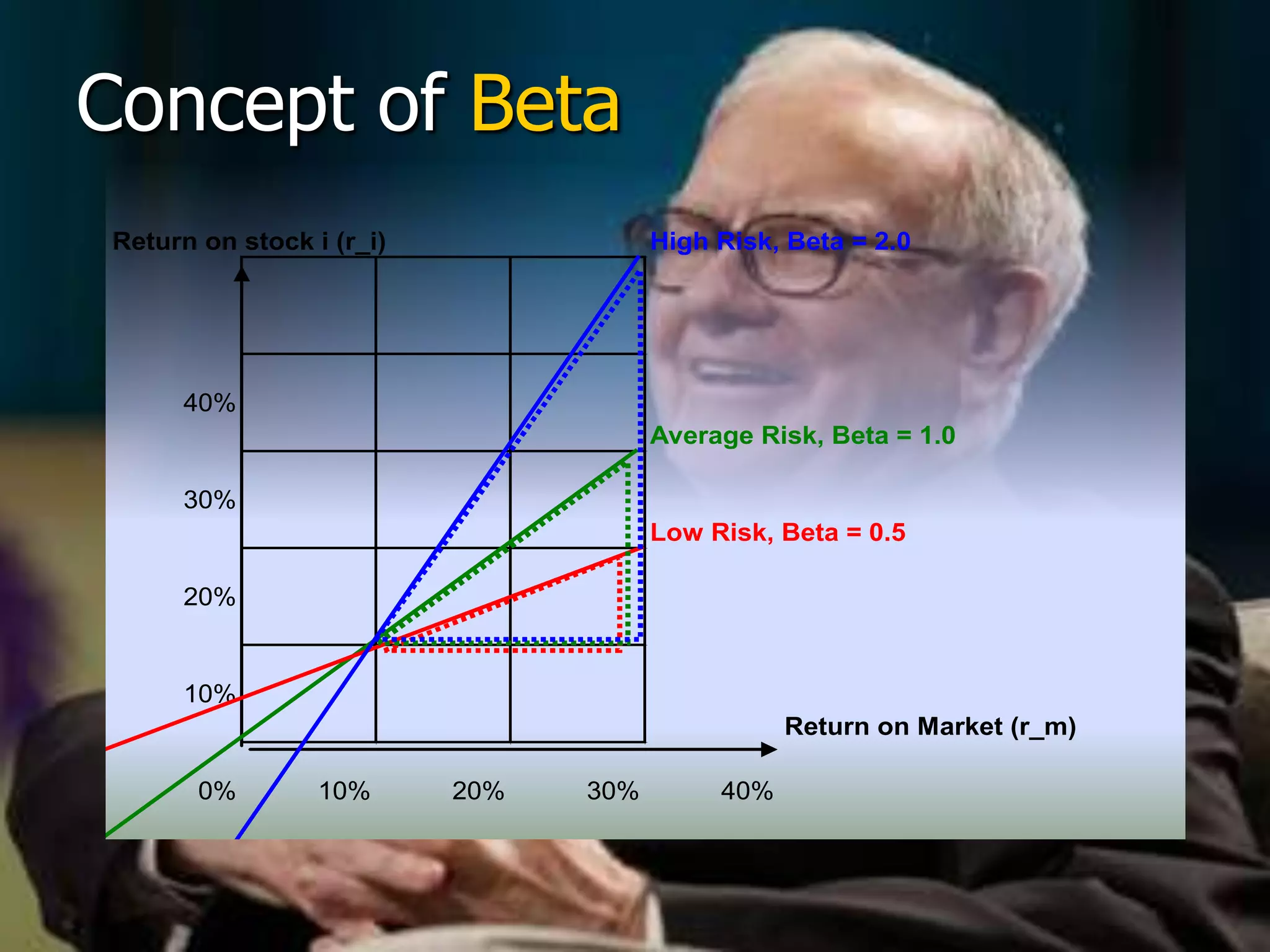
