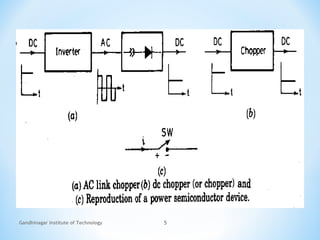
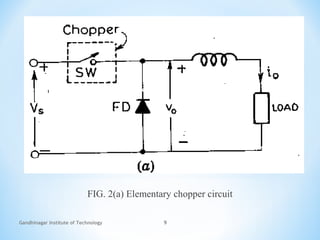
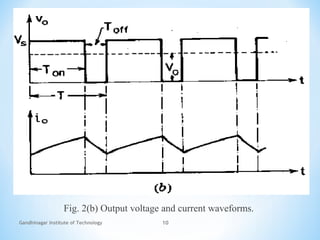
The document provides an overview of DC choppers, detailing their basic principle and operation, along with industrial applications that require variable DC voltage sources. It explains the distinction between AC link choppers and DC choppers, emphasizing the efficiency of choppers that convert fixed DC input to variable DC output. The text concludes with insights gained about the function and types of semiconductor devices used in chopper circuits.