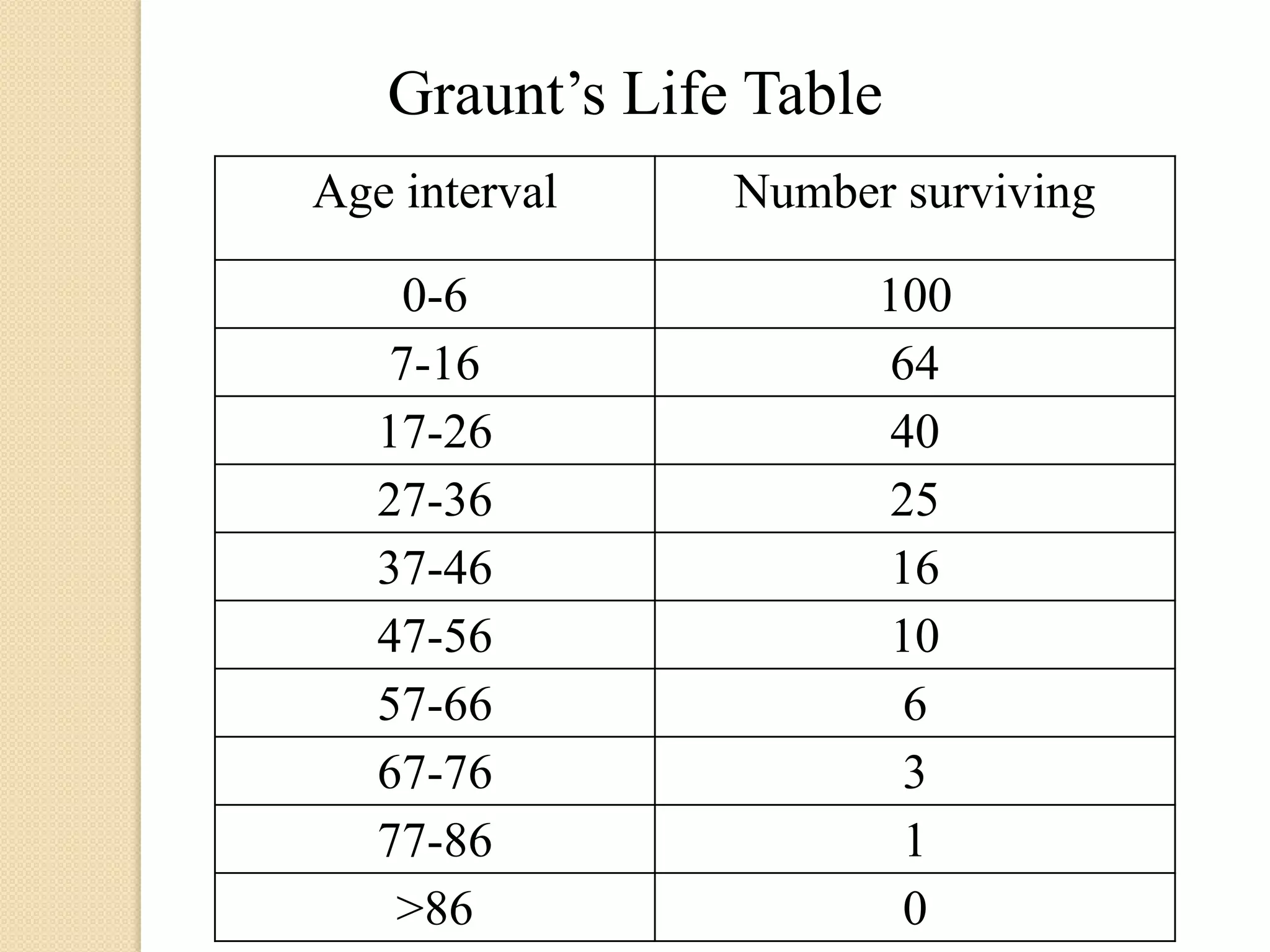
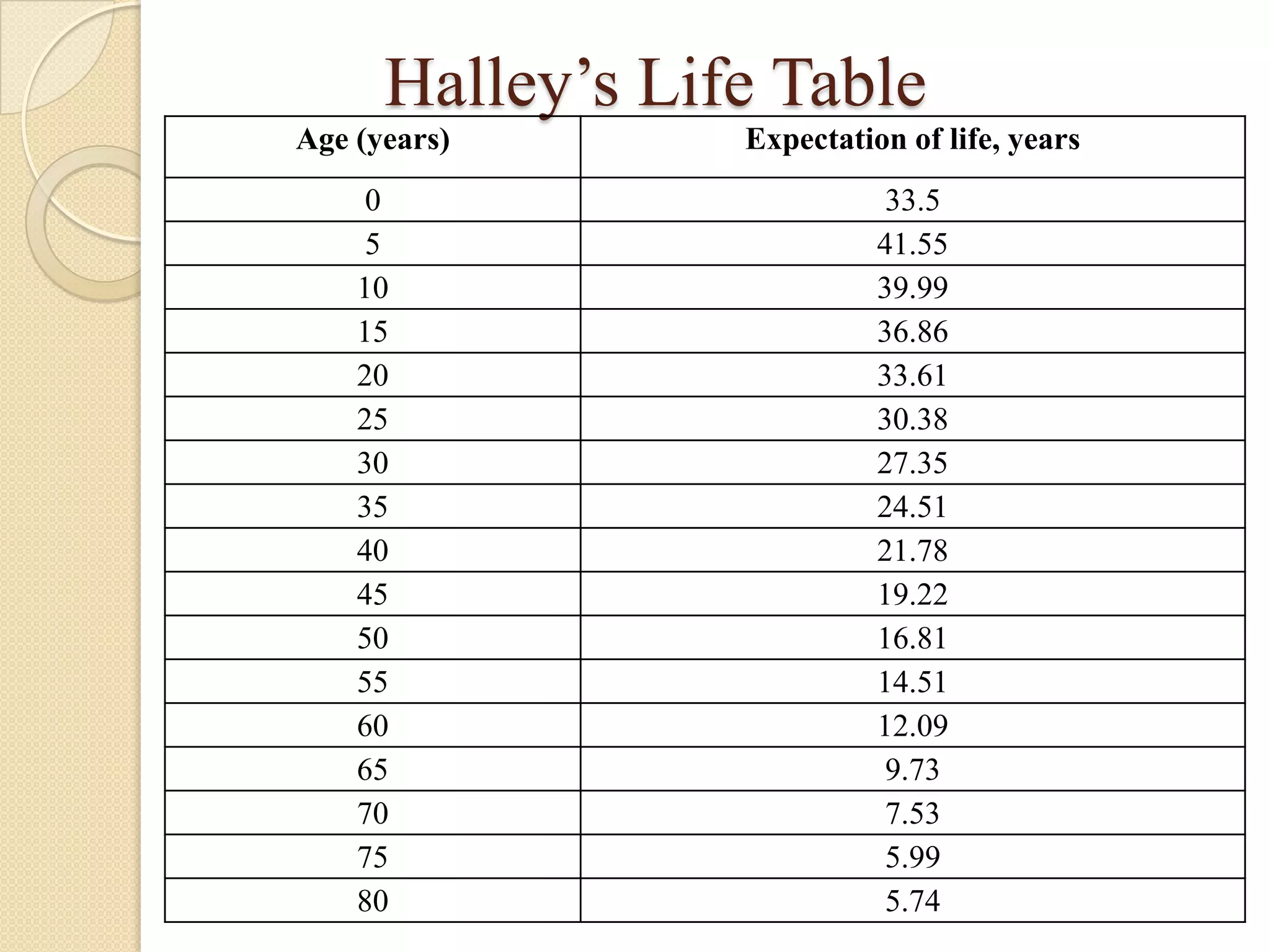
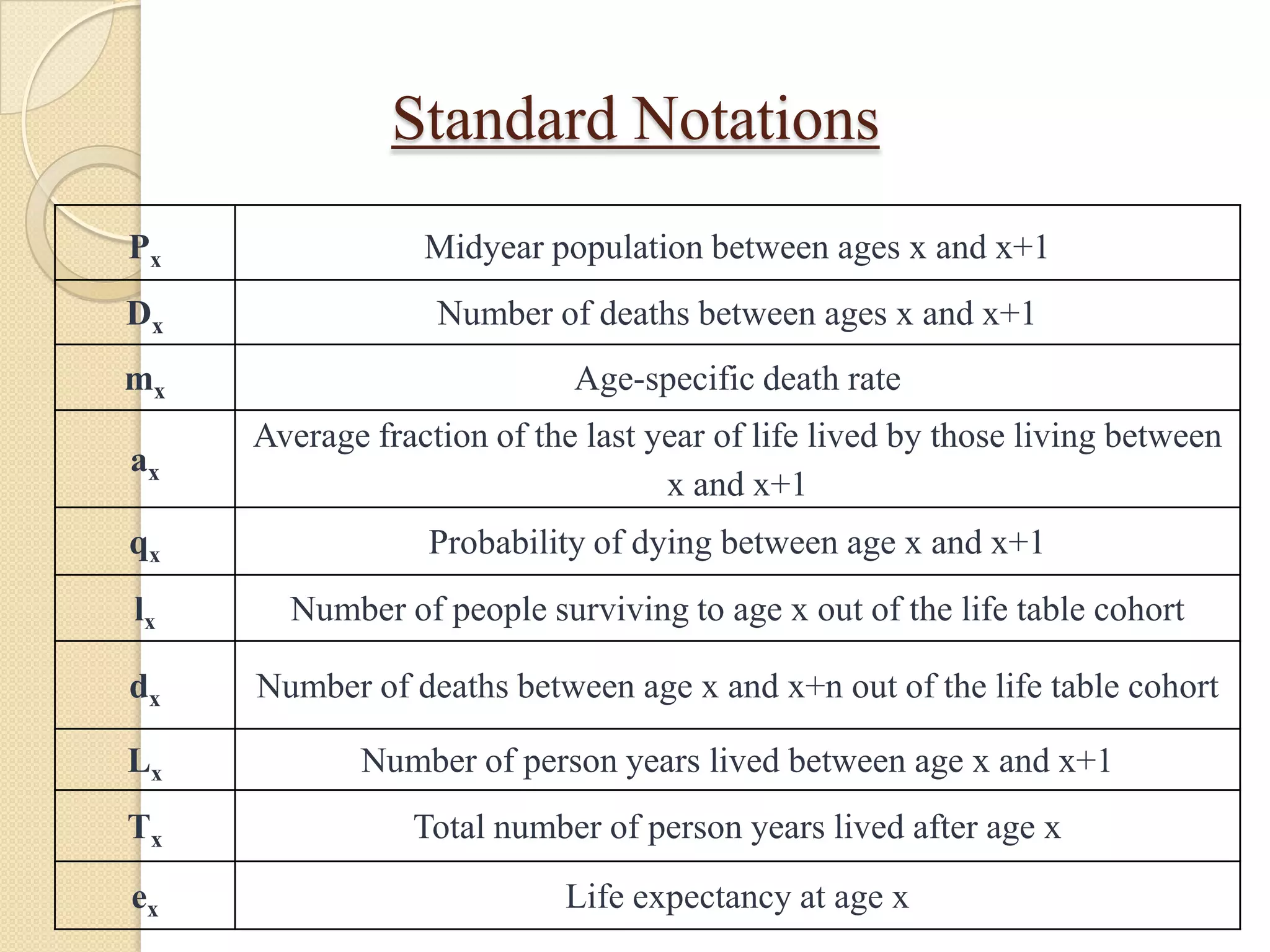