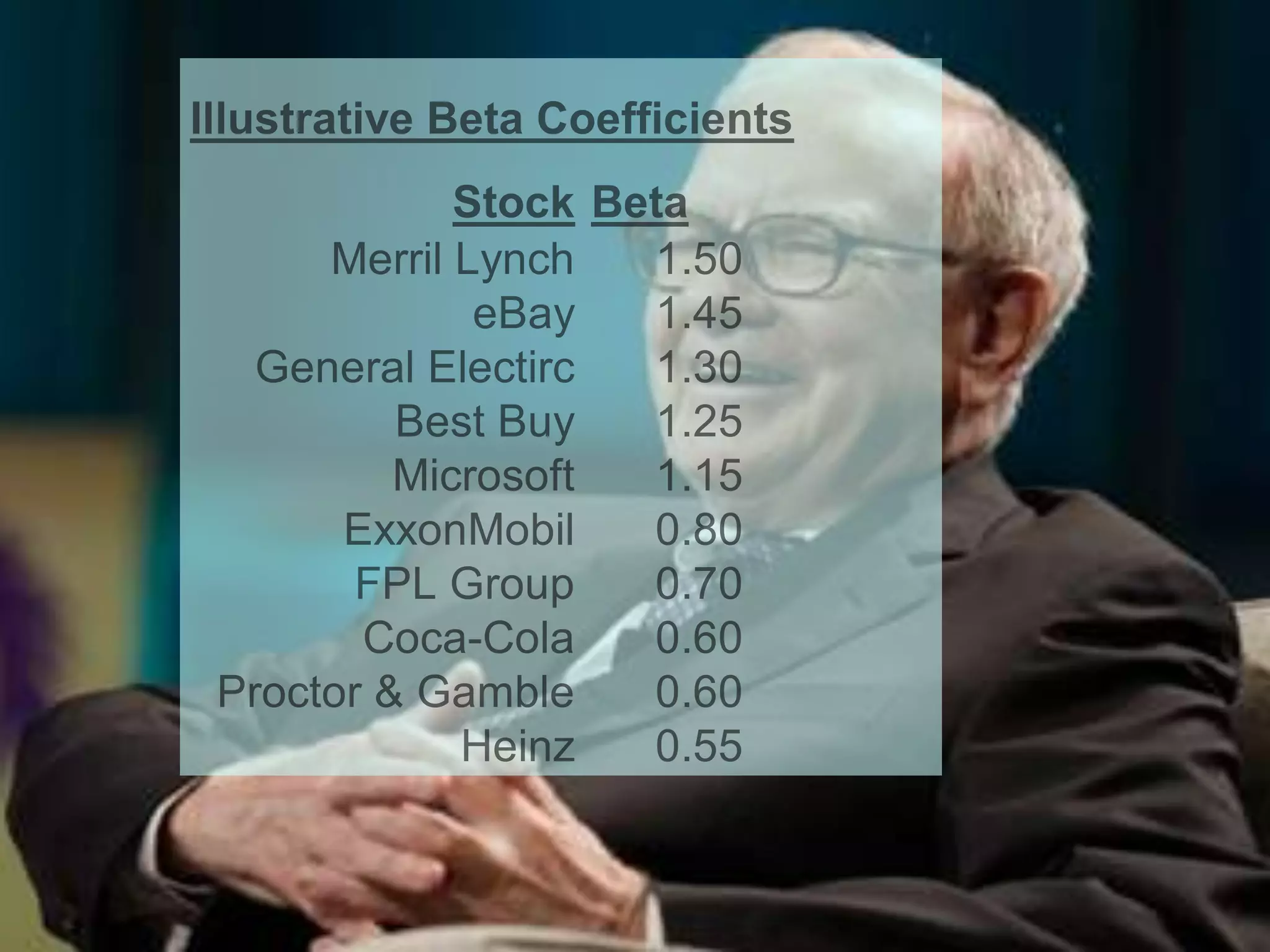
