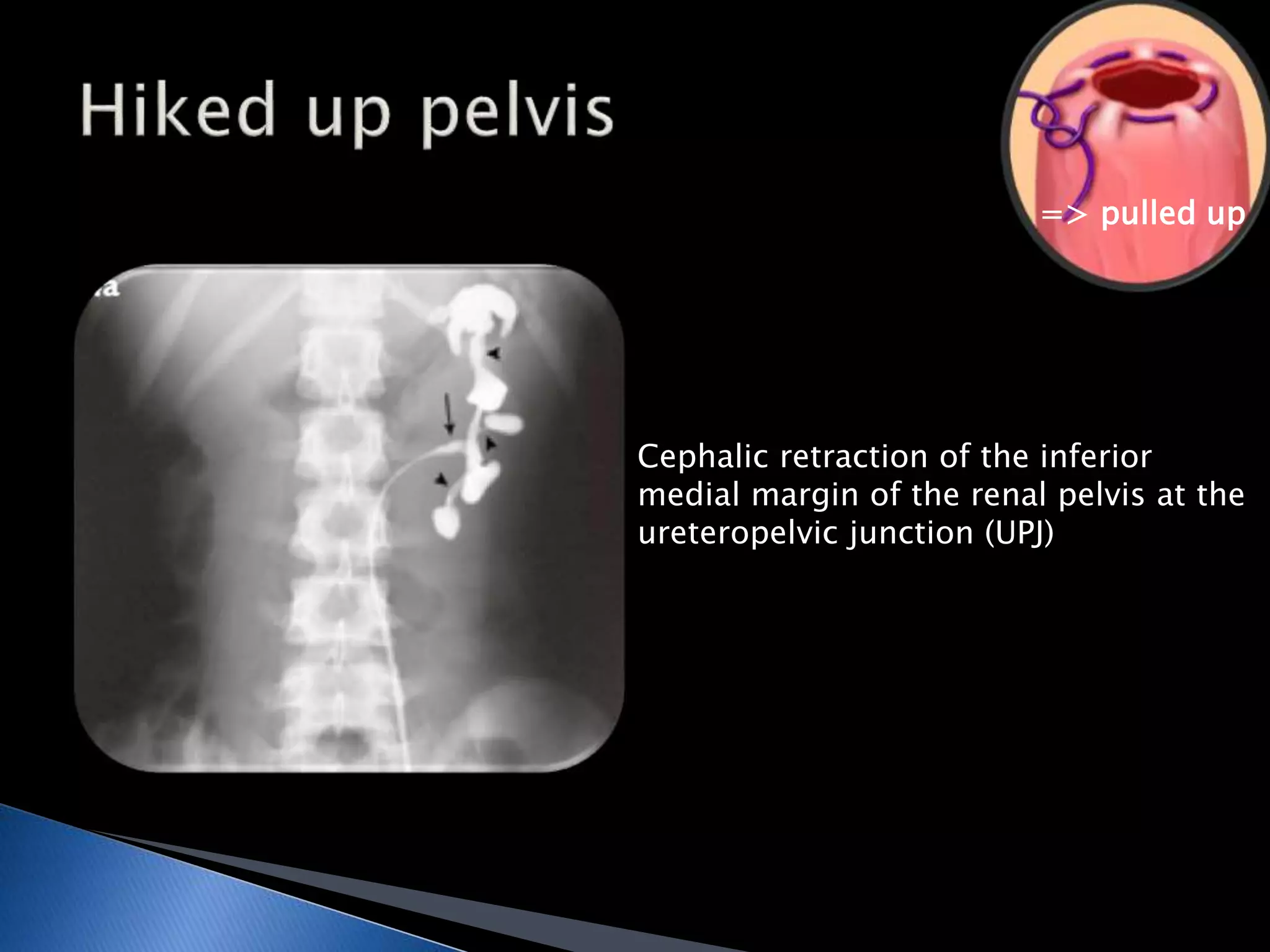
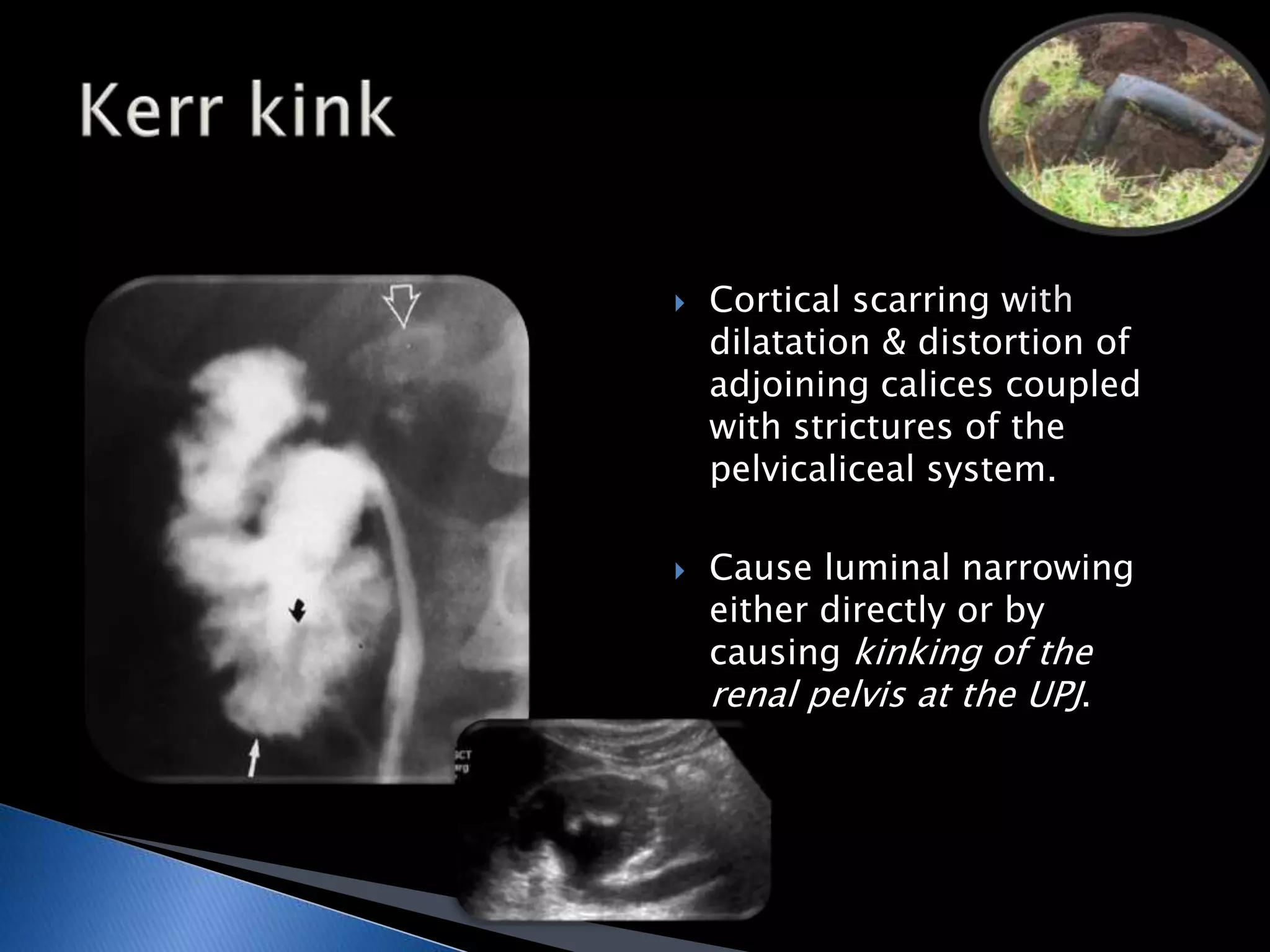
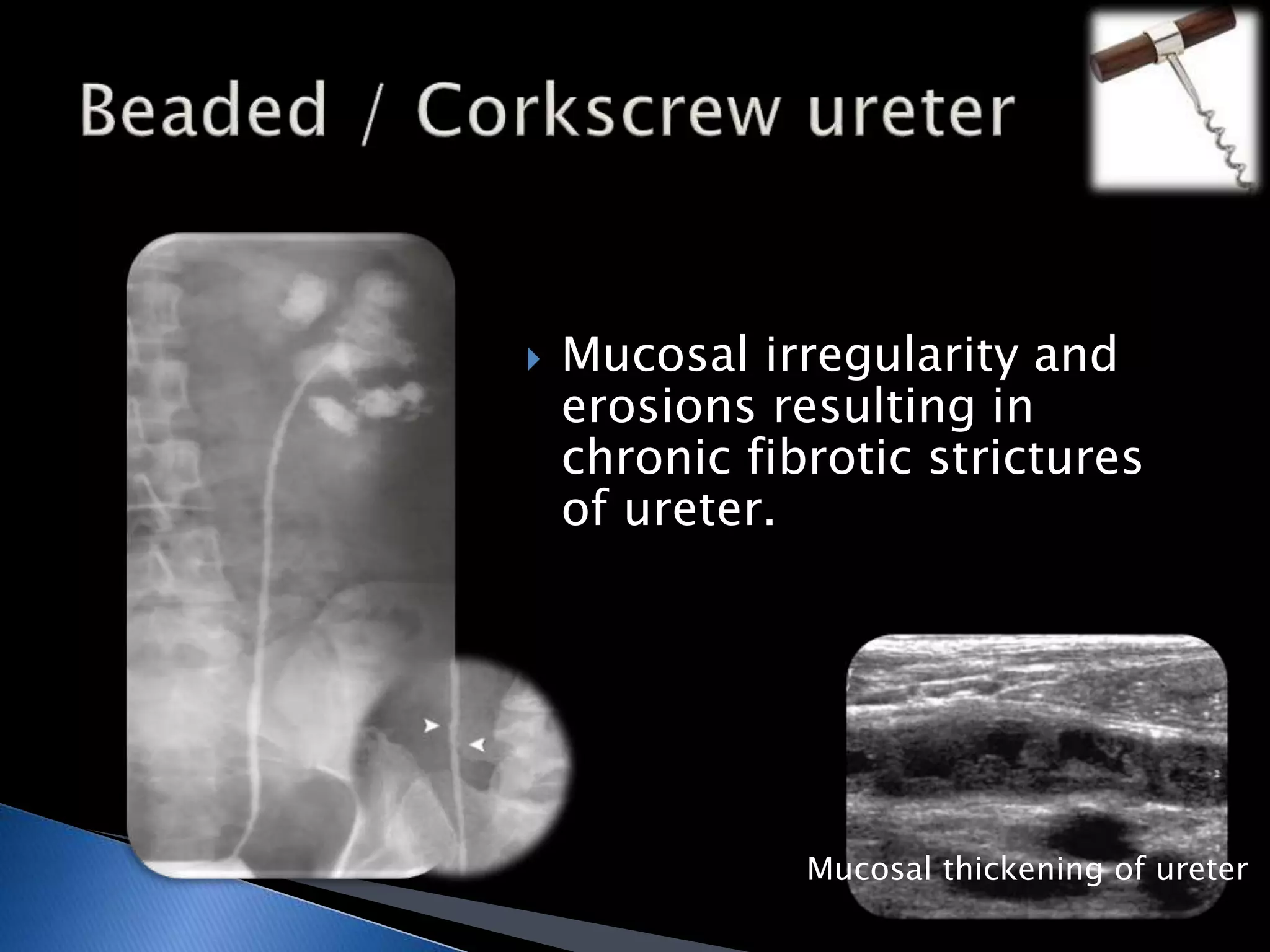
