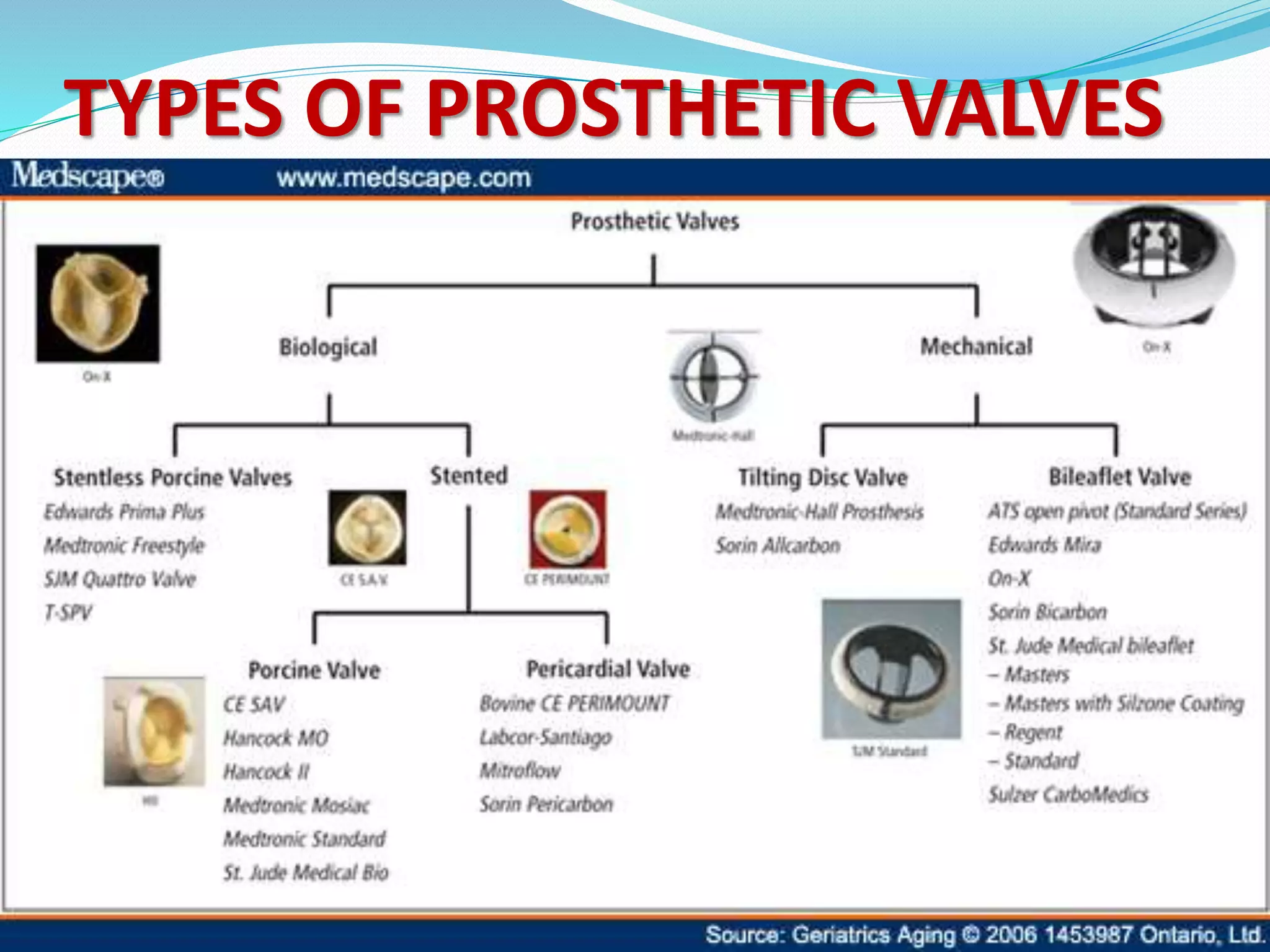
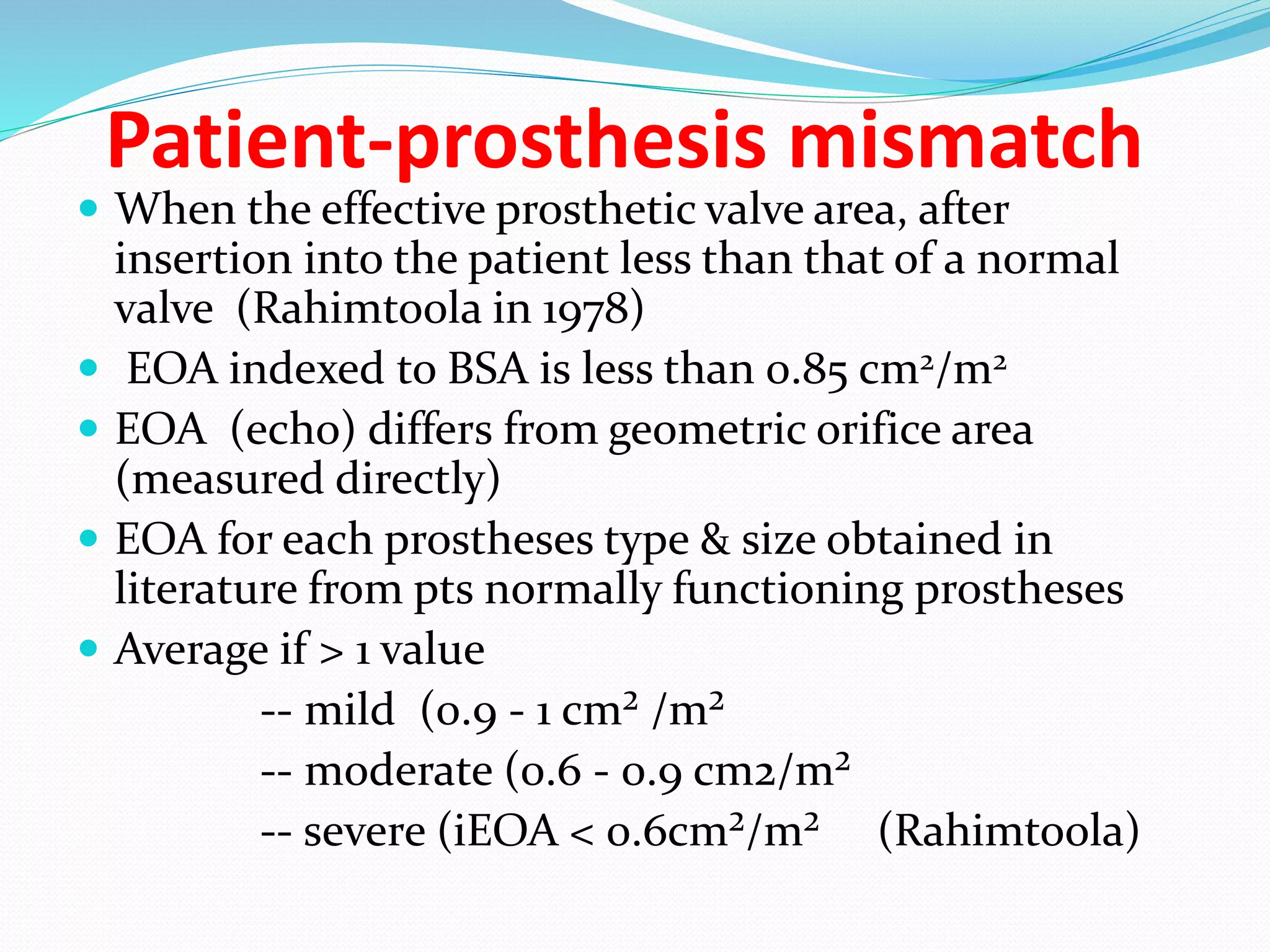
A prosthetic heart valve is a surgically implanted device used to replace a diseased heart valve. There are two main types: mechanical valves made of metal or other man-made materials, and tissue (biological) valves made from animal or human tissue. Mechanical valves have movable parts that open and close blood flow, while tissue valves function similarly to natural heart valves. Prosthetic heart valves can require lifelong anticoagulation medication to prevent blood clots. Complications include bleeding, infection, valve dysfunction, and tissue overgrowth. Echocardiography and cardiac catheterization are used to assess prosthetic heart valve function and complications.