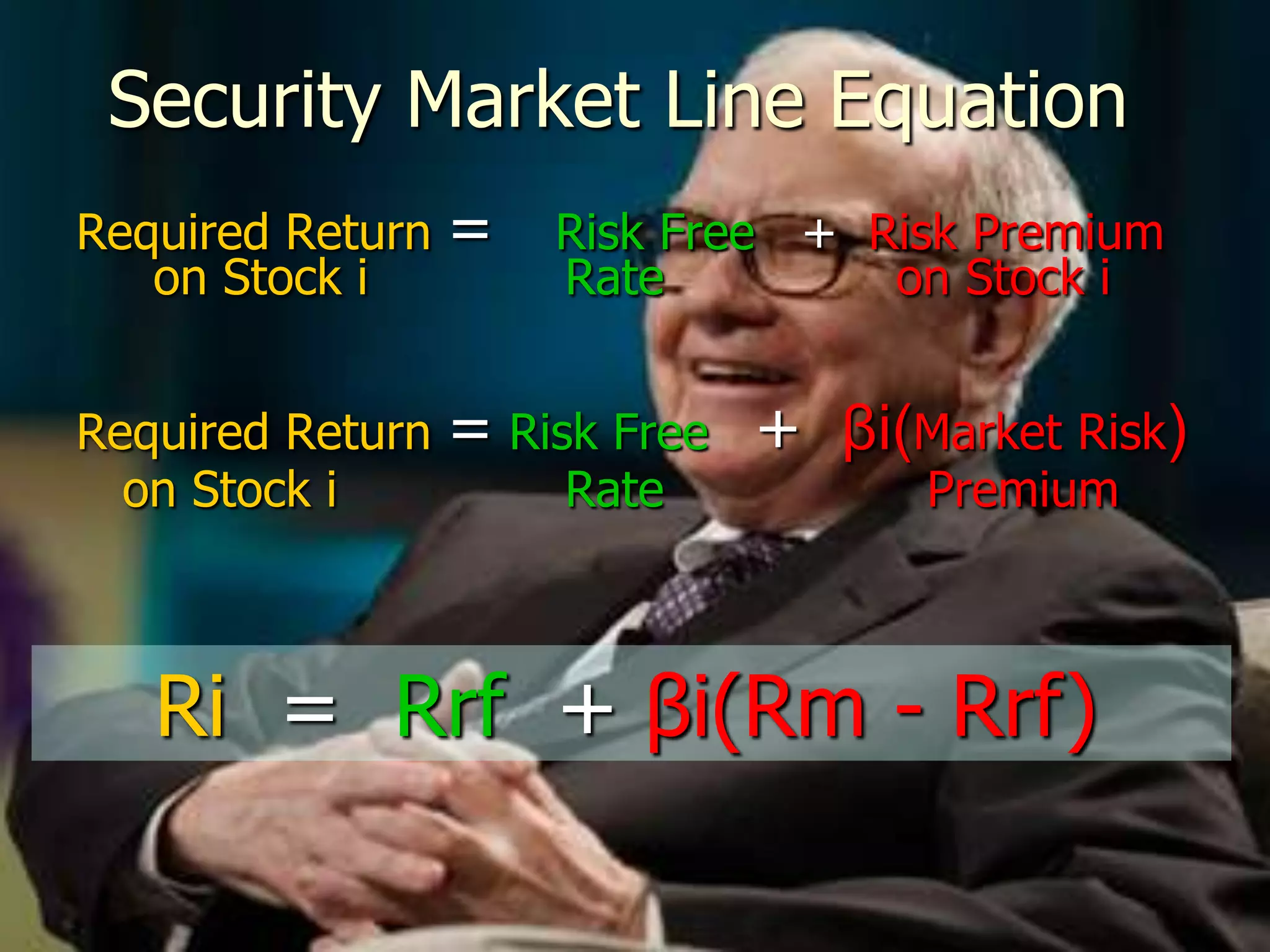
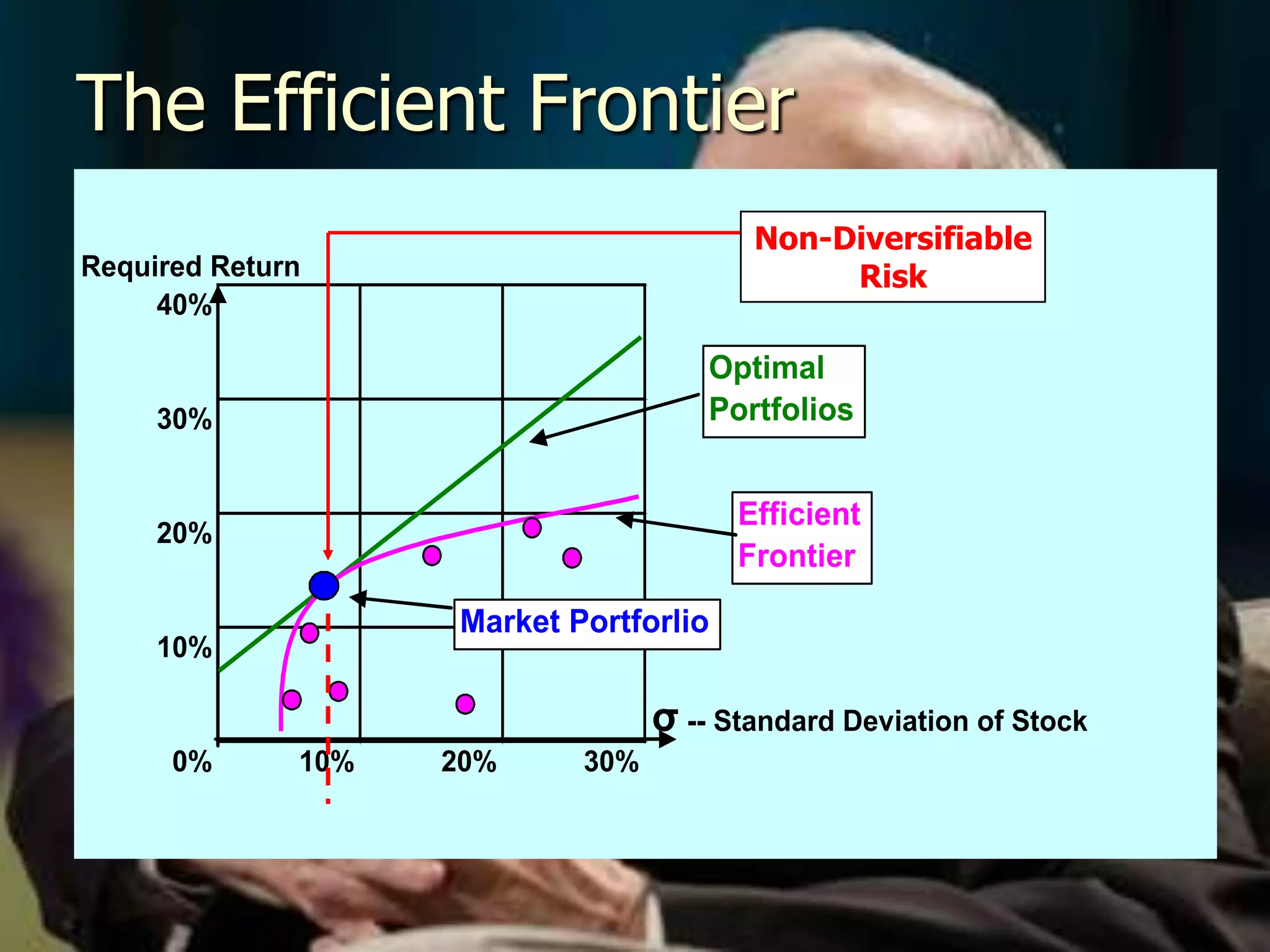