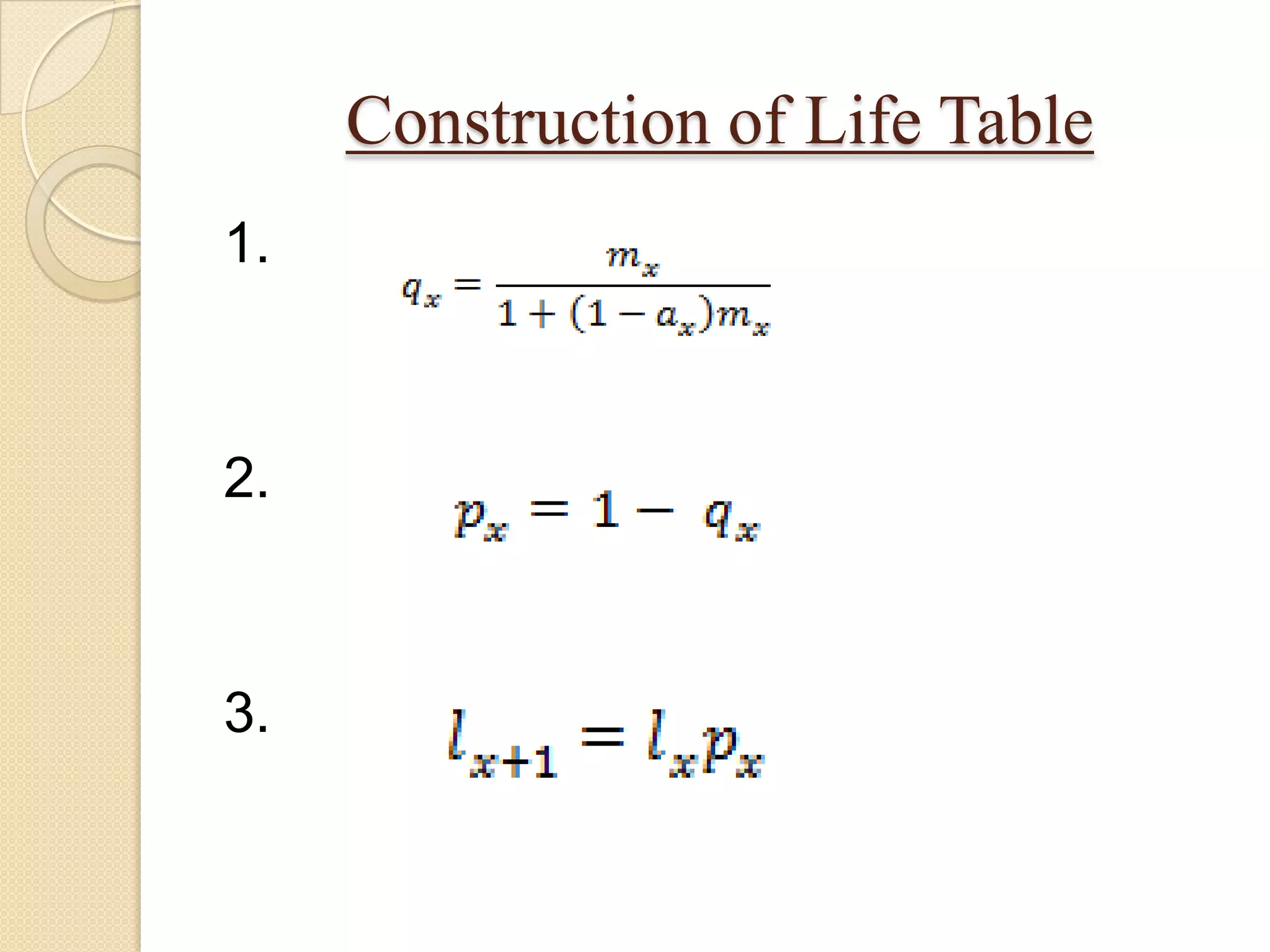
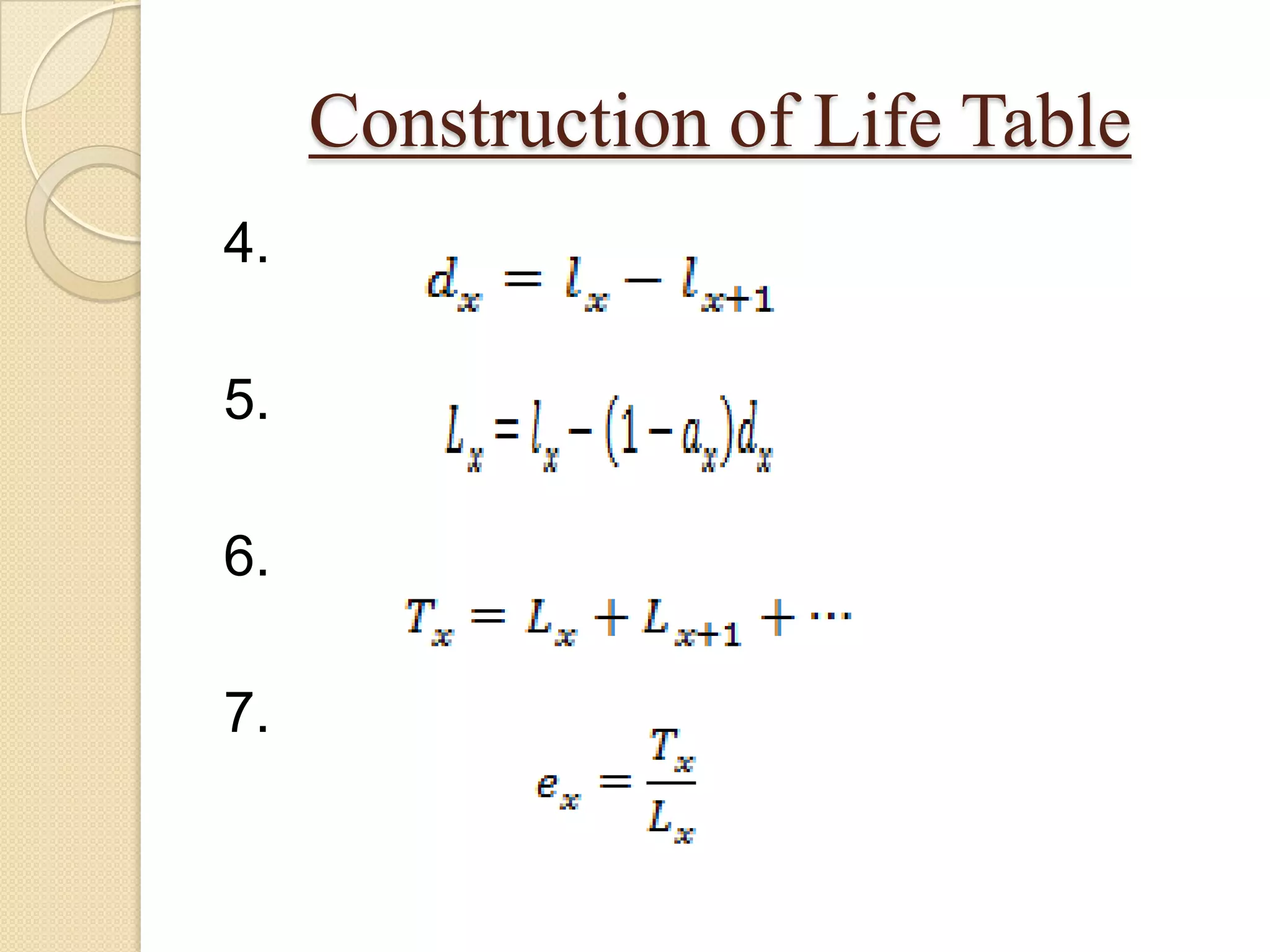
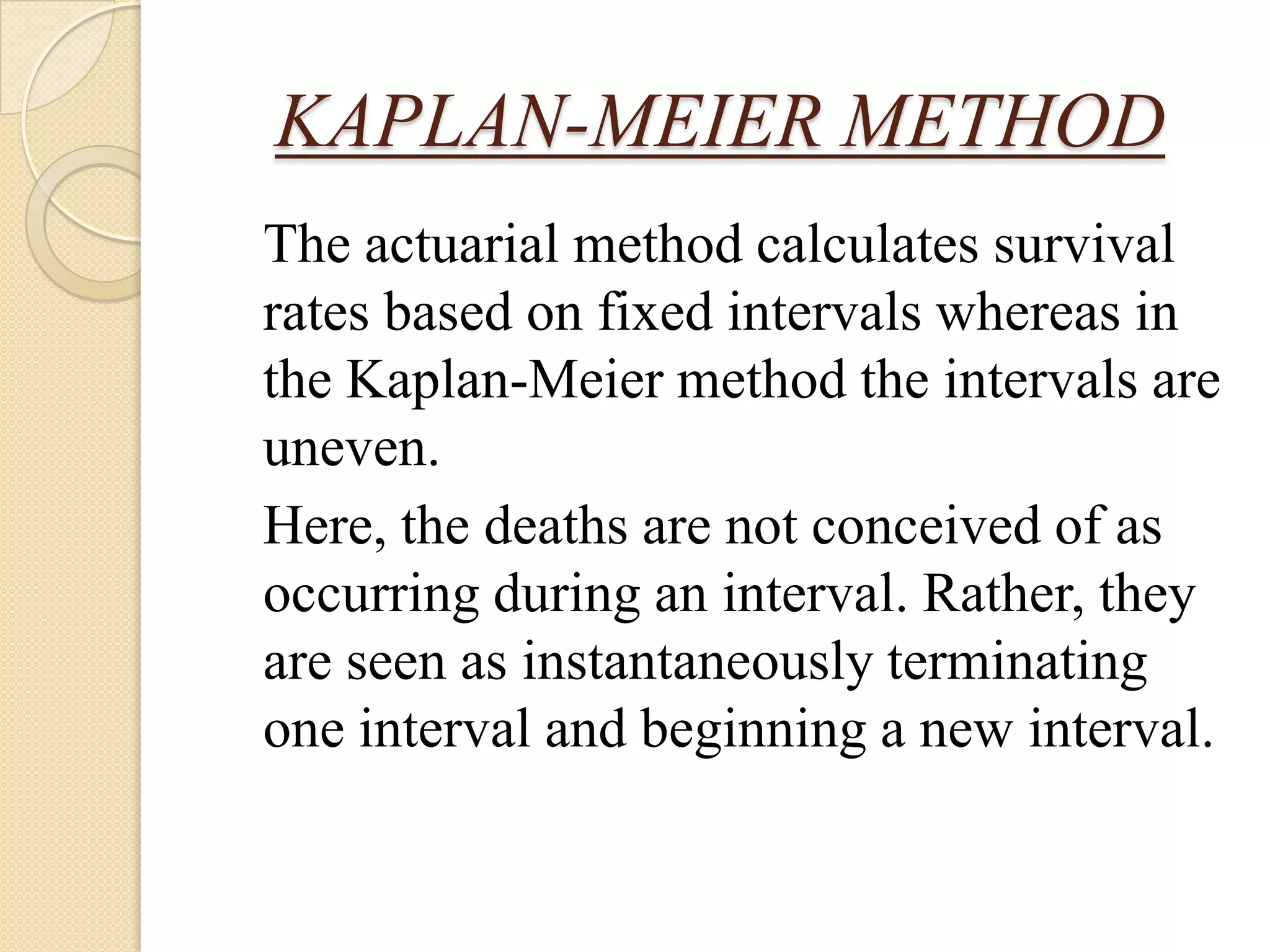
