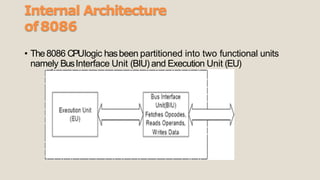
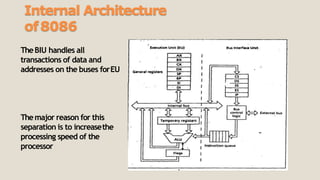
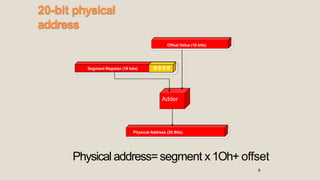
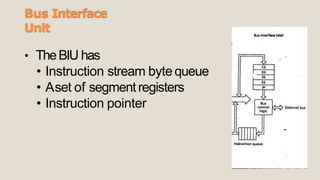
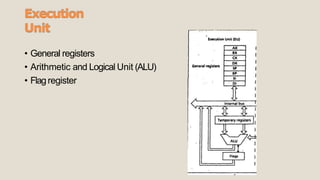
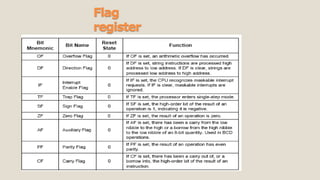
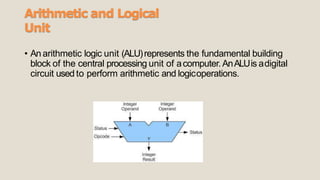
The 8086 microprocessor has a 16-bit architecture and was designed by Intel between 1976-1978. It has a 20-bit address bus allowing access to 1MB of memory. The 8086 gave rise to the x86 architecture and was used in the original IBM PC. The 8086 CPU logic is partitioned into a Bus Interface Unit and Execution Unit. The BIU handles data and address transactions on the buses for the EU. It contains an instruction queue, segment registers, and instruction pointer. The EU contains general registers, an ALU, and flag register for performing arithmetic and logical operations.