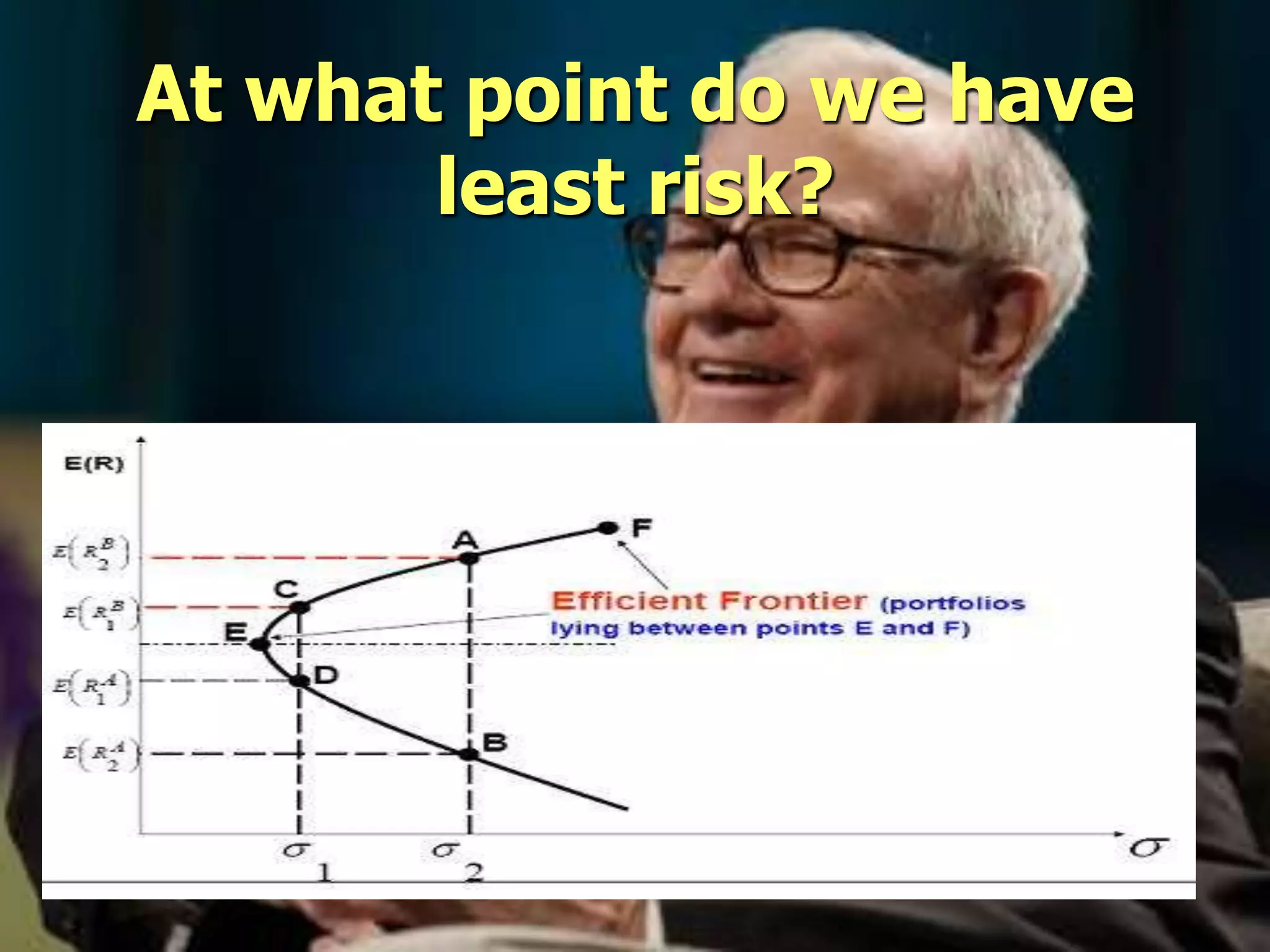
