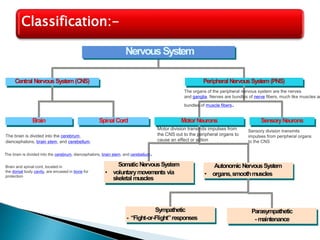
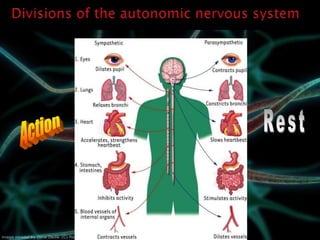
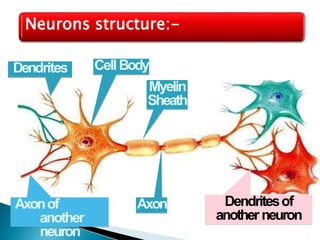
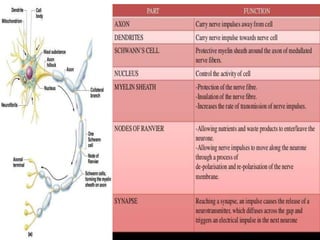
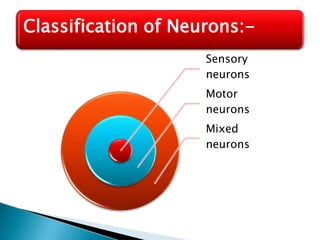
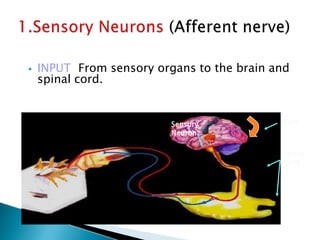
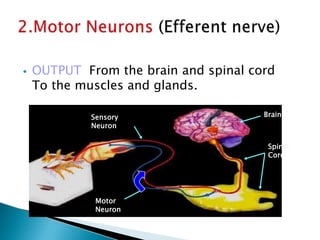
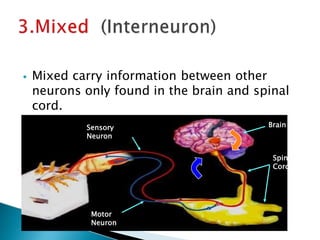
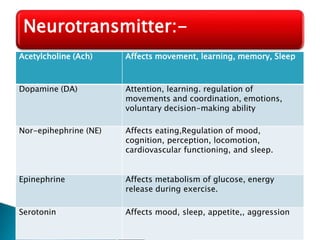
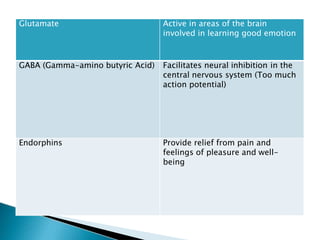
The document provides an overview of the nervous system, detailing its role as the chief controlling and coordinating system of the body, consisting of the central and peripheral nervous systems. It outlines the functions of sensory and motor divisions, the classification of neurons, and the importance of neurotransmitters in conveying information and regulating various bodily functions. Key components include the brain, spinal cord, and different types of neurons that facilitate communication within the nervous system.