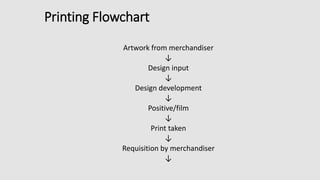
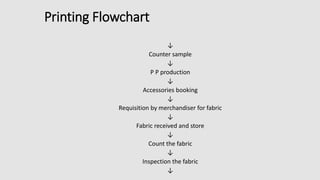
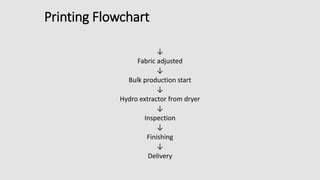
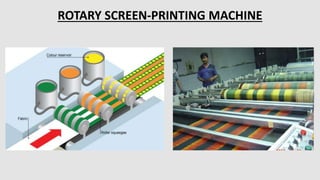
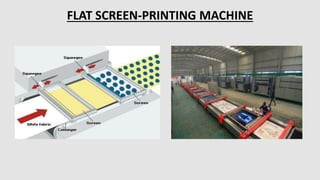
The document is a presentation on textile printing methods, specifically highlighting various techniques such as block printing, roller printing, resist printing, direct printing, burn-out printing, and rubber printing. It outlines the process flows involved in textile printing, from design input to final delivery, and details the characteristics of each printing method. The presentation emphasizes the significance of each technique and its application in the textile industry.