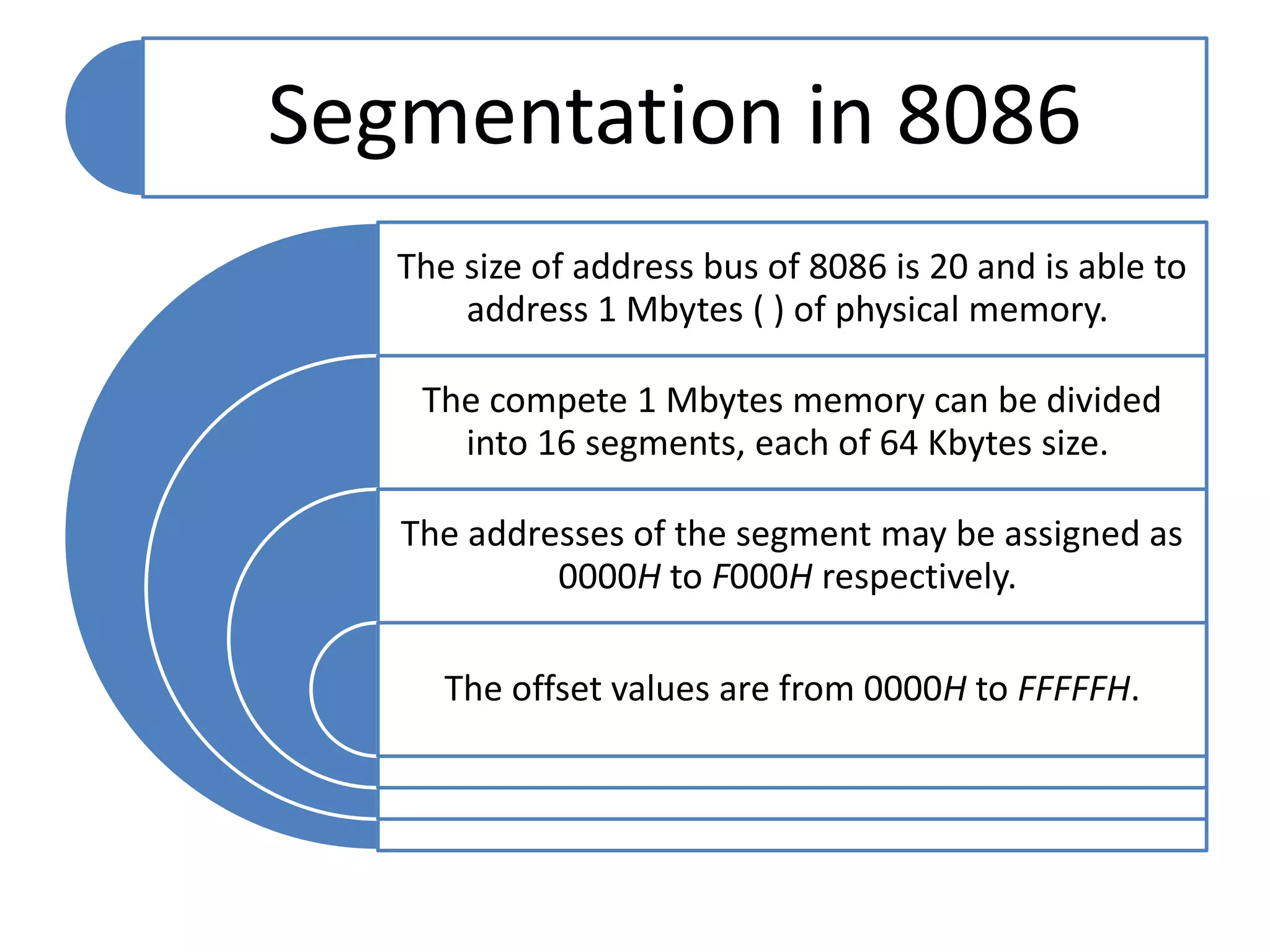
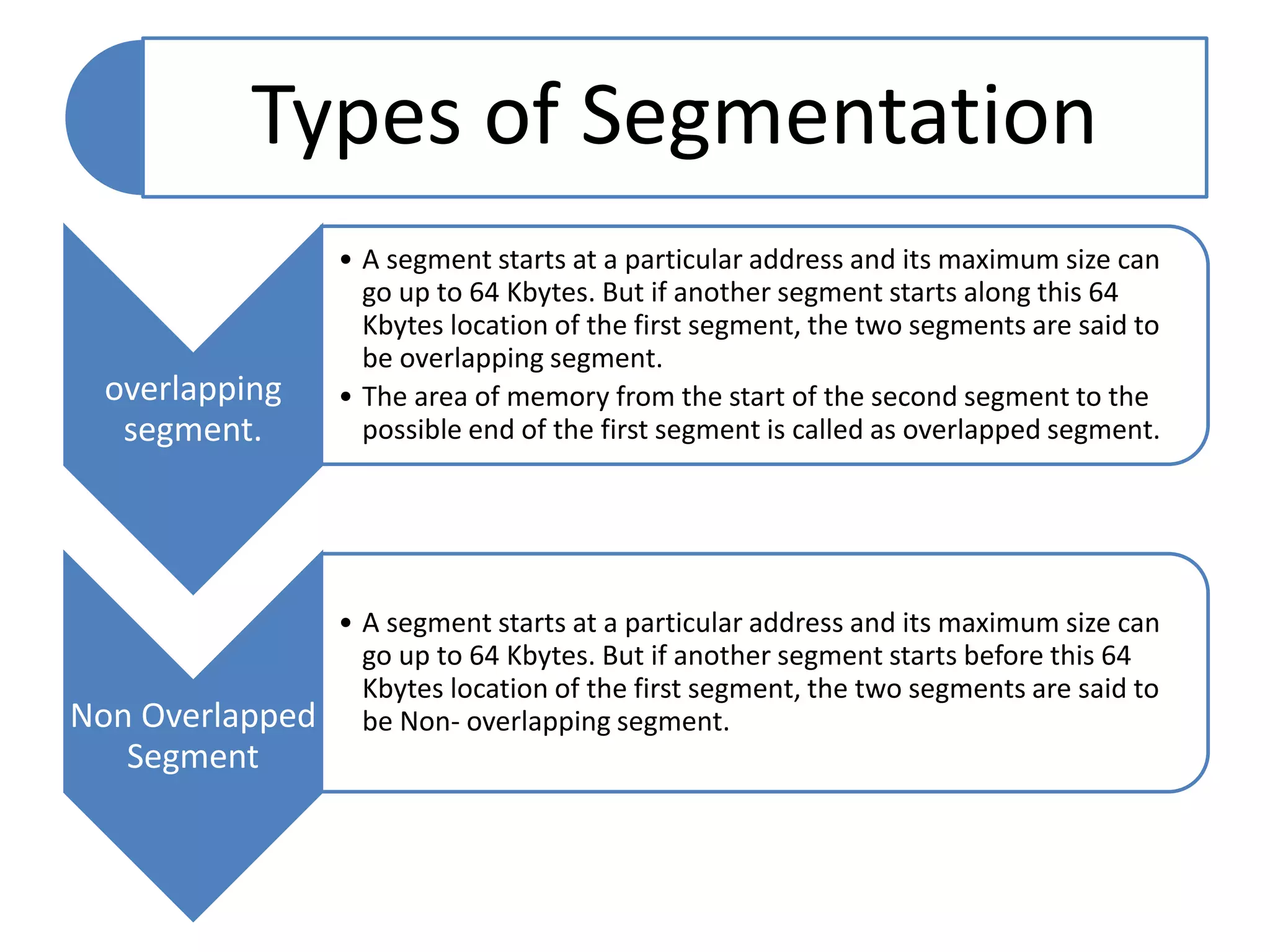
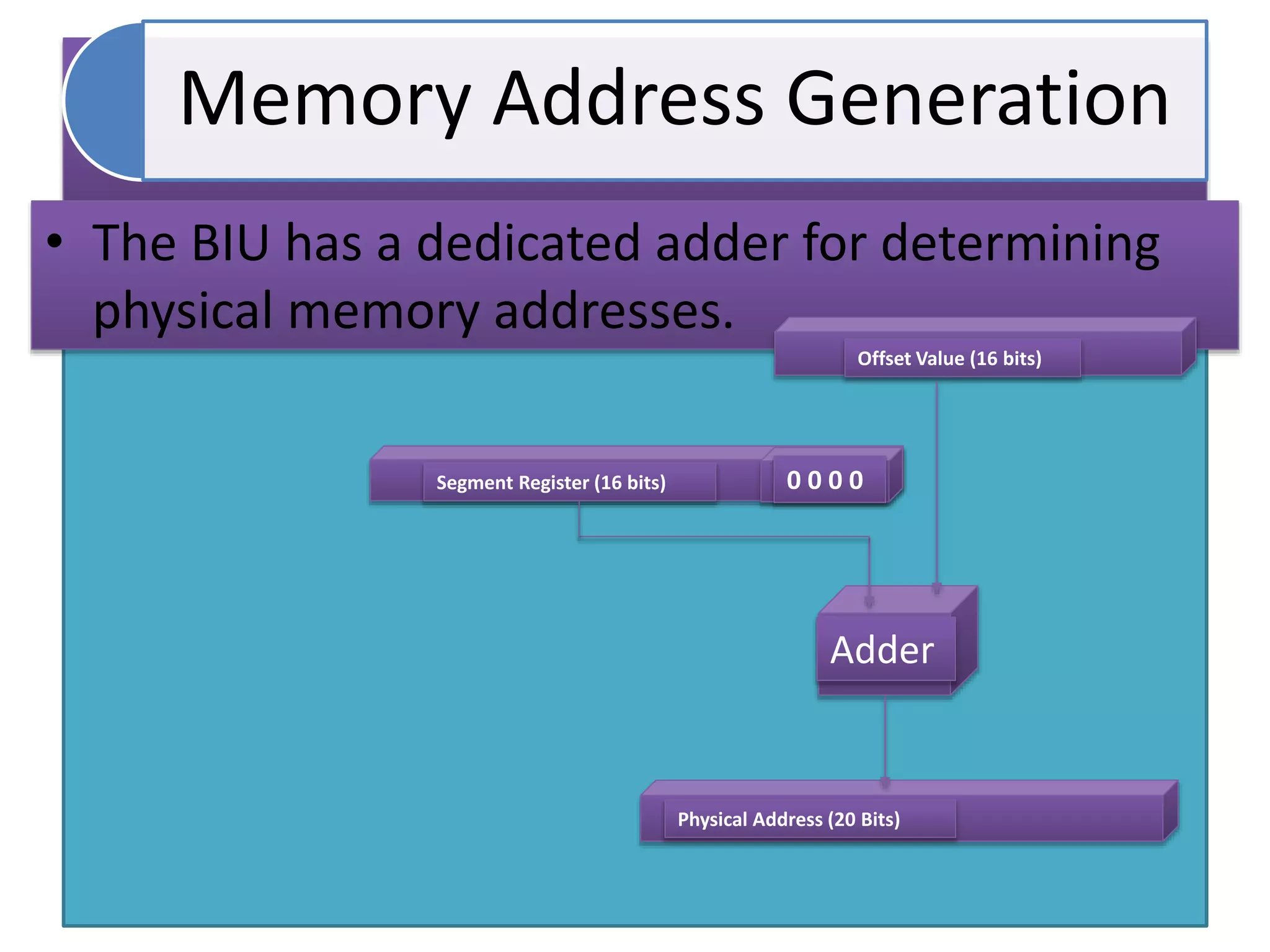
