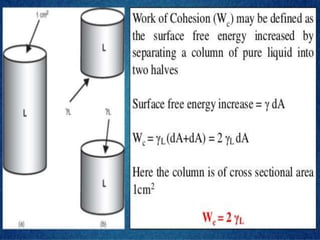
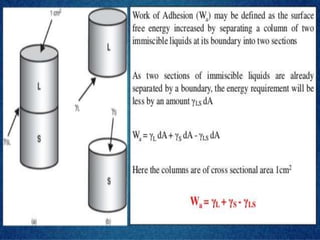
This document discusses surface and interfacial tension. It introduces surface tension and interfacial tension, and defines them as the force per unit length at liquid surfaces and between immiscible liquids, respectively. It then discusses detergency and the mechanisms by which detergents remove dirt. It also covers foaming and anti-foaming agents, spreading coefficients, wetting, and provides examples of applications for these concepts such as in emulsions and coating tablets.