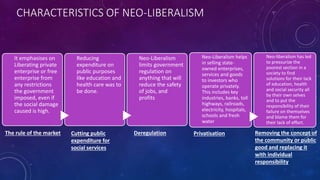
The document provides an overview of neo-liberalism, which advocates for free market capitalism and reduced restrictions on trade. It discusses how neo-liberalism emerged in response to economic crises in the late 20th century and was advanced by powerful international institutions like the IMF, World Bank, and WTO. While neo-liberalism aims to maximize profits and economic growth, the document notes it can negatively impact inequality, public services, and local industries in developing countries.