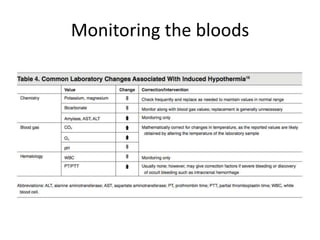
Therapeutic hypothermia, or induced hypothermia, involves deliberately cooling cardiac arrest patients to between 32-34°C for 12-24 hours after return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) to reduce reperfusion injury to organs like the brain, heart, liver and kidneys from hypoperfusion and ischemia during the cardiac arrest. It aims to improve outcomes by reducing the effects of post-cardiac arrest syndrome, which involves a complex pathophysiological cascade following ischemia. Current research shows benefits of inducing therapeutic hypothermia before or during the cardiac arrest event. Key aspects of care involve induction of hypothermia within 6 hours, preferably 2 hours, of ROSC, maintenance of target temperature for 12-24 hours,