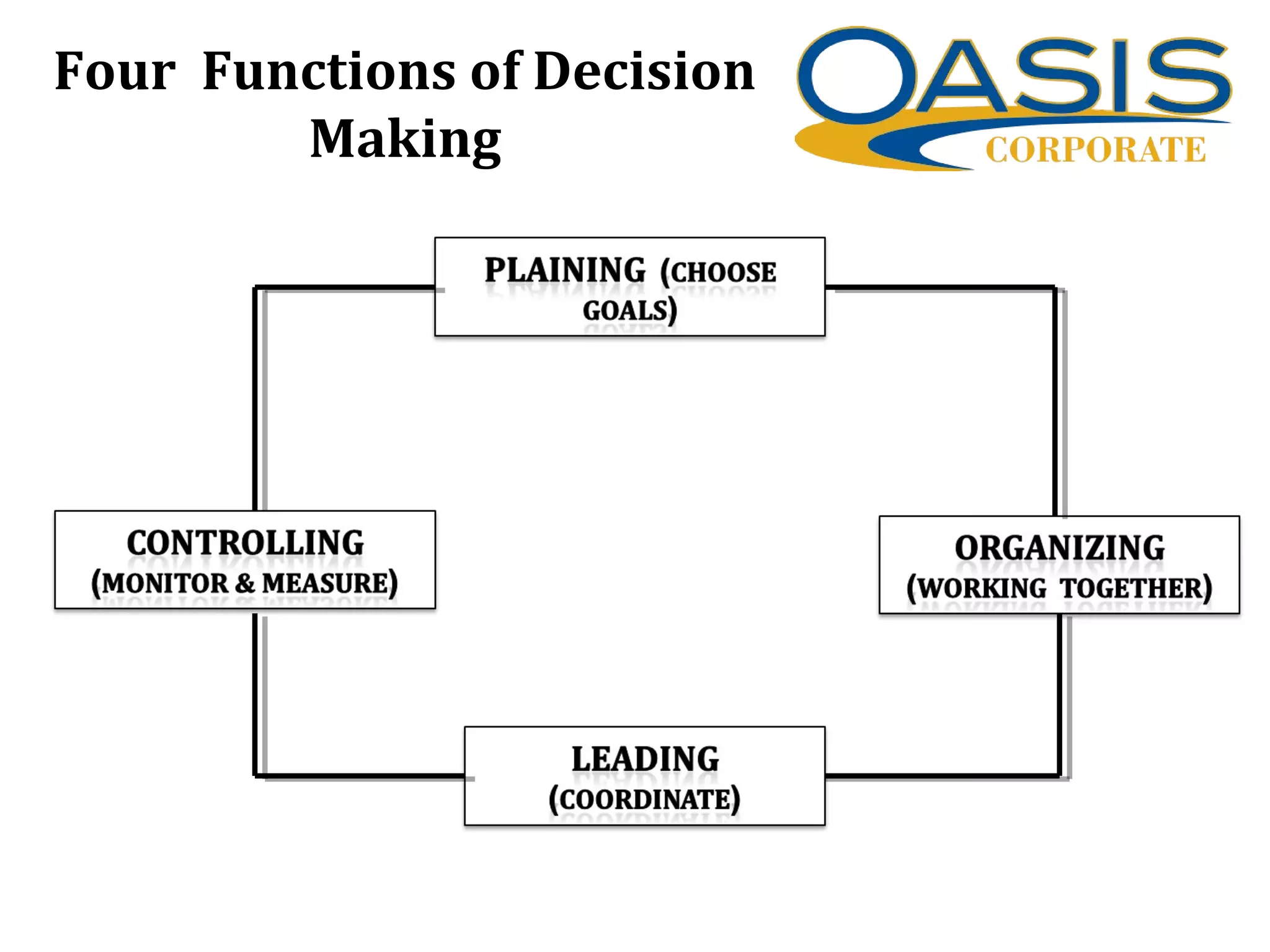
This presentation discusses decision making. It defines decision making as the act of making up your mind after consideration. There are two types of decision making situations: programmed, which are routine decisions made through predetermined rules, and non-programmed, which are novel situations without set rules. The presentation outlines factors for effective decision making like perception, priority, and judgment. It also describes the four functions of decision making: planning, controlling, organizing, and leading. Models of decision making discussed include the rational model and non-rational models like satisficing and incremental. The 6 C's of decision making and managing diversity in group decision making are also summarized.