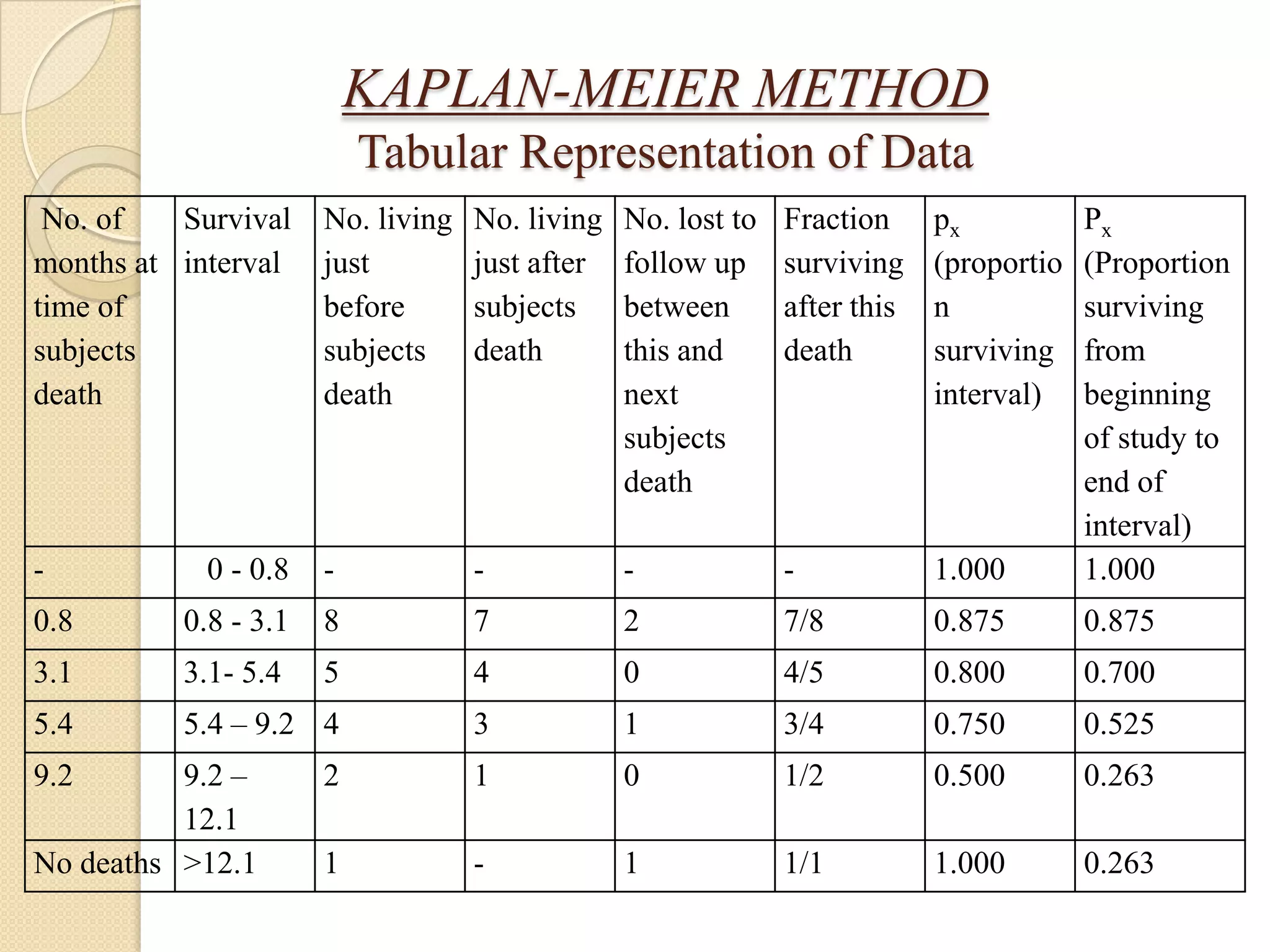
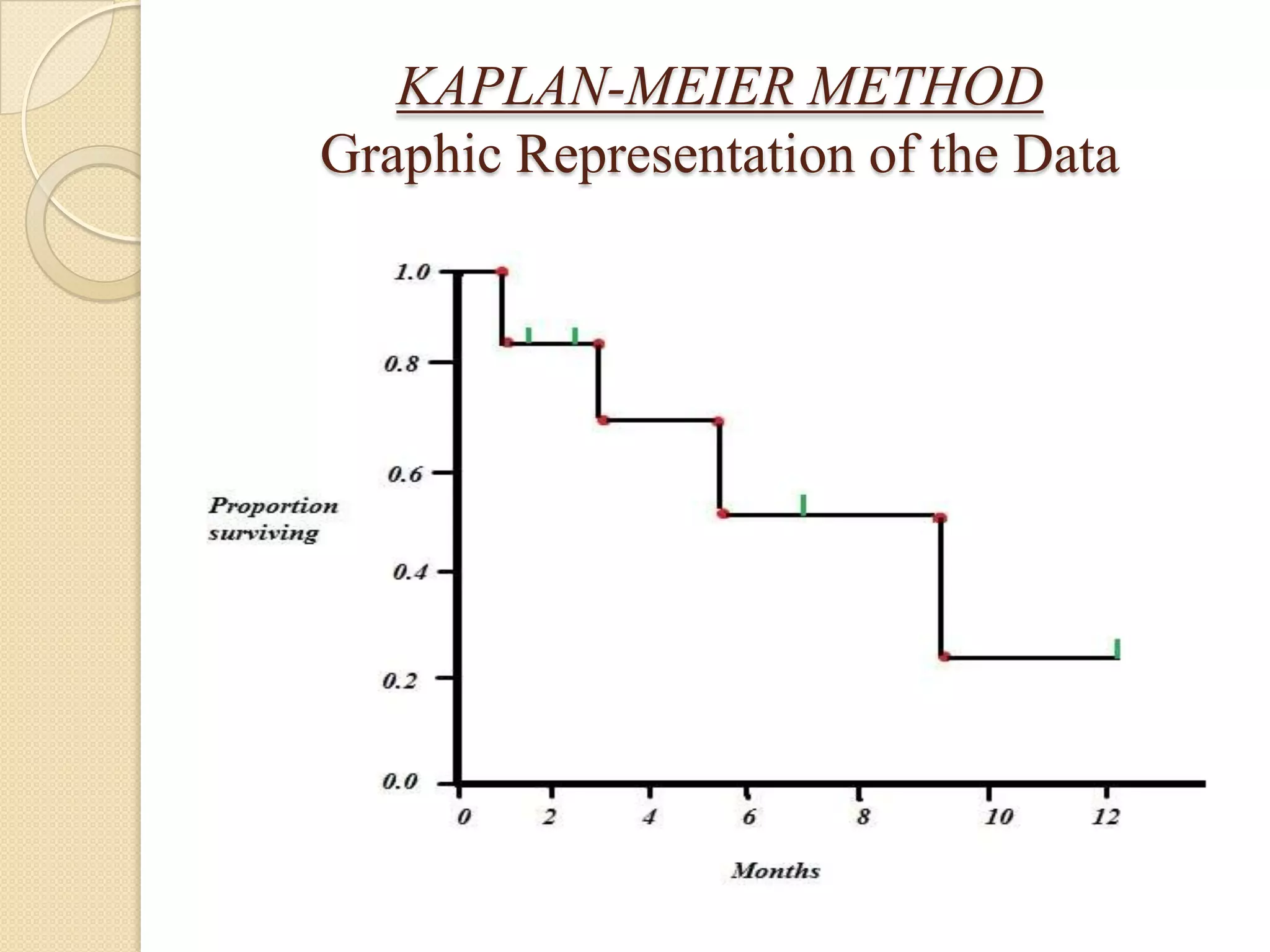
