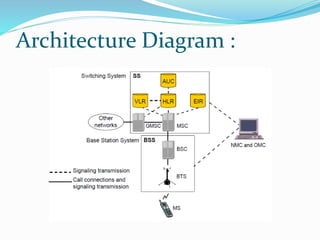
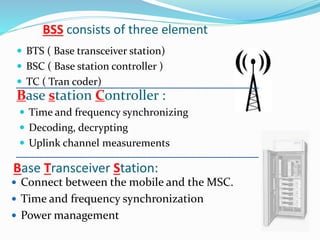
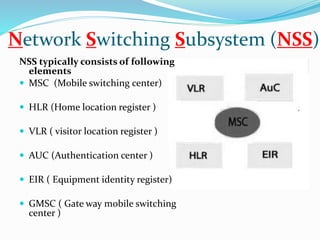
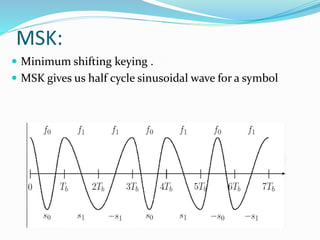
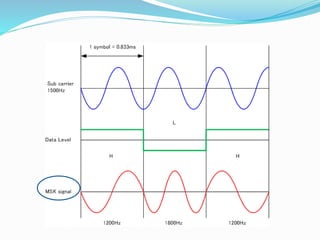
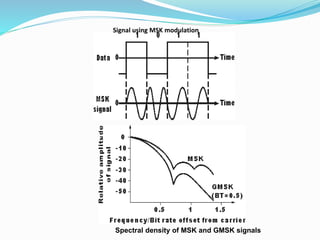
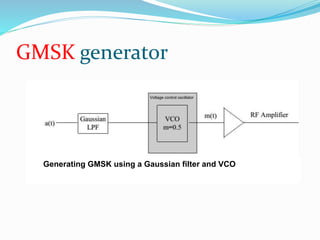
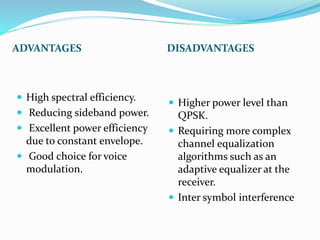
GSM, or Global System for Mobile Communications, is a standard for digital cellular networks. It was created in 1982 to standardize cellular networks and the first system was deployed in 1991. GSM uses technologies like MSK and GMSK modulation to achieve higher voice quality and lower costs. MSK provides half cycle sinusoidal waves per symbol while GMSK adds a Gaussian filter to MSK for improved spectral efficiency and reduced interference. GSM is widely used today due to its spectral efficiency and support for voice calls and SMS.