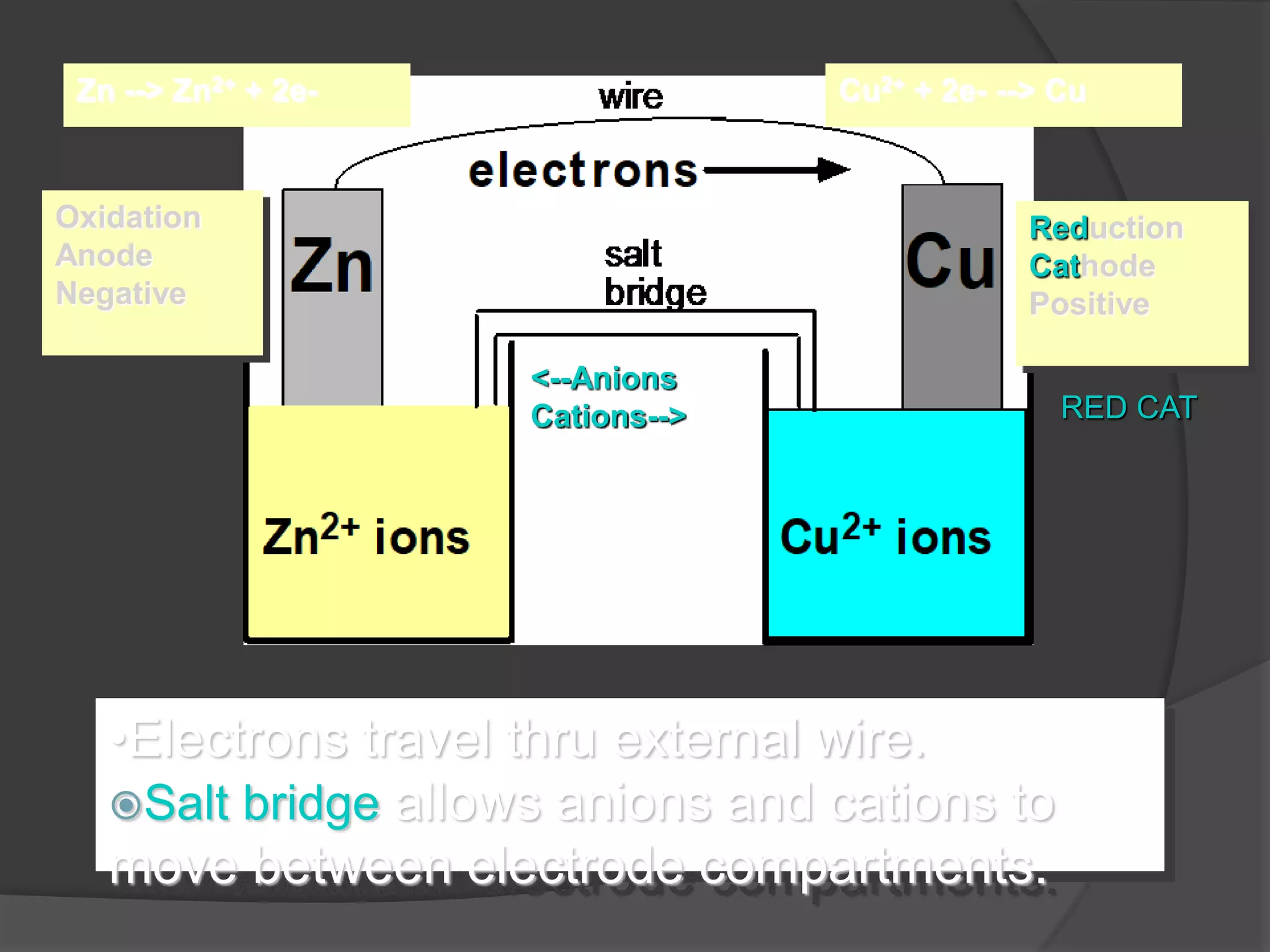
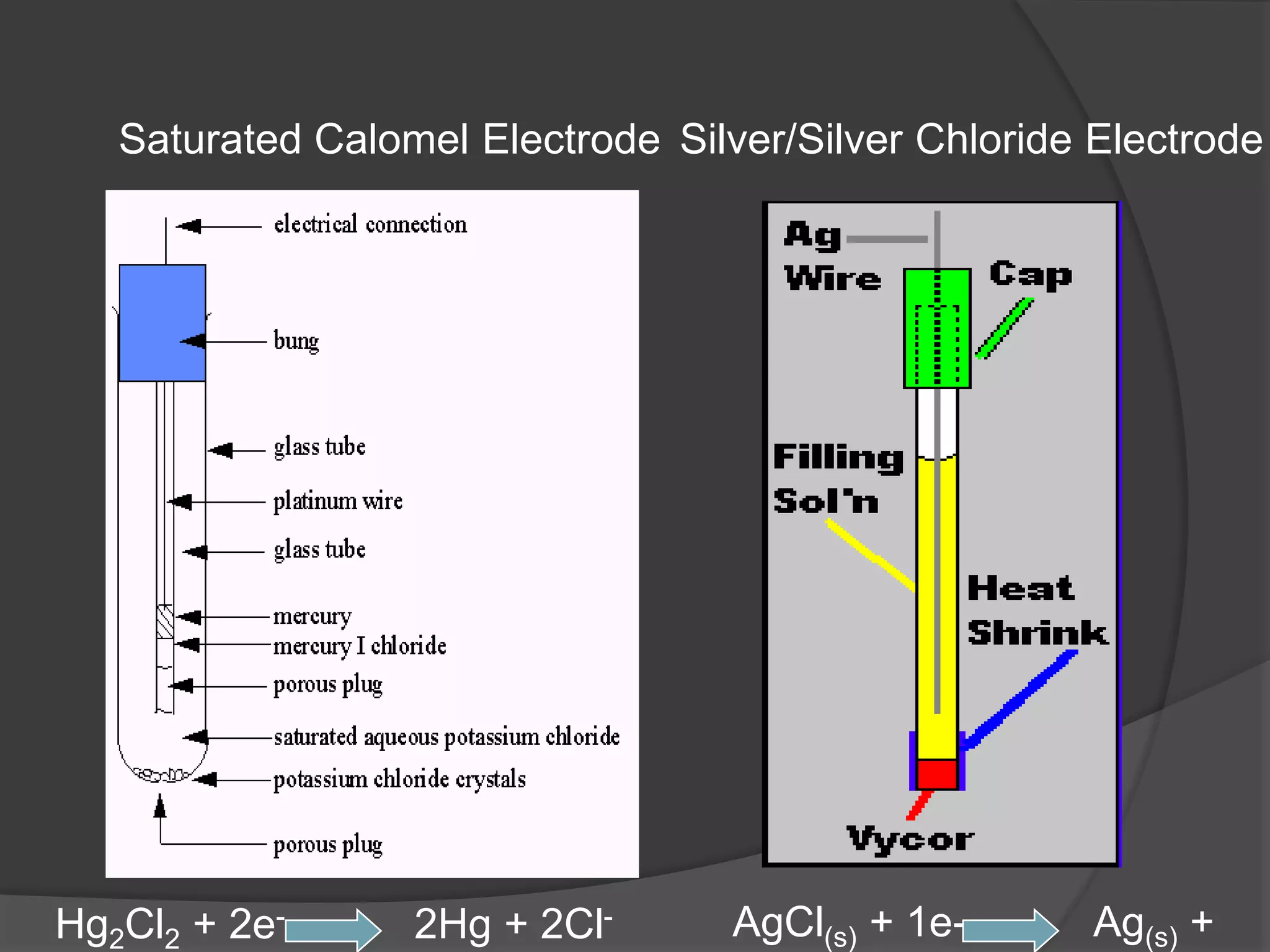
Electrochemistry deals with oxidation-reduction reactions where chemical energy is converted to electrical energy and vice versa. It involves the transfer of electrons between oxidizing and reducing agents. An electrochemical cell allows a redox reaction to occur by transferring electrons through an external connector. The potential difference between the anode and cathode is called the electromotive force (emf). Various electroanalytical techniques like potentiometry, voltammetry, conductometry, and coulometry are used for clinical applications such as measuring blood gases, electrolytes, and analytes. Optical chemical sensors called optodes are also used as they offer advantages over traditional electrodes.























































![METAL LIGAND COMPLEX ( Ruthenium [11]
tris [di pyridine],Pt & Pb metalloporphyrins)
in hydrophobic polymer films ( silicon rubber)
in which O2 is soluble
Decreased intensity of fluorescence is
proportional to PO2
APPLICATIONS
- Used for pCO2 determination
- Optically sense the electrolyte ions eg.
lipophilic ionophore for polymer memb.ISE with
lipophilic Ph indicator ( valinomycin for k+)
change in optical absorption or flourescence
spectrum of polymer layer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electrochemistry-221031034512-09e198aa/75/ELECTROCHEMISTRY-pptx-58-2048.jpg)

























