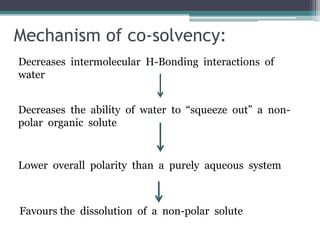
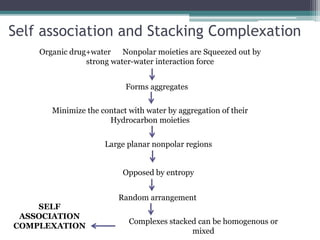
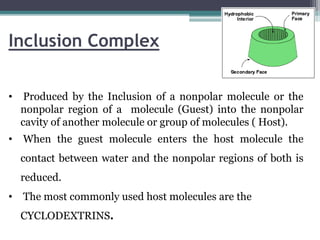
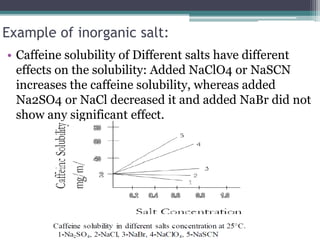
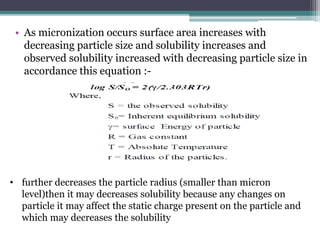
The document discusses various solubilization techniques essential for enhancing the solubility of poorly soluble drugs, including co-solvency, complexation, salt formation, micronization, and selective adsorption. Each technique has its advantages and disadvantages, with specific methods recommended based on the nature of the drug and desired outcomes. Additionally, various examples of drugs utilizing these techniques are provided, along with references for further reading.