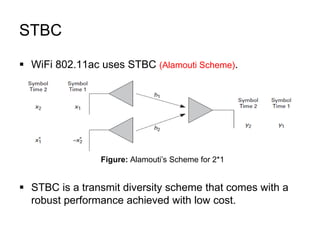
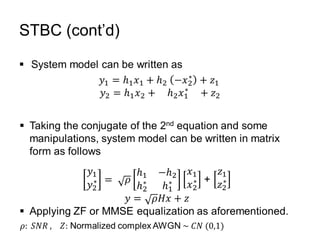
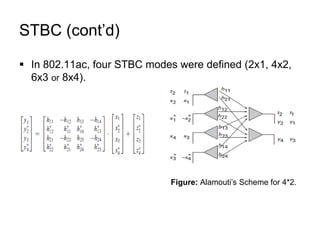
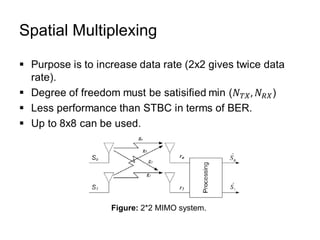
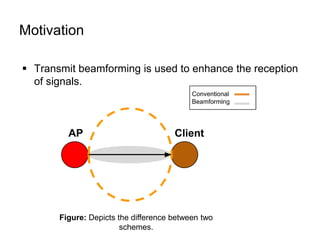
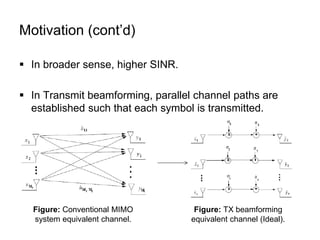
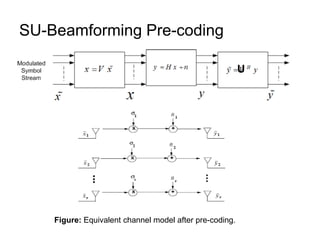
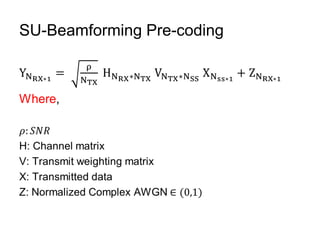
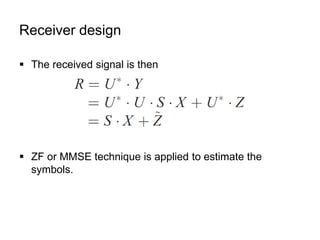
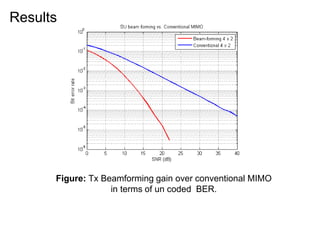
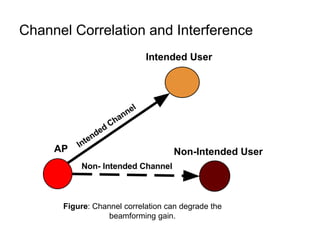
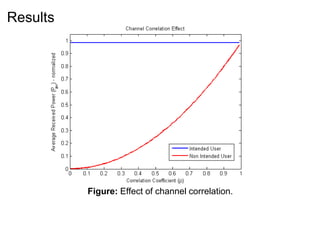
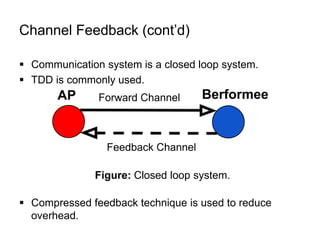
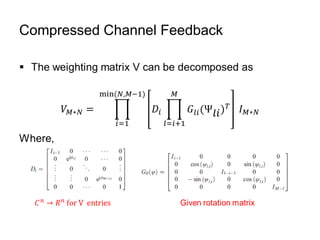
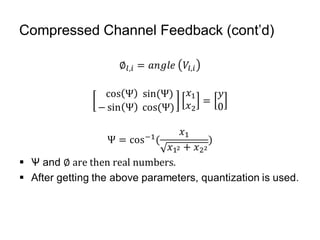
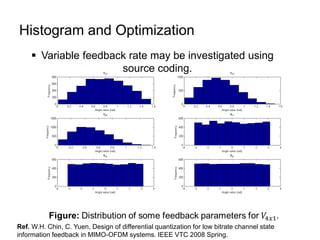
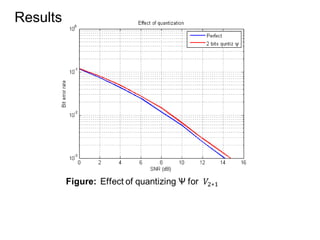
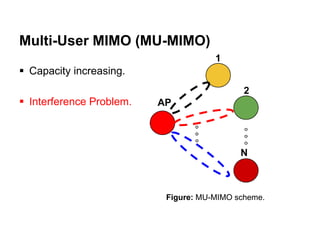
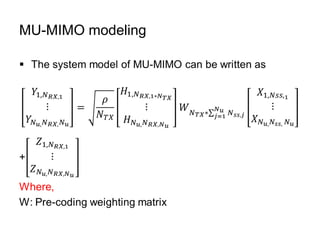
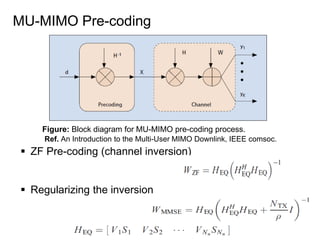
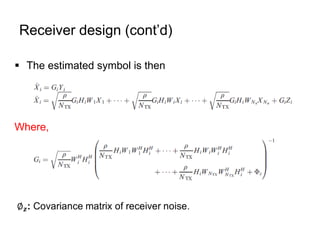
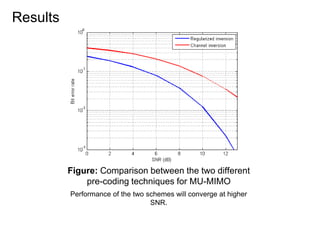
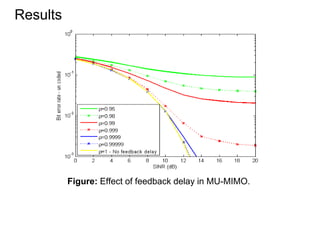
This document discusses various MIMO techniques including single-user and multi-user MIMO. It begins with an overview of STBC, which is used in 802.11ac and provides transmit diversity with low cost. Spatial multiplexing allows multiple parallel channels to improve throughput. For single-user MIMO, transmit beamforming enhances signal reception through precoding techniques like SVD that establish parallel channels. Multi-user MIMO further increases capacity but introduces interference that must be managed through precoding and receiver techniques like zero-forcing. Channel feedback is also required to implement beamforming and precoding.