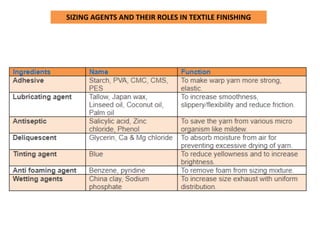
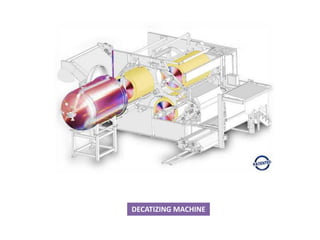
Textile finishes improve the appearance, feel, and functionality of fabrics. There are two main types of finishes - aesthetic finishes which improve visual qualities like texture or sheen, and functional finishes which provide benefits like stain resistance or crease resistance. Finishing processes include scouring to remove impurities, bleaching to produce a pure white color, dyeing or printing to add color patterns, and calendaring to produce a smooth texture. Properly finished fabrics have enhanced durability, comfort, and performance properties for long-lasting use.