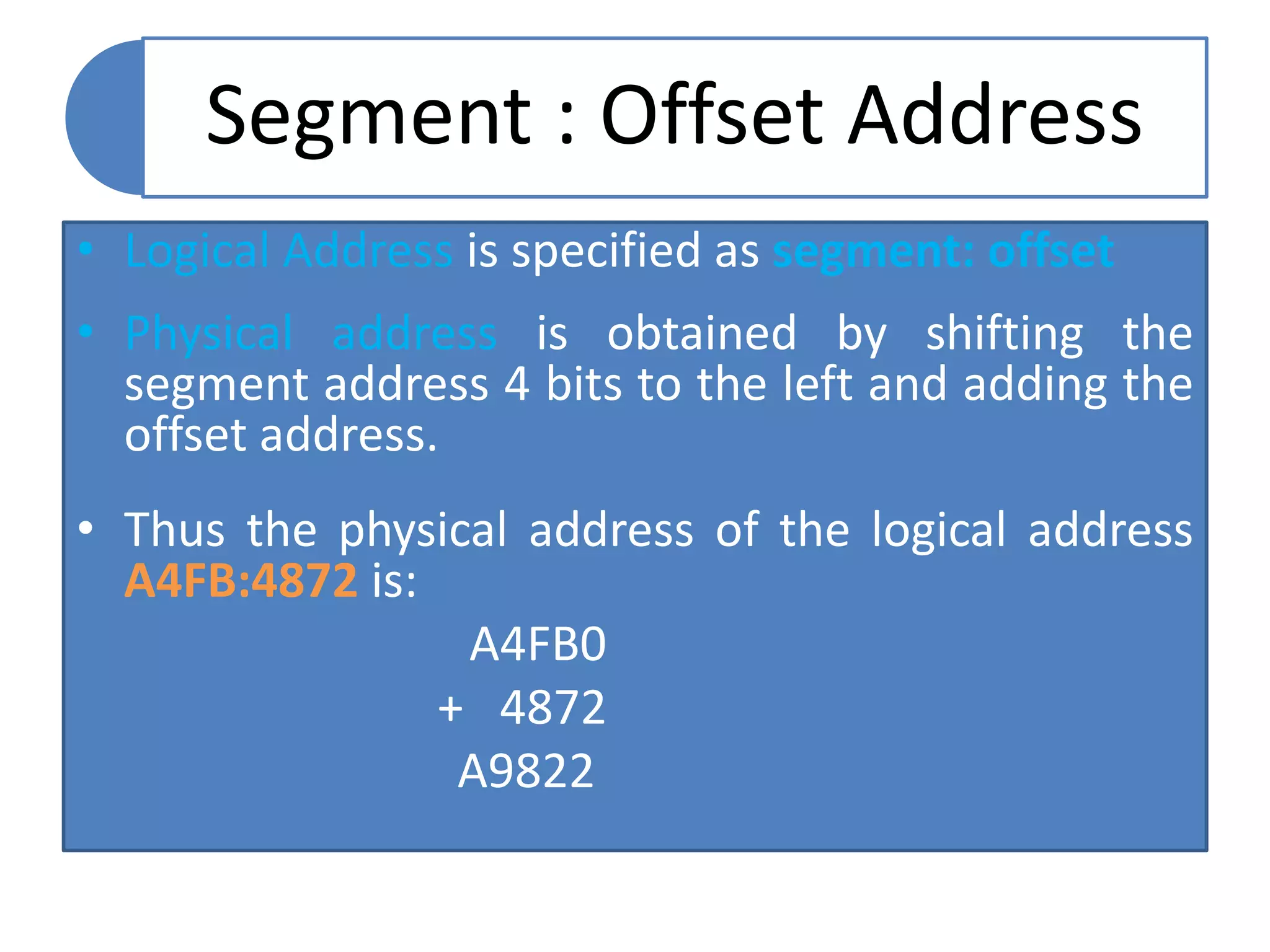
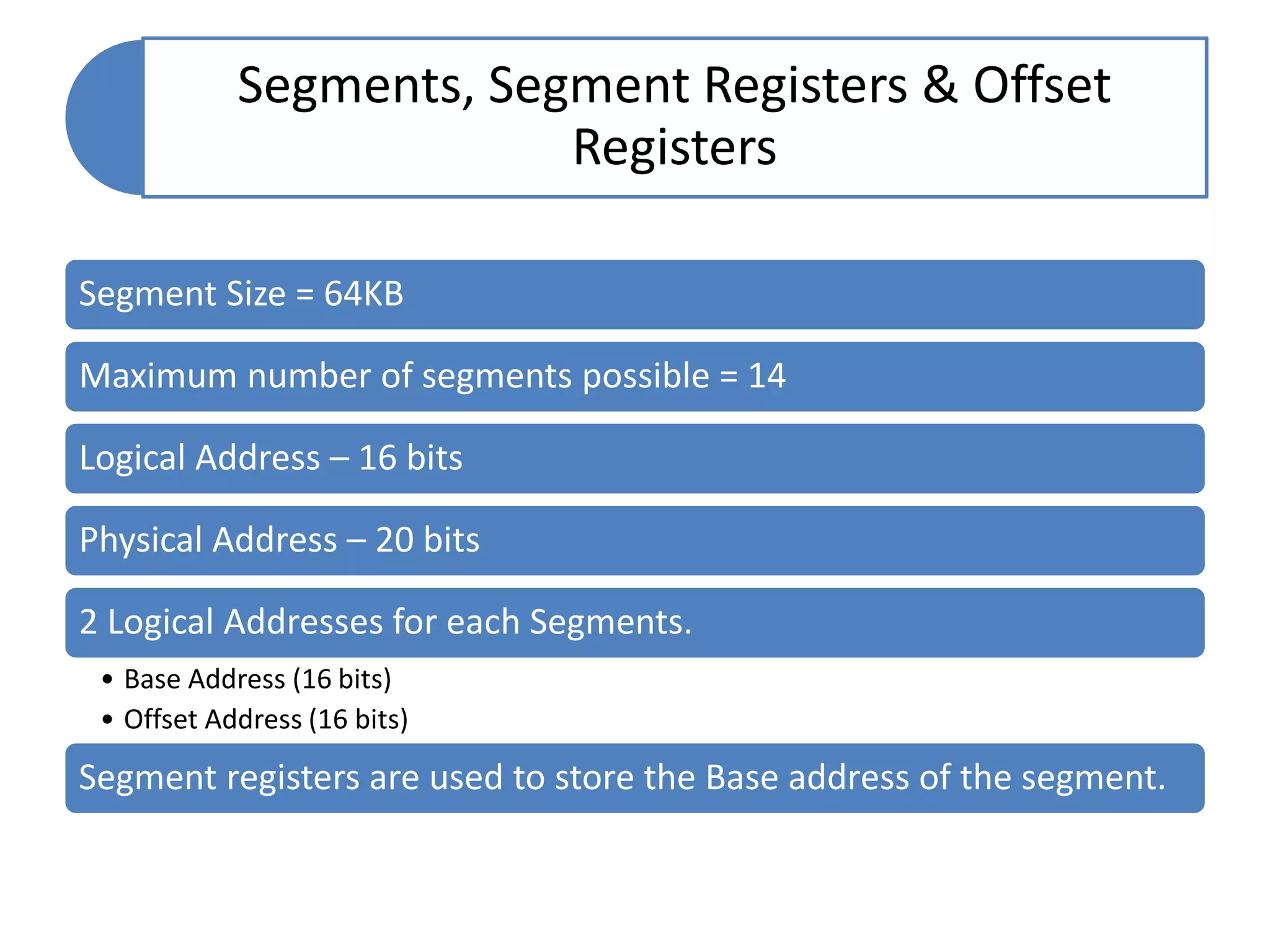
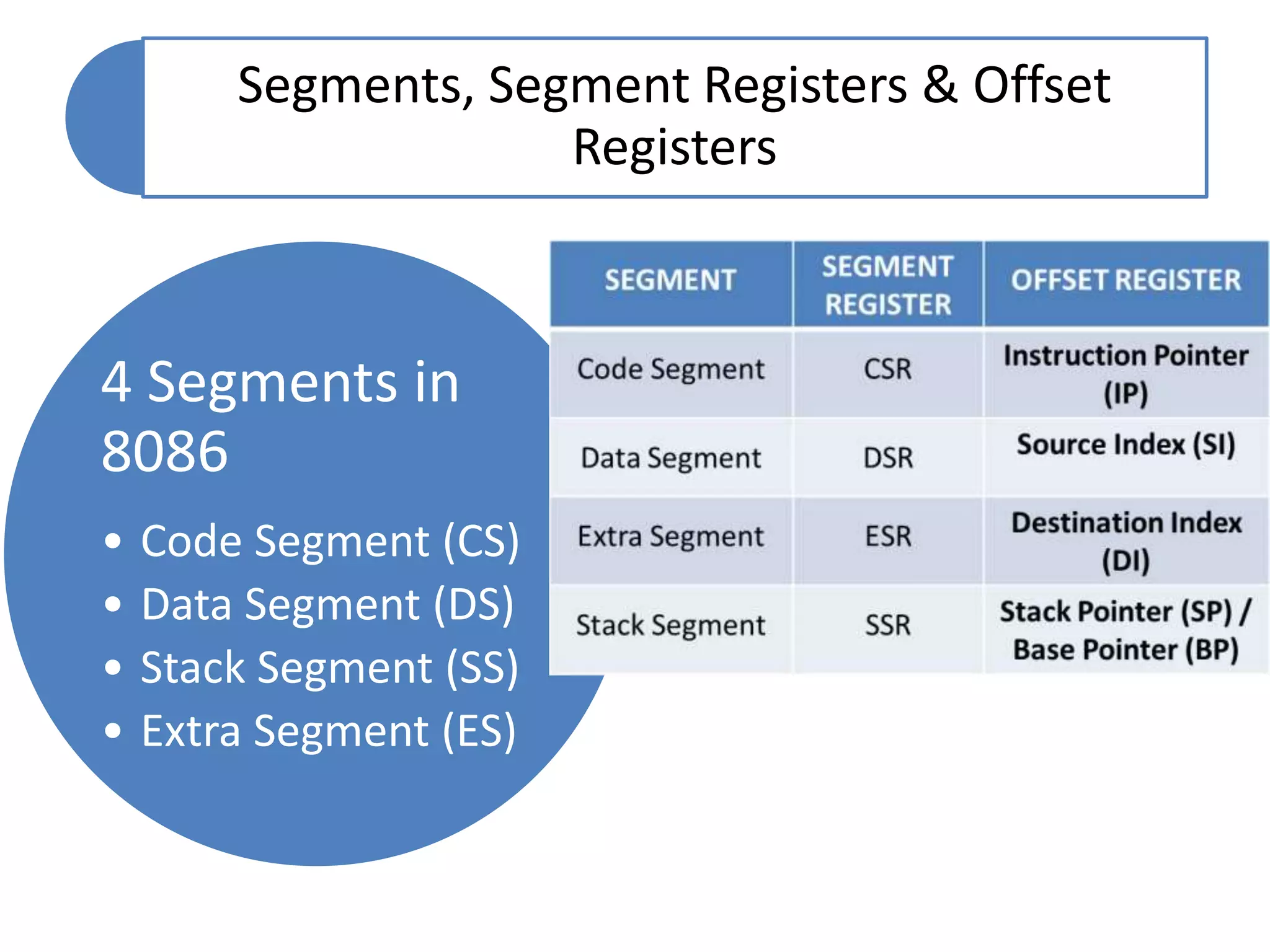
