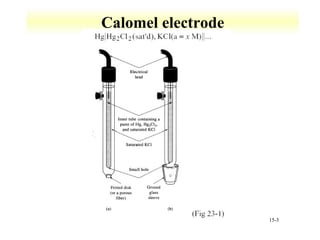
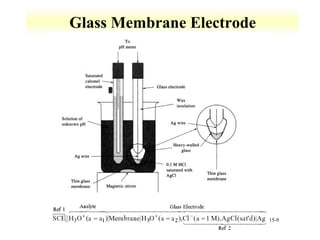
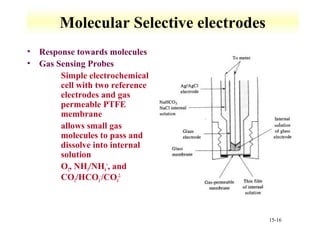
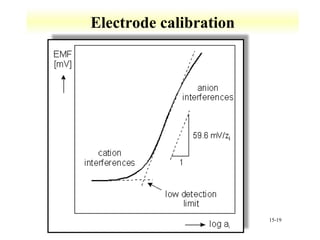
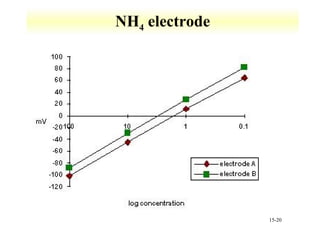
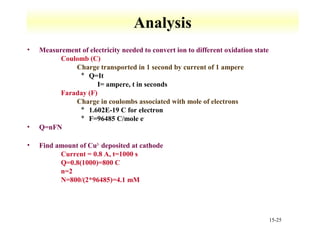
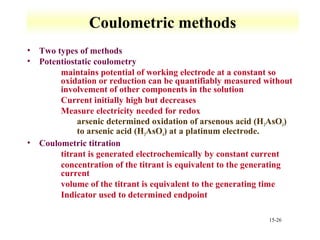
Potentiometry involves measuring the potential of electrochemical cells using ion selective electrodes. It requires a reference electrode with a known constant potential and an indicator electrode that responds to the ion of interest. The potential difference between the electrodes is measured and related to ion concentration or activity. Common types of ion selective electrodes include glass membrane electrodes, crystalline membrane electrodes, and liquid membrane electrodes which incorporate different materials like glasses, crystals, or liquid membranes to selectively bind target ions. Calibration allows the electrode potential measurements to be converted to analytical results.