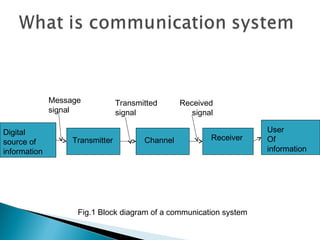
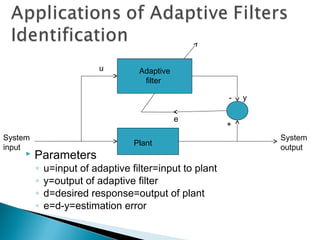
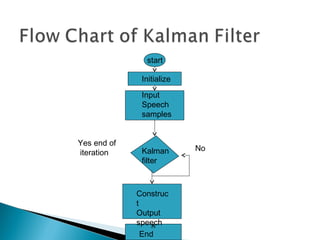
The document discusses estimation theory and its application in fields like communication and radar. It describes two major impairments in communication systems as inter-symbol interference and noise. It discusses adaptive filters and their ability to operate satisfactorily in unknown environments and track input statistics, making them useful for signal processing. Applications of adaptive filters include system identification, inverse modeling, prediction, and interference cancellation. Kalman filters are also discussed as being widely used in speech enhancement.









![ To enter a matrix
2 5 3
6 4 1
>> A = [2 5 3; 6 4 1]
>> B = [1:1.5:6; 2 3 4 5]
>> for i=1:4
for j=1:3
C(i,j)=i*j;
end
end
>> D =[]; D=[D;5]; D=[D;6;7]
>> E = zeros(4, 5)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptonspeechprocessingranbeer-161011190504/85/Ppt-on-speech-processing-by-ranbeer-13-320.jpg)