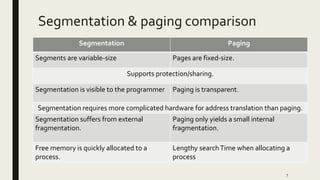
Memory is divided into segments to enhance system performance. There are four main types of segments: code, data, stack, and extra. Each segment has its own register for addressing memory locations. Segments can overlap or be non-overlapping. Segmentation supports variable size segments, protection, and sharing between processes by referencing the same segment. It allows logical addresses to access physical memory but requires more complex hardware than paging.