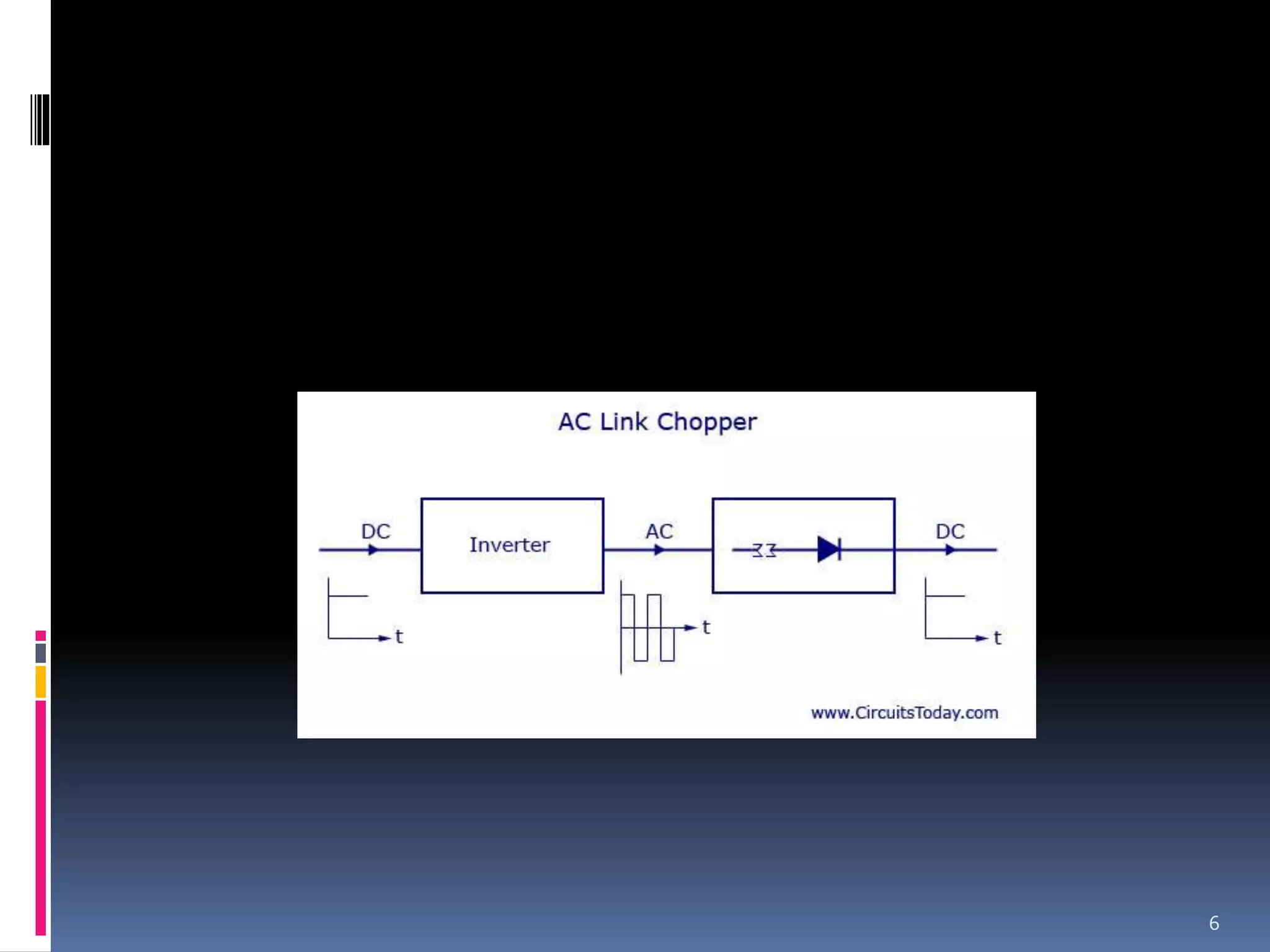
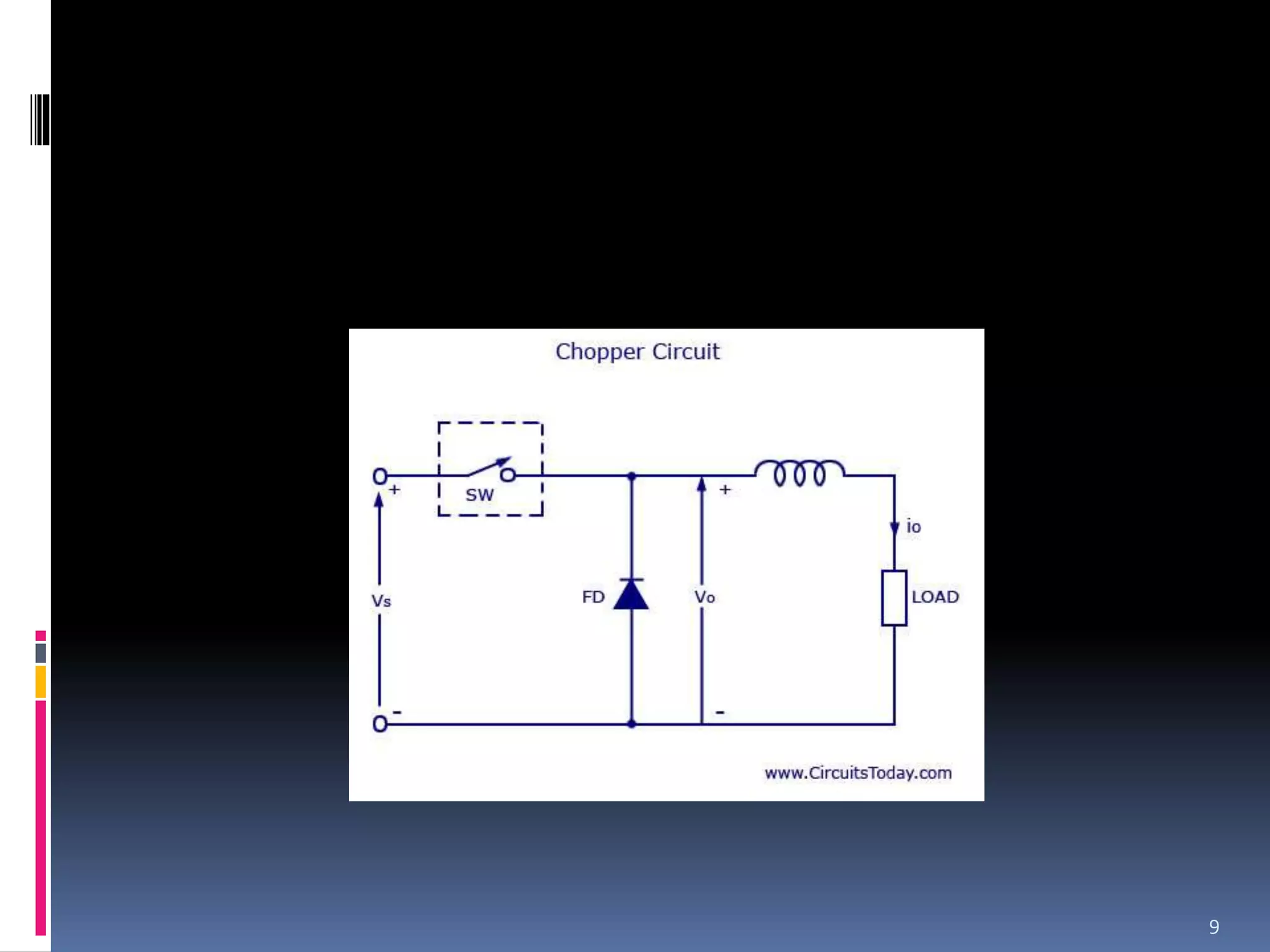
A chopper is a static device that converts a fixed DC input voltage into a variable DC output voltage. There are two main types of choppers: AC choppers and DC choppers. AC choppers first convert DC to AC with an inverter, then step up or down the AC voltage with a transformer, before rectifying it back to DC. DC choppers directly convert the voltage in one stage and are more efficient. Choppers work by using high-speed semiconductor switches to rapidly connect and disconnect the load from the power source. They are commonly used for motor control, solar/wind energy conversion, and powering electronics like computers and instruments.