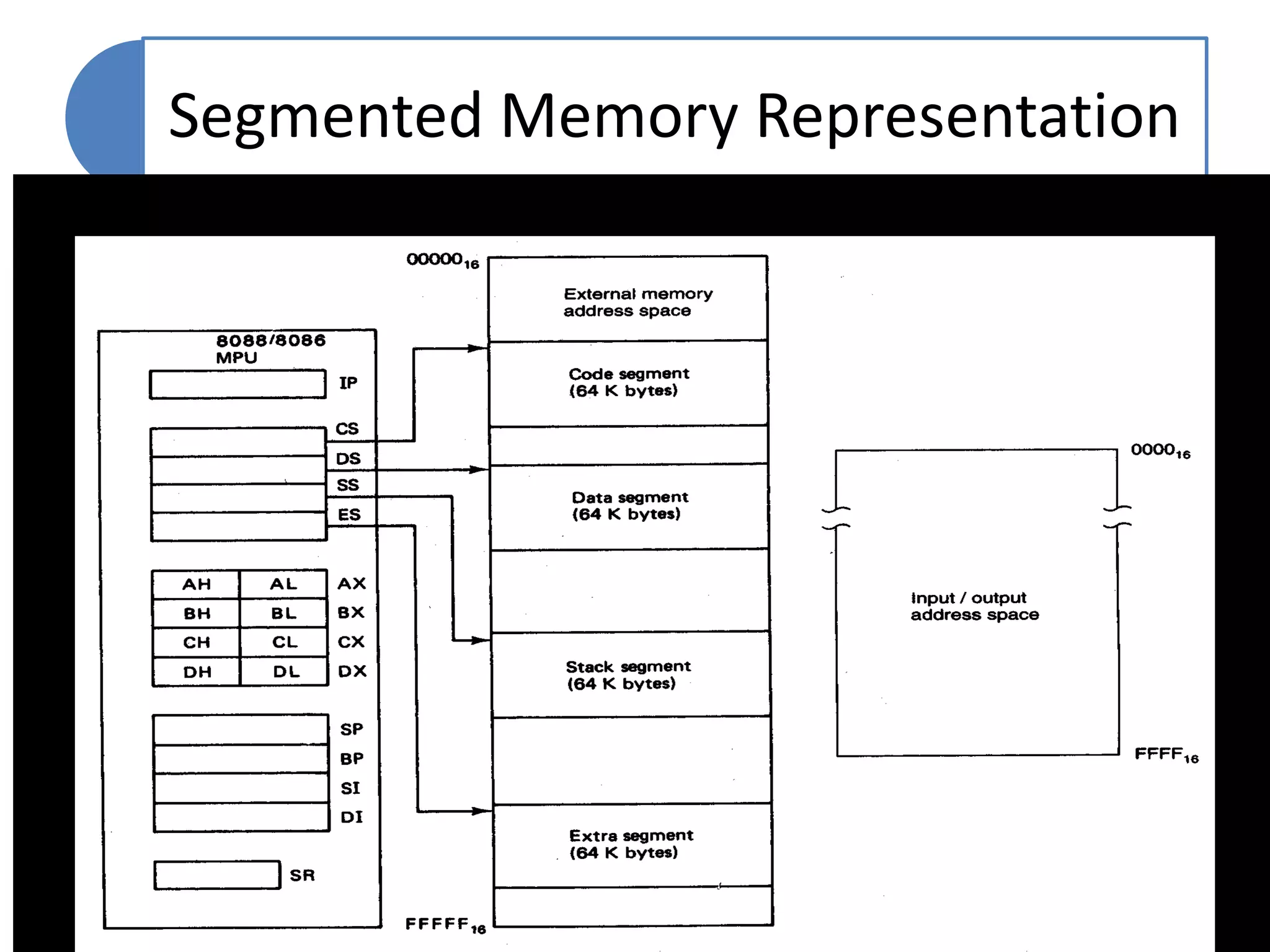
The document discusses memory segmentation in the 8086 microprocessor. It explains that the 8086 has a 20-bit address bus that can address 1MB of physical memory. This memory can be divided into 16 segments of 64KB each, addressed from 0000H to F000H. Segments are combined with offset values within each segment to form a logical address. The physical address is generated by shifting the segment address left by 4 bits and adding the offset. Segment registers store the base addresses of segments like code, data, stack, and extra. This segmentation scheme allows memory capacity greater than the 16-bit addresses and protects code and data.