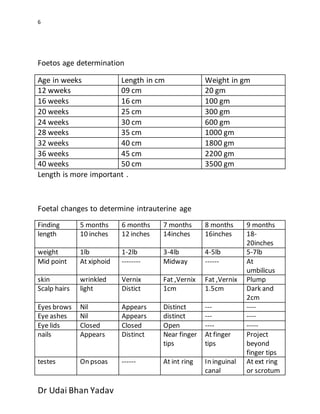
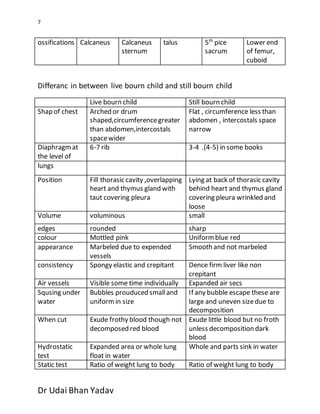
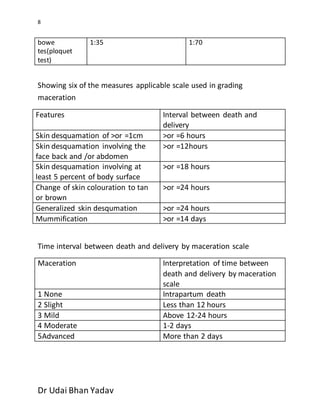
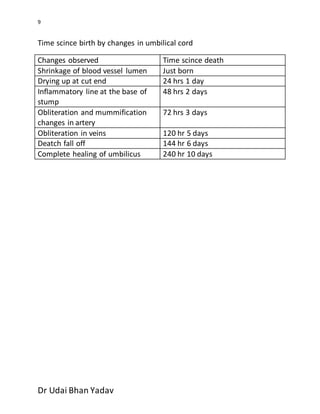
The document outlines procedures for conducting a fetal autopsy, focusing on key factors such as intrauterine age, viability, and determining the cause of death. It covers external and internal examinations, including hydrostatic tests to assess respiration and methods to evaluate live birth using various findings like stomach contents and umbilical vessels. Additionally, it provides criteria for distinguishing between live-born and stillborn infants based on physical changes and maceration, along with the time intervals related to death and delivery.