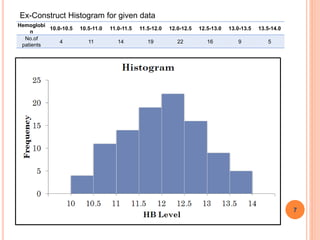
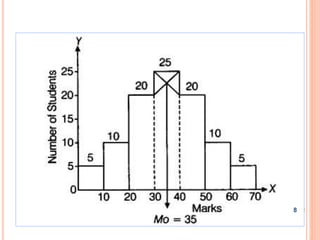
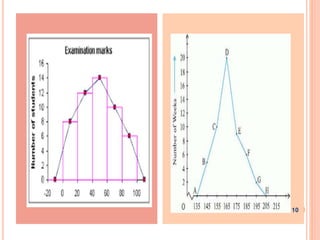
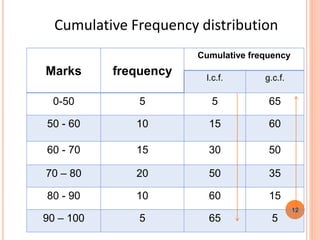
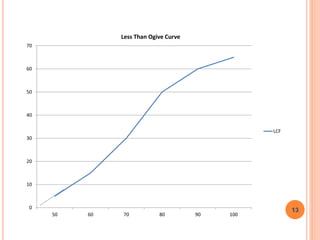
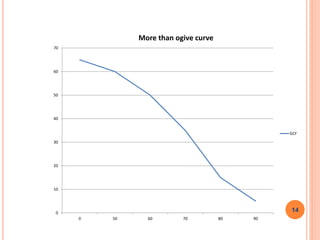
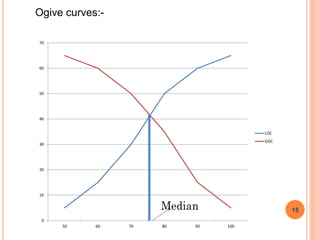
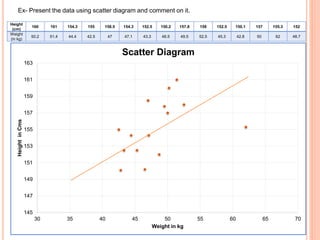
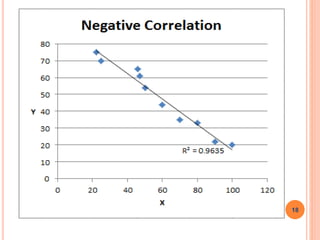
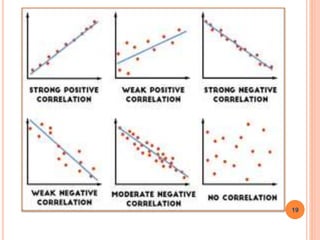
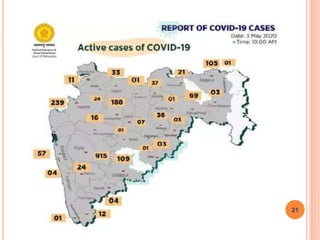
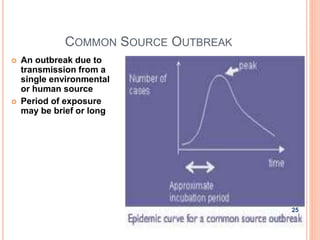
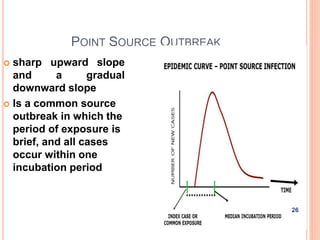
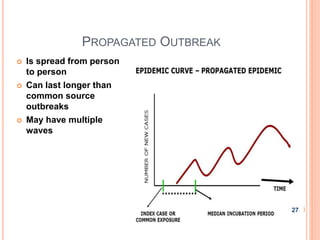
The document is a presentation on statistical methods relevant to community medicine, focusing on the collection, classification, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of statistical data. It explains various data presentation techniques including histograms, frequency polygons, ogive curves, scatter diagrams, and epidemic curves. The document outlines the construction and interpretation of these graphs, emphasizing their application in understanding data trends and outbreak characteristics.