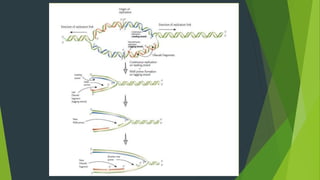
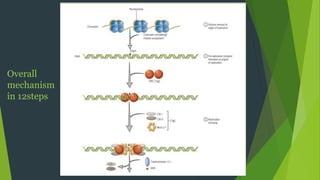
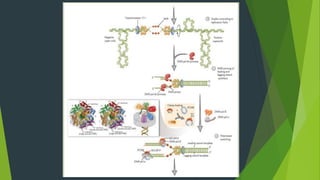
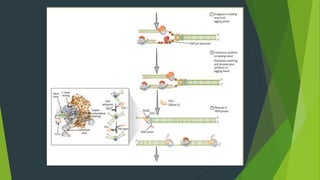
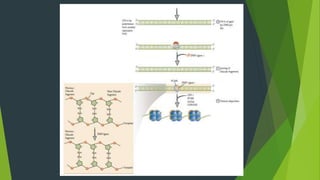
The document summarizes the mechanism of DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. It describes that DNA replication is initiated at origins of replication and involves unwinding of the DNA double helix by helicases. RNA primers are synthesized by primase and DNA polymerase extends the DNA strands. DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides in the 5' to 3' direction, so the leading strand is continuously replicated while the lagging strand is replicated in fragments called Okazaki fragments. Additional enzymes involved include DNA ligase, topoisomerases, histone deposition factors and proofreading exonucleases. The overall process occurs through 12 steps and ensures each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genome.