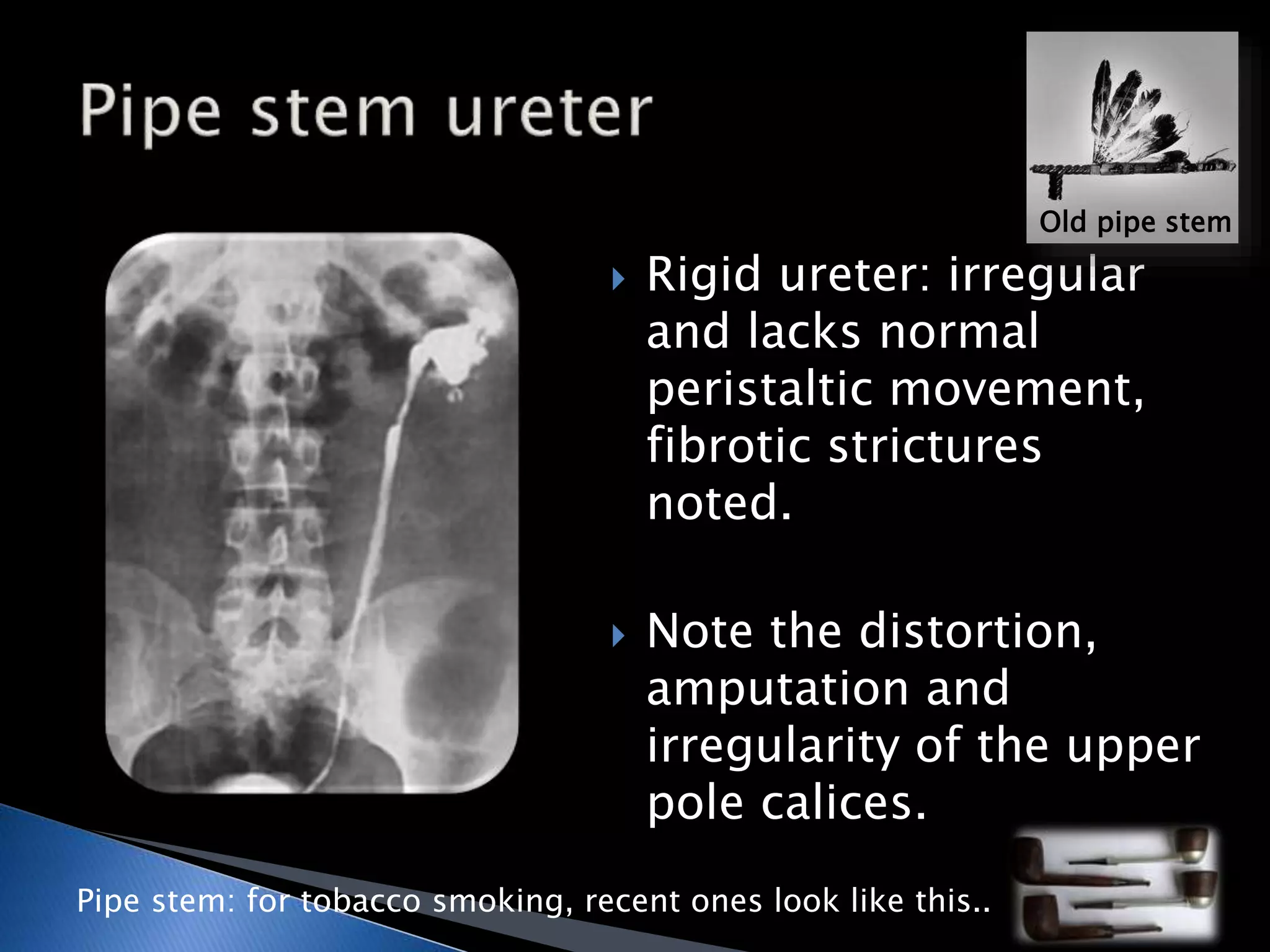
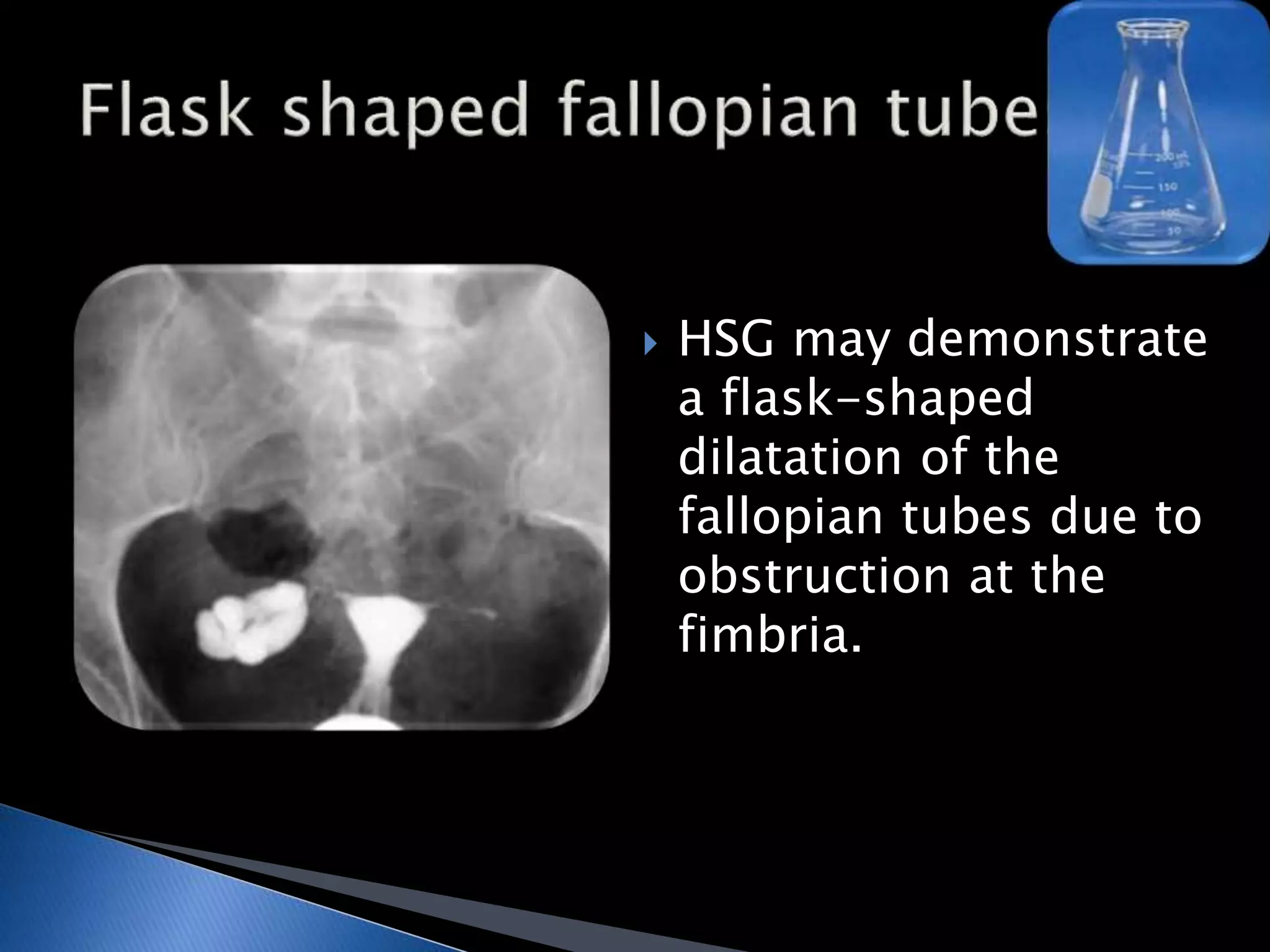
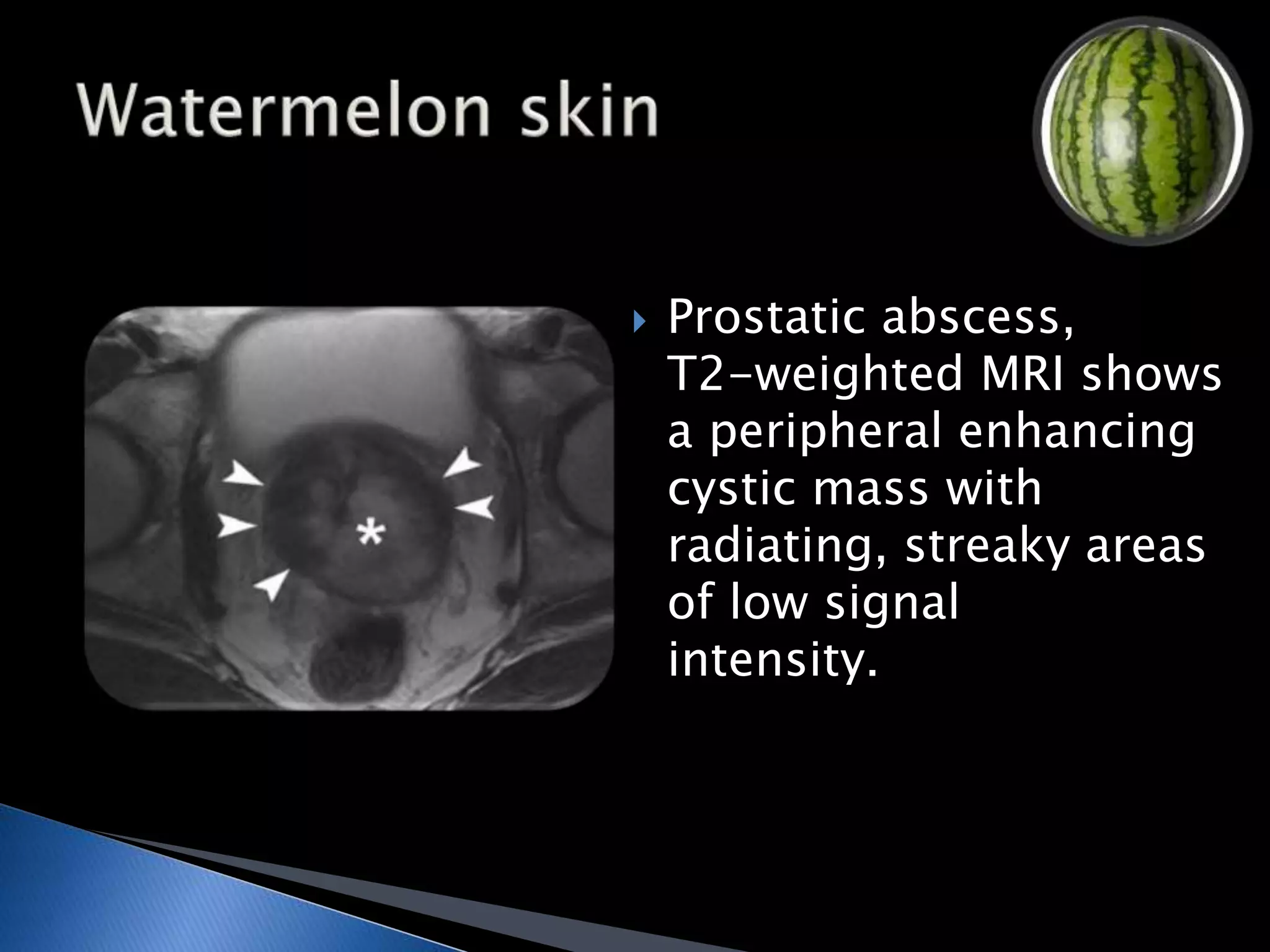
GUTB is the second most common form of extrapulmonary tuberculosis in developing countries, primarily affecting the kidneys through hematogenous spread. It is associated with infertility in women, with significant imaging findings including calcifications and ureter distortion due to strictures and necrosis. Diagnostic imaging such as CT and urography can reveal characteristic features, including the 'cobra head sign' and other pathologies in the urinary system.