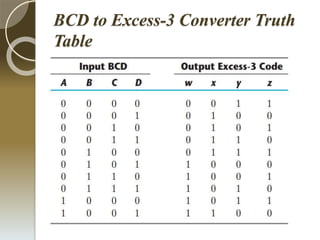
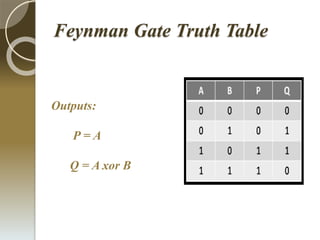
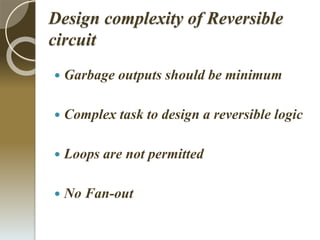
This document discusses energy efficient code converters using reversible logic gates. It outlines the drawbacks of irreversible computing such as energy dissipation and information loss. Reversible computing is more energy efficient and improves performance by recovering inputs from outputs. Code converters are used for encryption and decryption and allow for portability and tractability. A BCD to excess-3 converter is presented along with its truth table and block diagram. Reversible gates like the Feynman gate and NG gate are also discussed. The advantages of reversible gates include less energy dissipation and heat management. Designing reversible circuits is complex as garbage outputs must be minimized and loops and fan-out are not permitted. Reversible logic can be applied to code converters,










![References:
[1] Manjula Gandhi S, J Devishree “Design of
Reversible Code Converters for Quantum Computer
based system” proceedings published by International
Journal of Computer Applications.
[2] Generation in computational process, IBM J.
Research and Development,5: 183-191.
[3] Bennet, C.H.,1973.Logical Reversibility of
Computation, IBM J Research and Development ,pp:
525-532.
[4] Haghparast, M. and K. Navi, 2008. Design of a
Novel Fault Tolerant Reversible Full Adder For
Nanotechnology Based Systems, World Applied
Science Journal3(1): 144-188.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationenergyefficientcodeconvertersusingreversiblelogicgates-160222132640/85/Presentation-energy-efficient-code-converters-using-reversible-logic-gates-14-320.jpg)