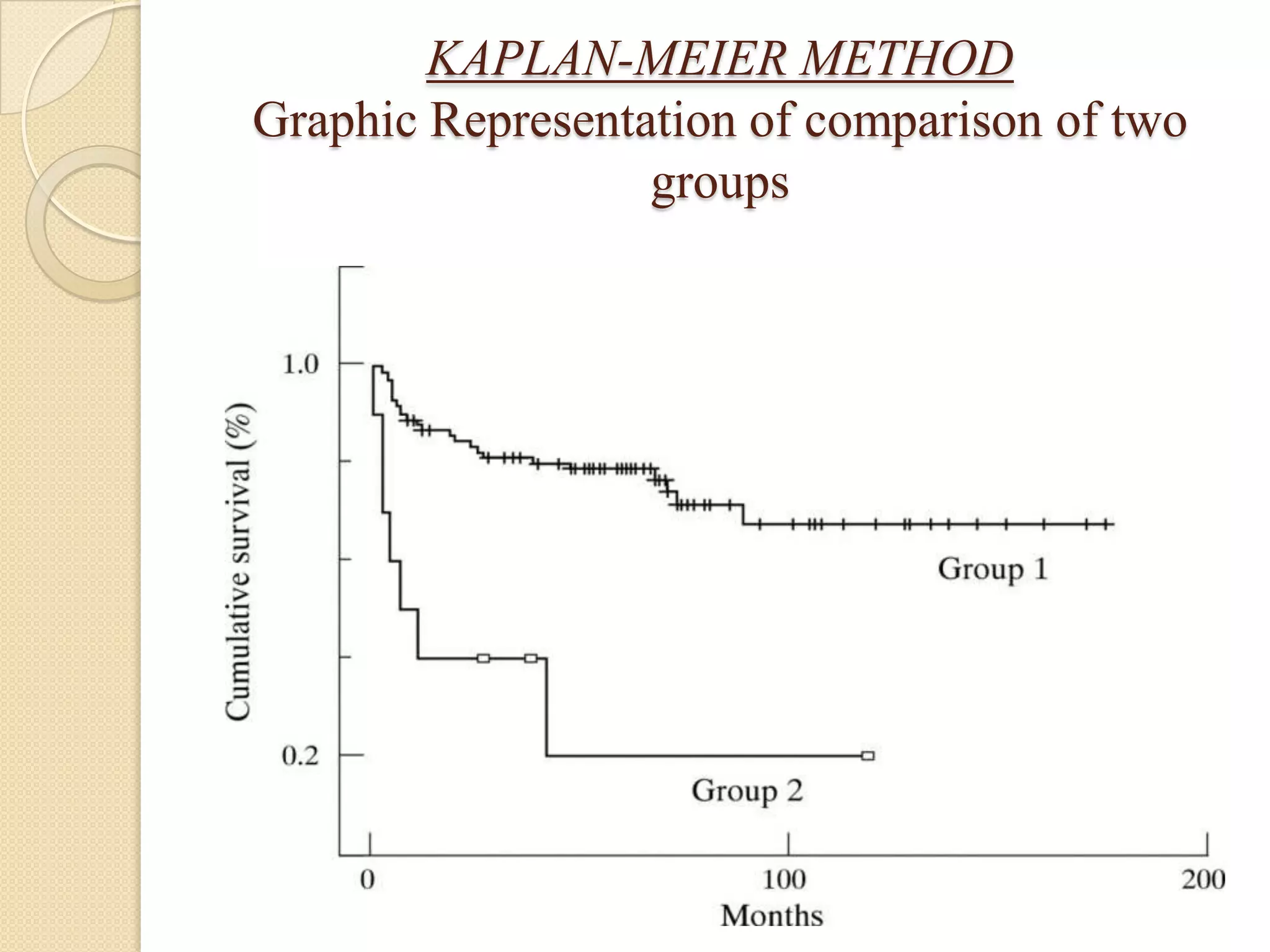
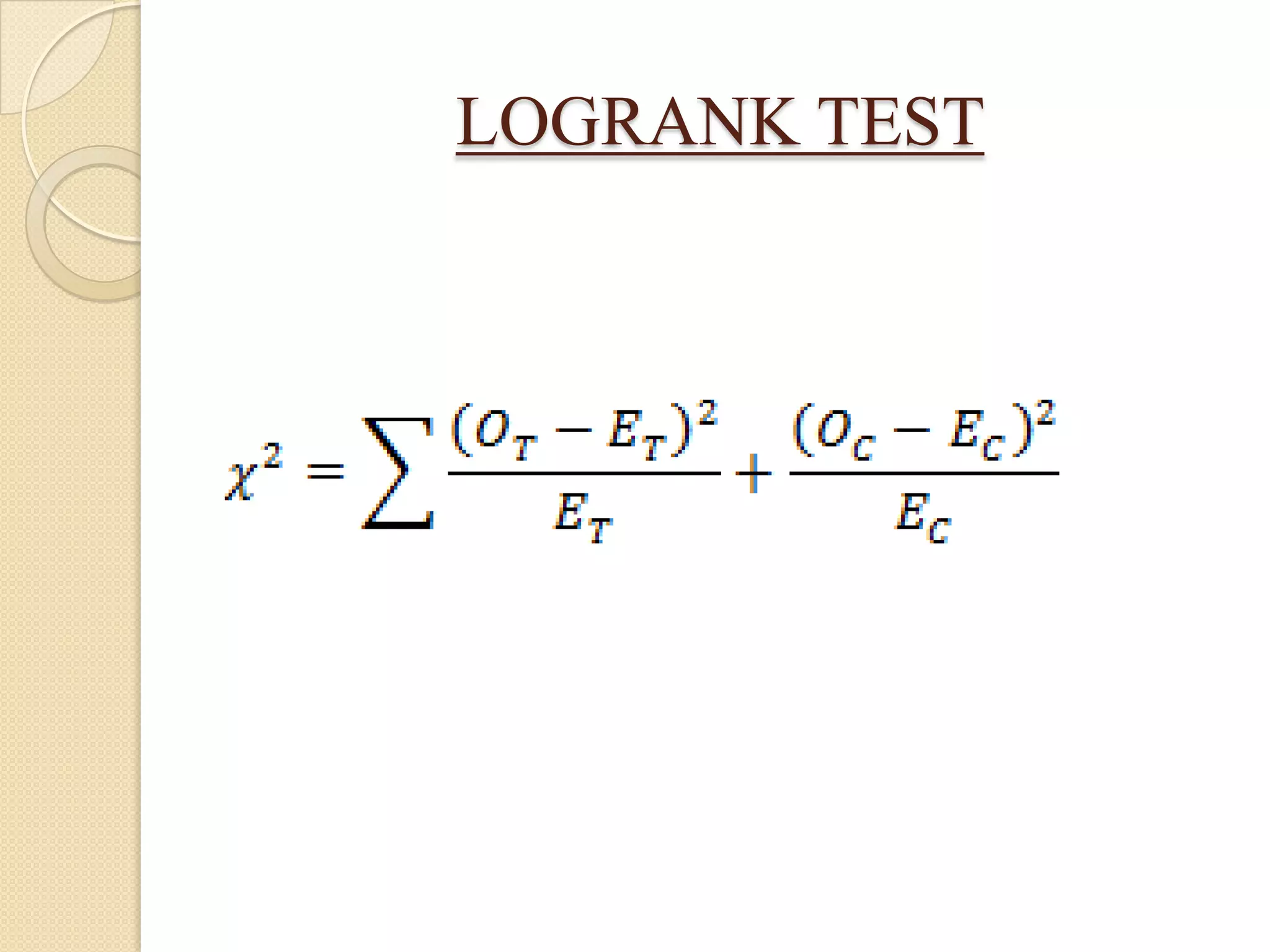This document discusses life tables and their importance. It provides a brief history of life tables, noting their development by John Graunt and Edmund Halley. Life tables are useful for estimating survival rates, mortality rates, and other vital statistics. They allow calculation of life expectancy and comparison of mortality between populations. The document then describes how to construct a life table and provides examples of their use in clinical medicine using the Kaplan-Meier method.