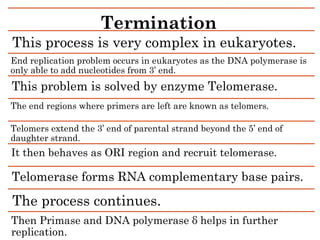
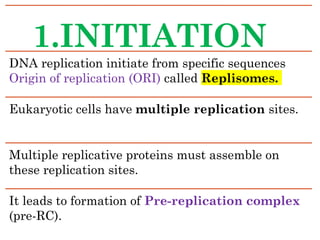
DNA replication in eukaryotes is a fundamental biological process critical for heredity, occurring through a semi-conservative method consisting of initiation, elongation, and termination phases. Initiation requires the assembly of a pre-replication complex at specific origins, while elongation involves DNA polymerases synthesizing new strands and handling both leading and lagging strand replication. Termination is complex due to the end replication problem, which is addressed by telomerase, extending the telomers and ensuring complete DNA replication.



![Pre-replication complex has steps
First - association of Origin Recognizing Complex (ORC) with
replication origin.
Second - binding of Cdc6 [cell division cycle 6] protein to
ORC
Third - binding of Cdt1 [Chromatin licensing and DNA replication factor
1] and minichromosome maintenance protein (MCM).
This replicative complex assembly occurs during G1 phase prior
to S phase.
During the transition between G1 phase to S phase, CDK [Cyclin-dependent
kinases] proteins and DDK [Dbf4-dependent kinase] proteins get attached
to the Pre-replication complex.
It transforms the Pre-replication complex into active
replication fork.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eukaryoticdnareplication-240925150930-812765a3/85/EUKARYOTIC-DNA-REPLICATION-pptx-pharmacology-5-320.jpg)


![Once the complex forms and cell pass into S phase, then
unwinding of DNA strand takes place.
Unwinding takes place by enzyme Helicases, and it leads
of exposure of 2 DNA templates.
After unwinding, polymerization of the daughter strands
takes place.
It occurs with help of DNA polymerase enzymes.
They are :
• DNA polymerase alpha [α]
• DNA polymerase epsilon [ε]
• DNA polymerase delta [δ]
2. ELONATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eukaryoticdnareplication-240925150930-812765a3/85/EUKARYOTIC-DNA-REPLICATION-pptx-pharmacology-8-320.jpg)