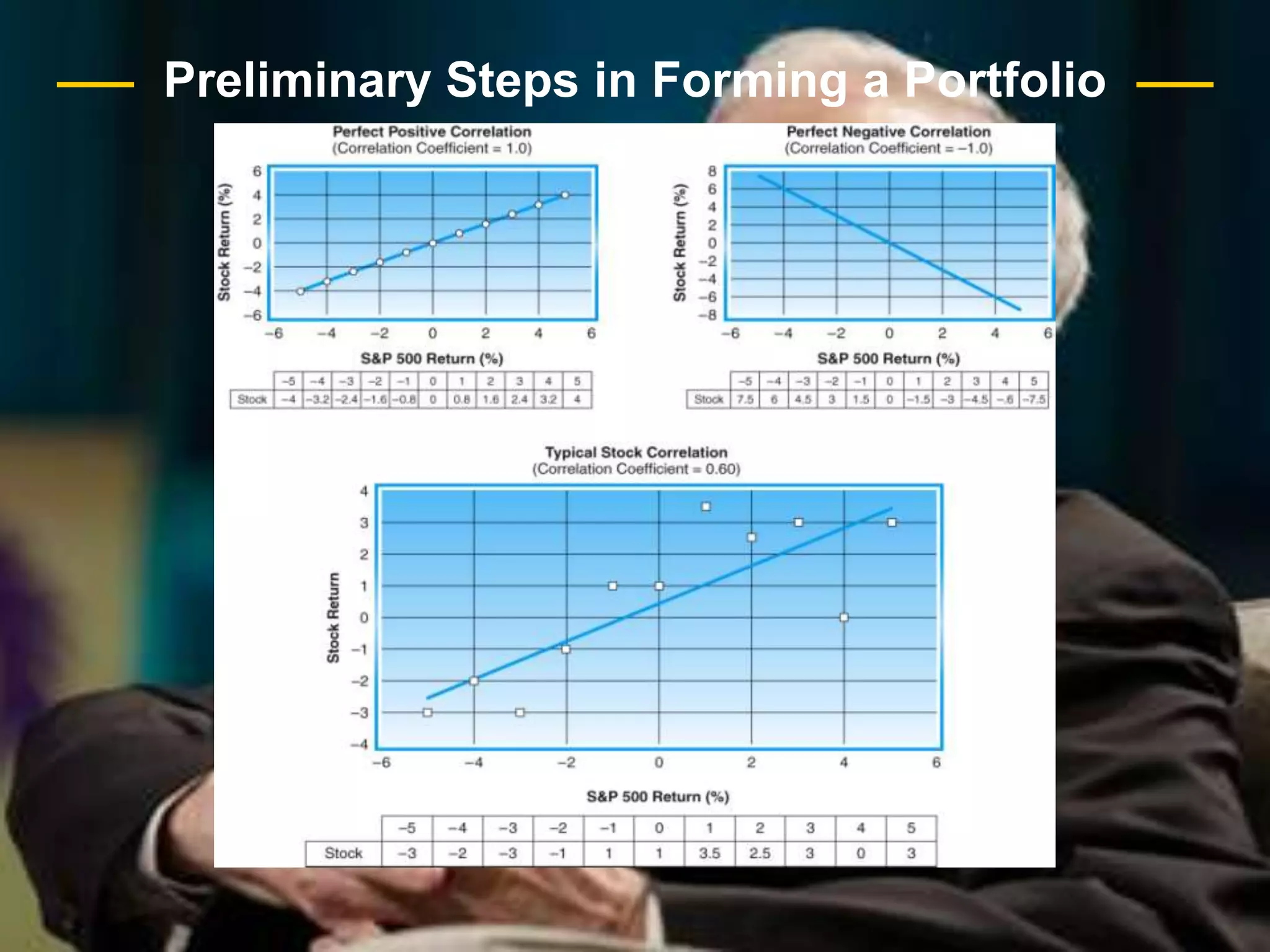
