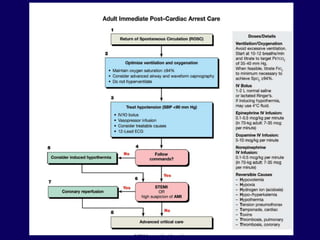
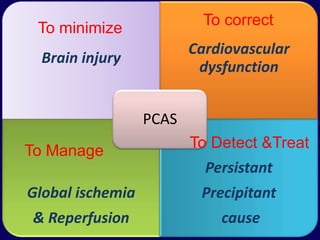
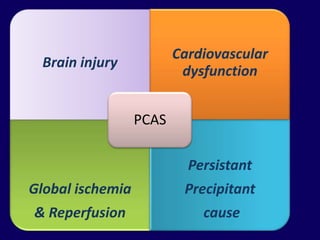
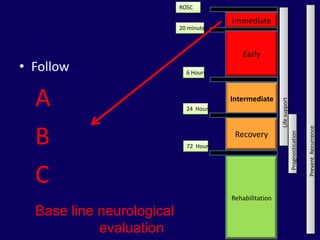
1. Post resuscitation care involves not only return of spontaneous circulation but return to pre-arrest status through management of global ischemia, cardiovascular dysfunction, and persistent precipitant causes.
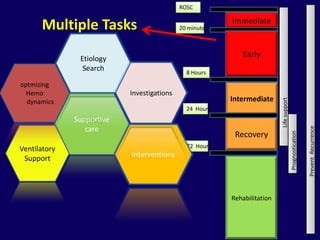
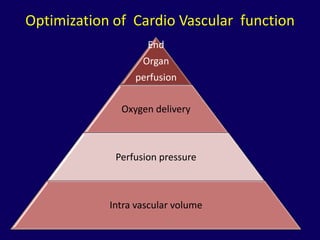
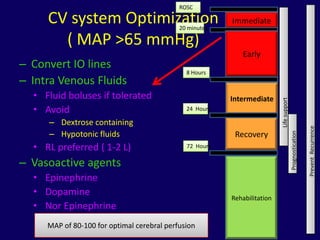
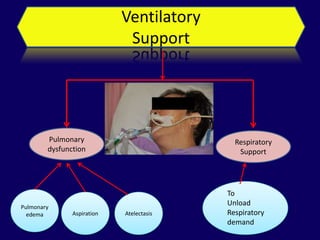
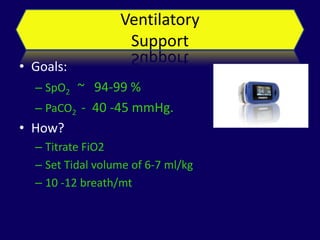
2. Immediate goals after ROSC include optimization of cardiovascular function and oxygen delivery, ventilation support, temperature management, etiology investigation, and interventions to prevent recurrence.
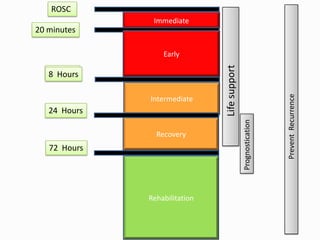
3. Prognostication is an essential component using markers like neurological exams, EEGs, imaging and biomarkers to predict outcomes in comatose post-cardiac arrest patients.











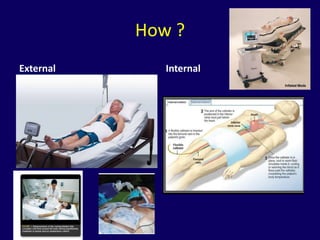












![Prognosticative markers
(Poor outcome)
• Neuroimaging:
– MRI:
• Extensive cortical and subcortical lesions
– CT parameters
• quantitative measure of gray matter:white matter
Hounsfield unit ratio
• Biomarkers:
– Neuron-specific enolase [NSE], S100B, GFAP, CK-
BB)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postresuscitationcare-120921013759-phpapp01/85/Post-resuscitation-care-36-320.jpg)