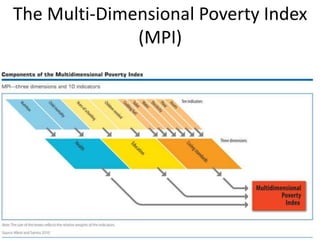
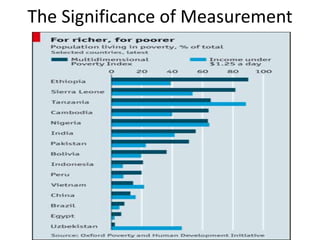
Poverty is defined as a denial of choices and opportunities, impacting individuals' dignity and ability to participate in society. It can be understood through absolute poverty, which refers to a consistent standard of severe deprivation, and relative poverty, which depends on social context and income inequality. Measurement remains challenging; while the Multi-Dimensional Poverty Index attempts to offer a more comprehensive view, issues with data persist, and all countries have individuals experiencing poverty.