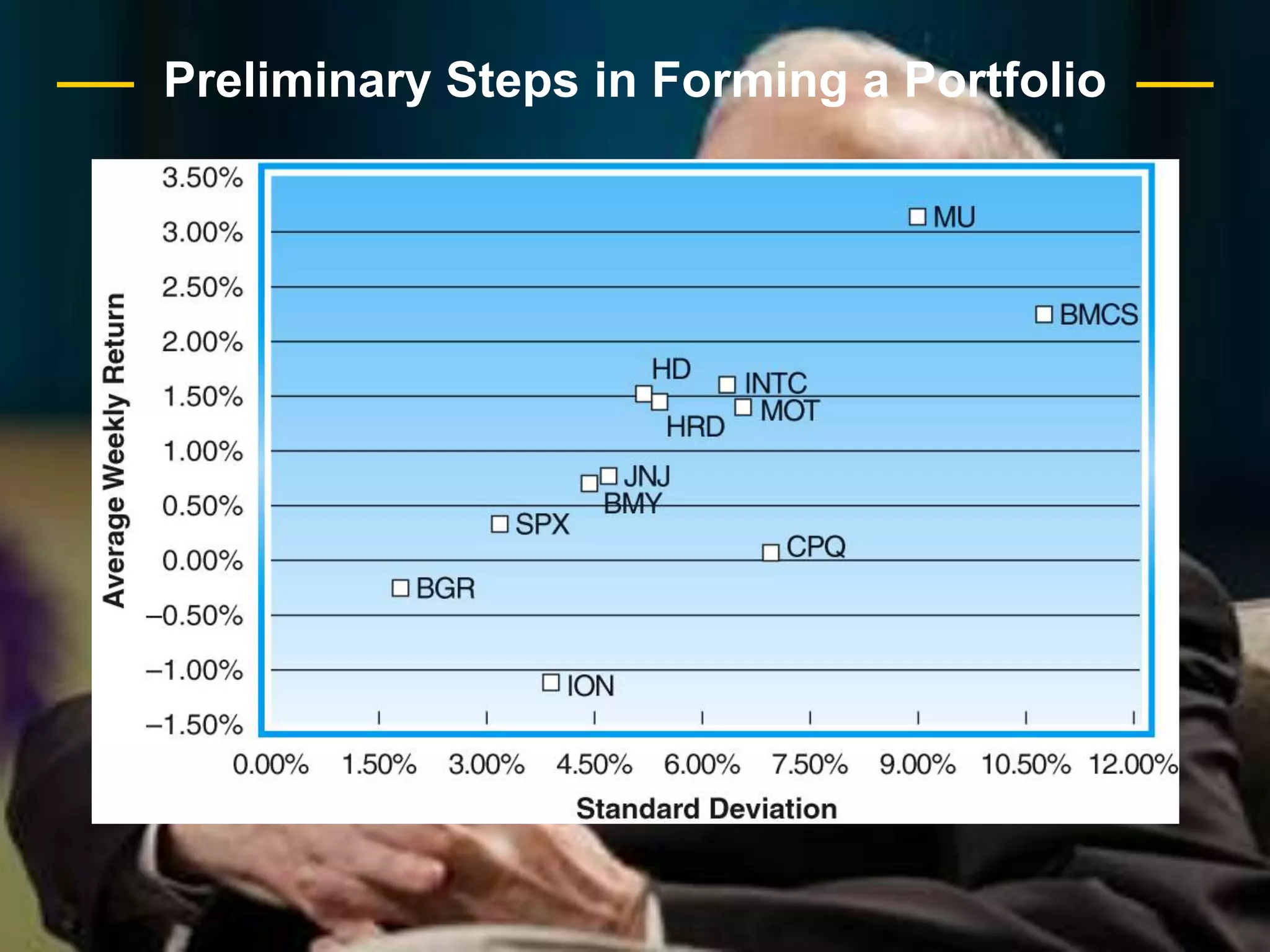
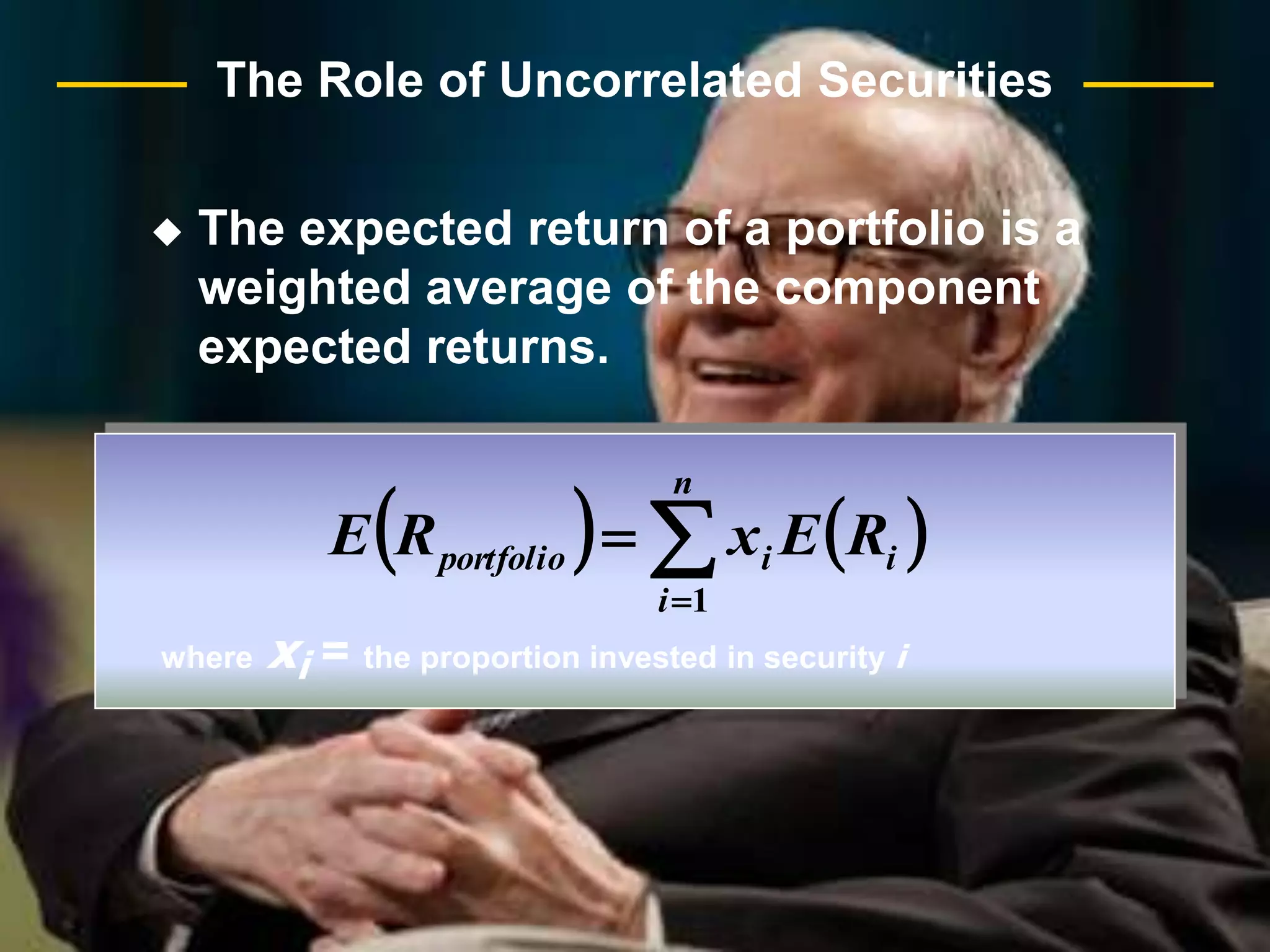
