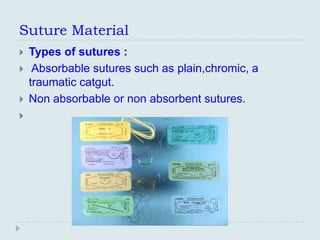
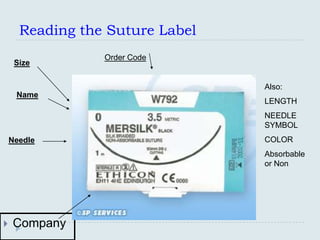
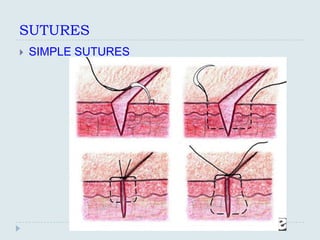
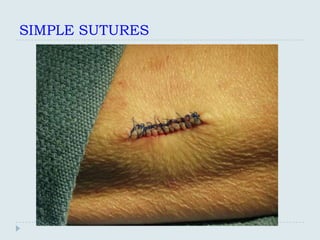
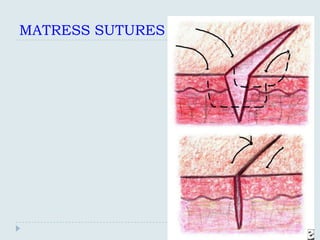
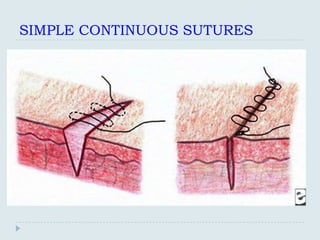
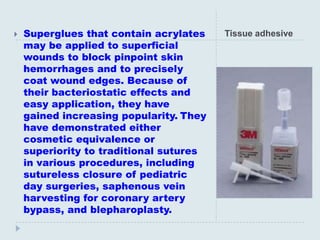
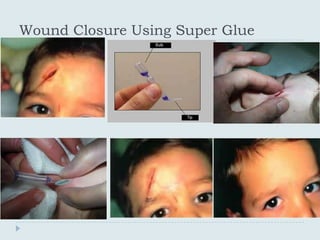
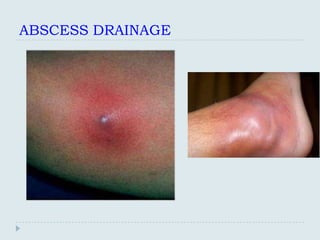
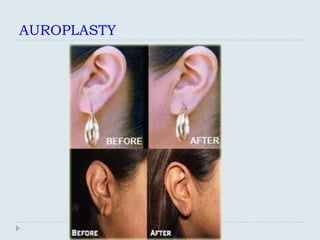
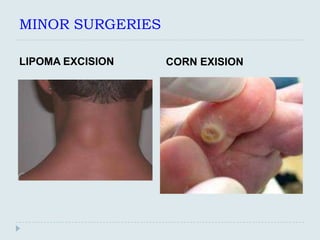
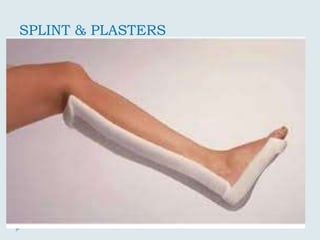
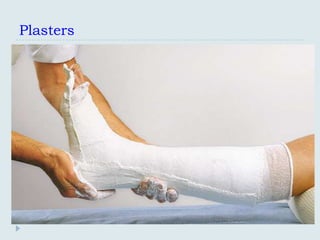
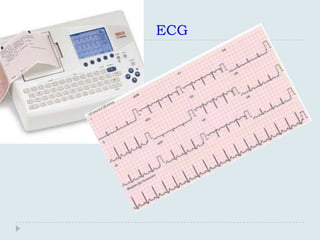
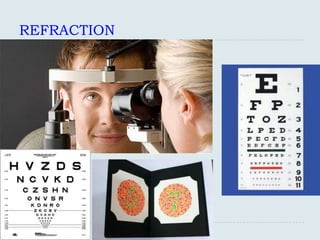
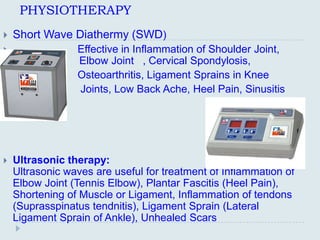
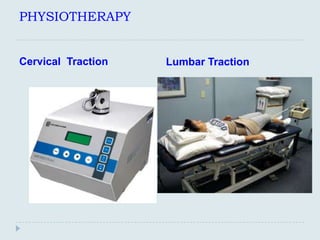
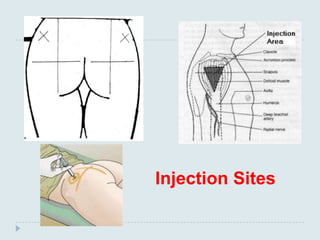
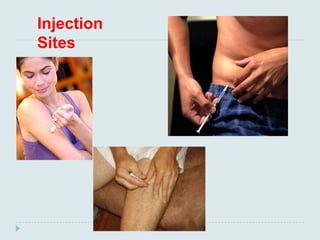
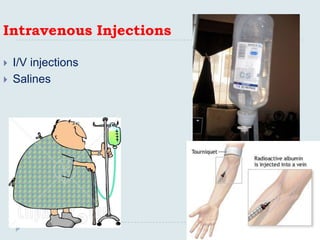
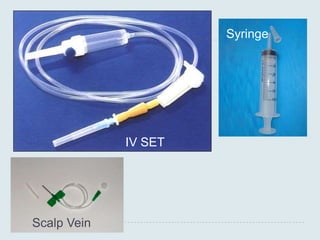
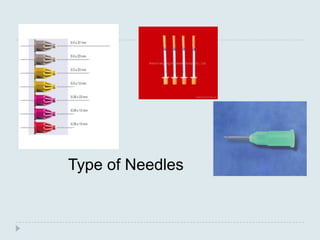
The document discusses various practical clinical skills including minor surgeries, injections, intravenous injections, suturing techniques, wound closure methods, dressings, splints, electrocardiography, spirometry, refraction, and physiotherapy modalities. It describes procedures like abscess drainage, cyst excision, and lipoma excision. It also covers topics like types of sutures, needles, bandaging methods, and physiotherapy options like shortwave diathermy, ultrasonic therapy, and interferential therapy.




![SUTURING
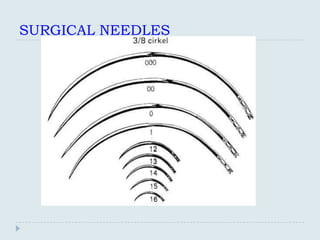
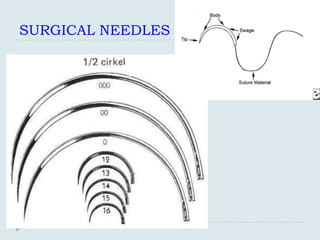
There are several shapes of surgical needles:
Straight
1/4 circle
3/8 circle
1/2 circle. Subtypes of this needle shape
include, from larger to smaller size, CT, CT-1, CT-2
and CT-3.[3]
5/8 circle
compound curve
half curved (also known as ski)
half curved at both ends of a straight segment (also
known as canoe)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practicalskillsinmedicalpractice-130306143523-phpapp02/85/Practical-skills-in-medical-practice-11-320.jpg)