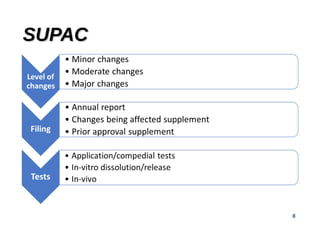
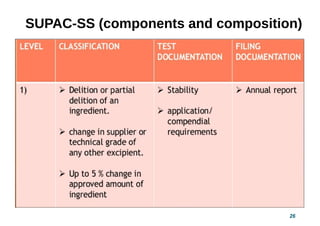
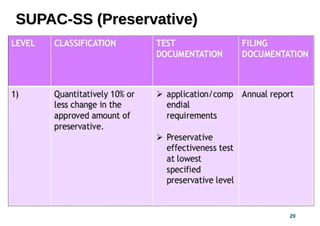
This document provides guidelines for scale-up and post-approval changes (SUPAC) as outlined by the FDA. It discusses SUPAC documents, levels of changes, and recommendations for changes to components and composition, manufacturing site, batch size, and manufacturing process and equipment. The guidelines provide recommendations for submitting documentation to the FDA for level 1, 2, and 3 changes to ensure quality and performance of drug products after approval. It notes some limitations of the SUPAC guidelines, including that they have not been updated since 1995/1997 and do not cover all potential changes.