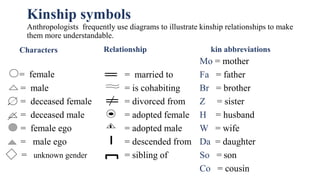
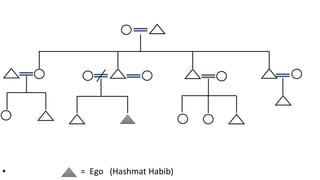
This document discusses the concept of kinship in anthropology. It defines kinship as the bonds of blood or marriage that bind people together in groups. There are two main types of kinship - affinal based on marriage, and consanguineal based on blood. Kinship is important for determining social status, inheritance, power, and who one can marry. Anthropologists study kinship because it reveals how societies are organized and how power and economics function. Kinship can be traced through unilineal descent down either the male or female line or through both lines. Kin terms are the labels used to identify different relatives in a culture. Diagrams are often used to illustrate kinship relationships.