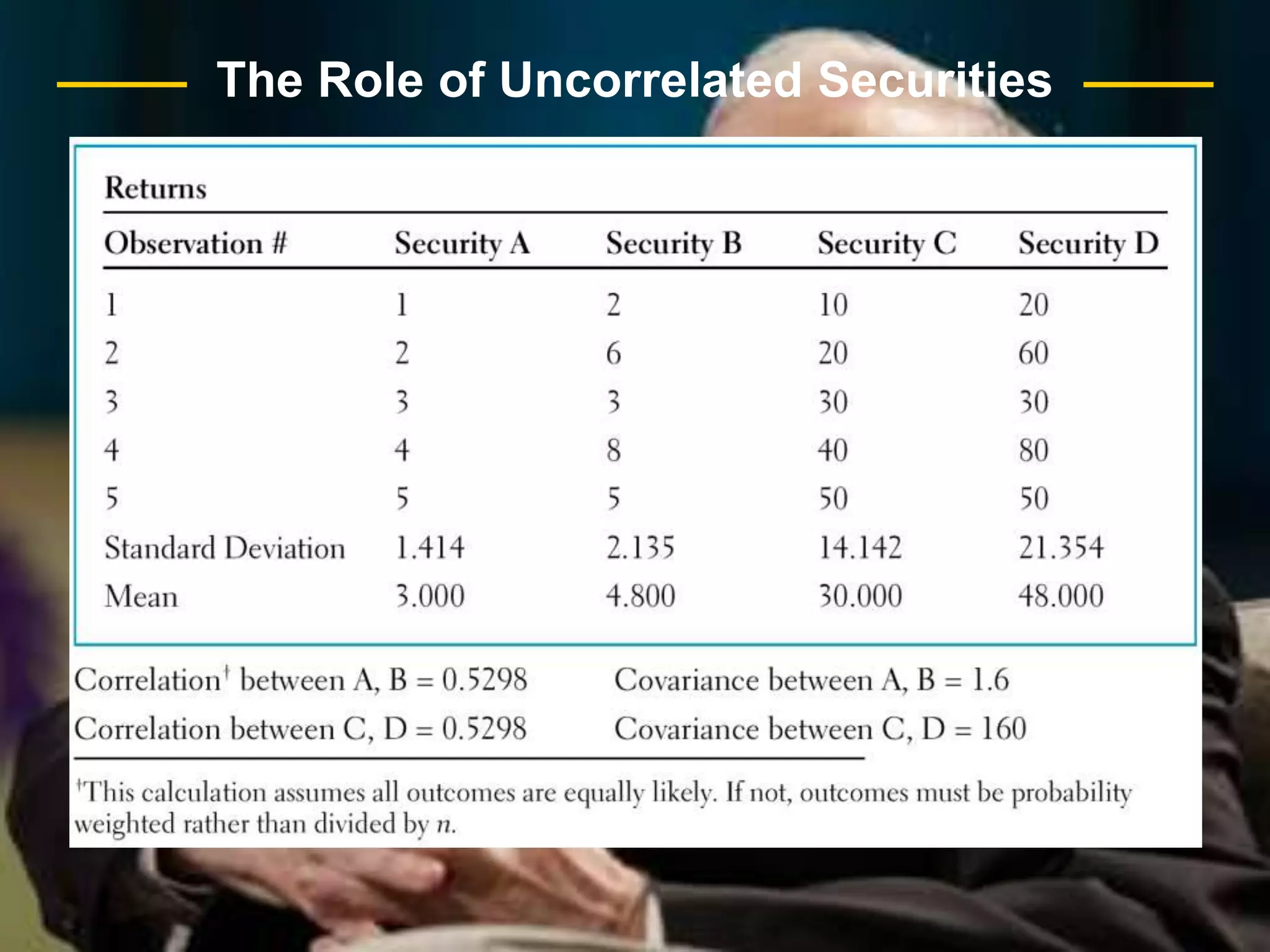
