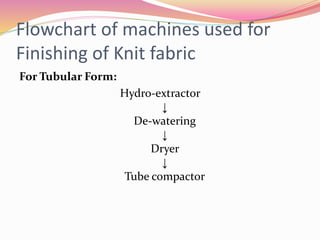
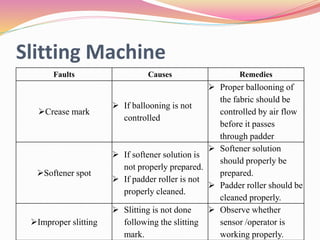
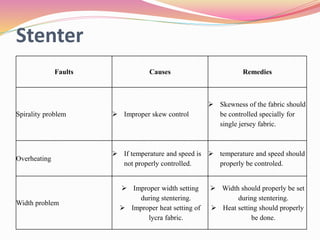
The document discusses finishing processes for knit fabrics and provides details about common faults, causes, and remedies. It covers processes like dewatering, slitting, drying, stentering, and compacting. For each process, controlling points are identified and typical faults like crease marks, softener spots, and GSM variations are summarized along with likely causes such as improper speed control or softener mixing. Remedies for the faults including proper ballooning, cleaning equipment, and maintaining consistent process parameters are also outlined. The document aims to improve understanding of finishing for knit fabrics.