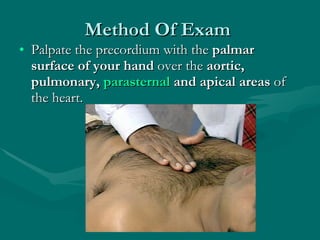
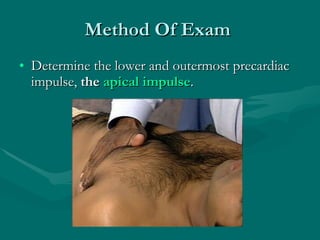
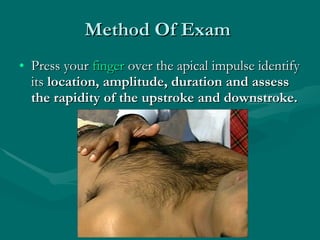
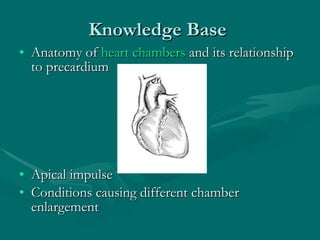
This document describes how to palpate the precordium to evaluate the heart. It outlines how to locate the apical impulse and assess its characteristics. Abnormal findings include precordial bulges or thrills which may indicate conditions like ventricular hypertrophy. The timing and location of thrills can provide clues about underlying heart valves or vessels. A thorough precordial exam requires knowledge of cardiac anatomy, physiology, and how abnormalities affect hemodynamics and present on physical exam.