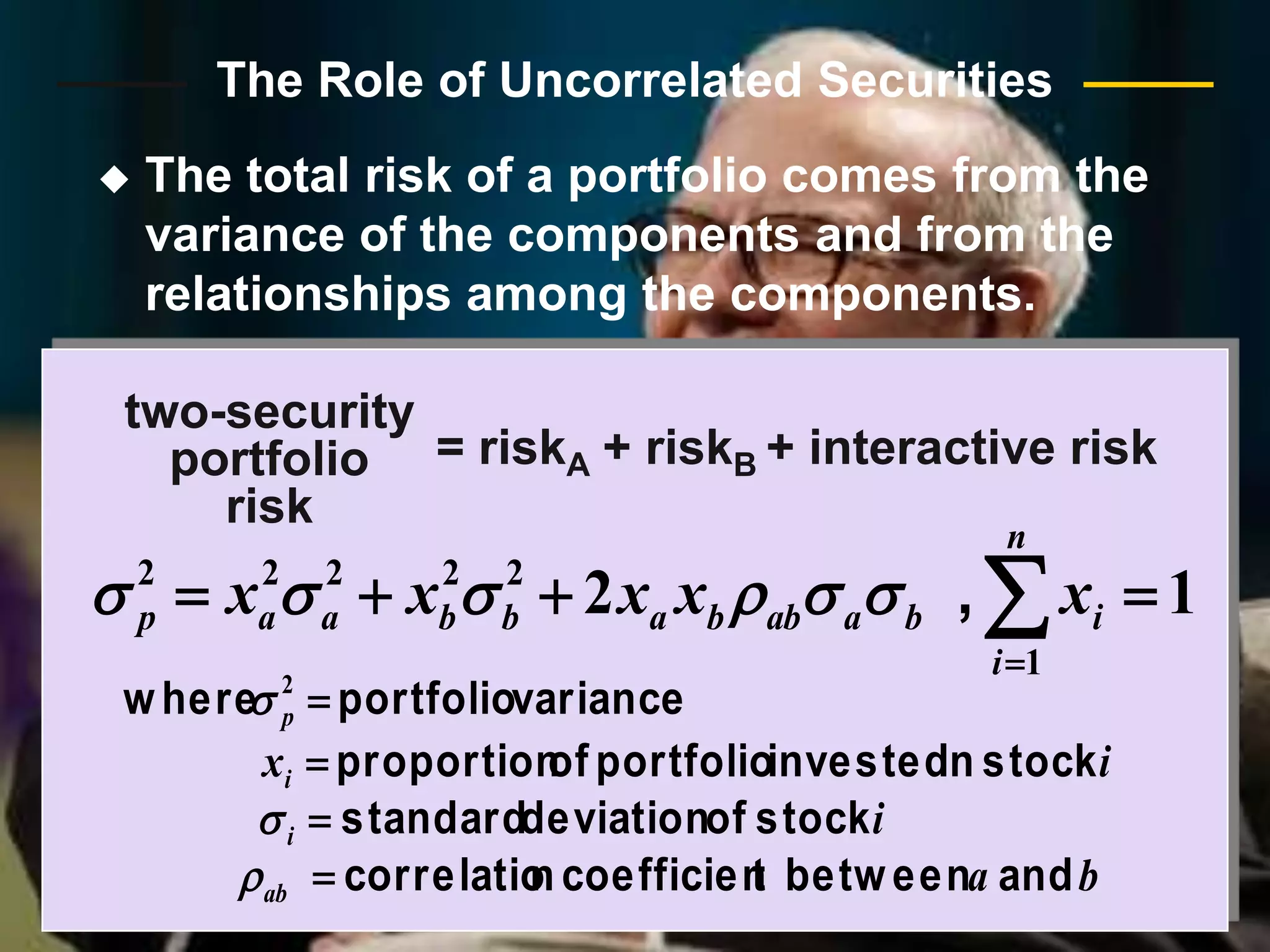
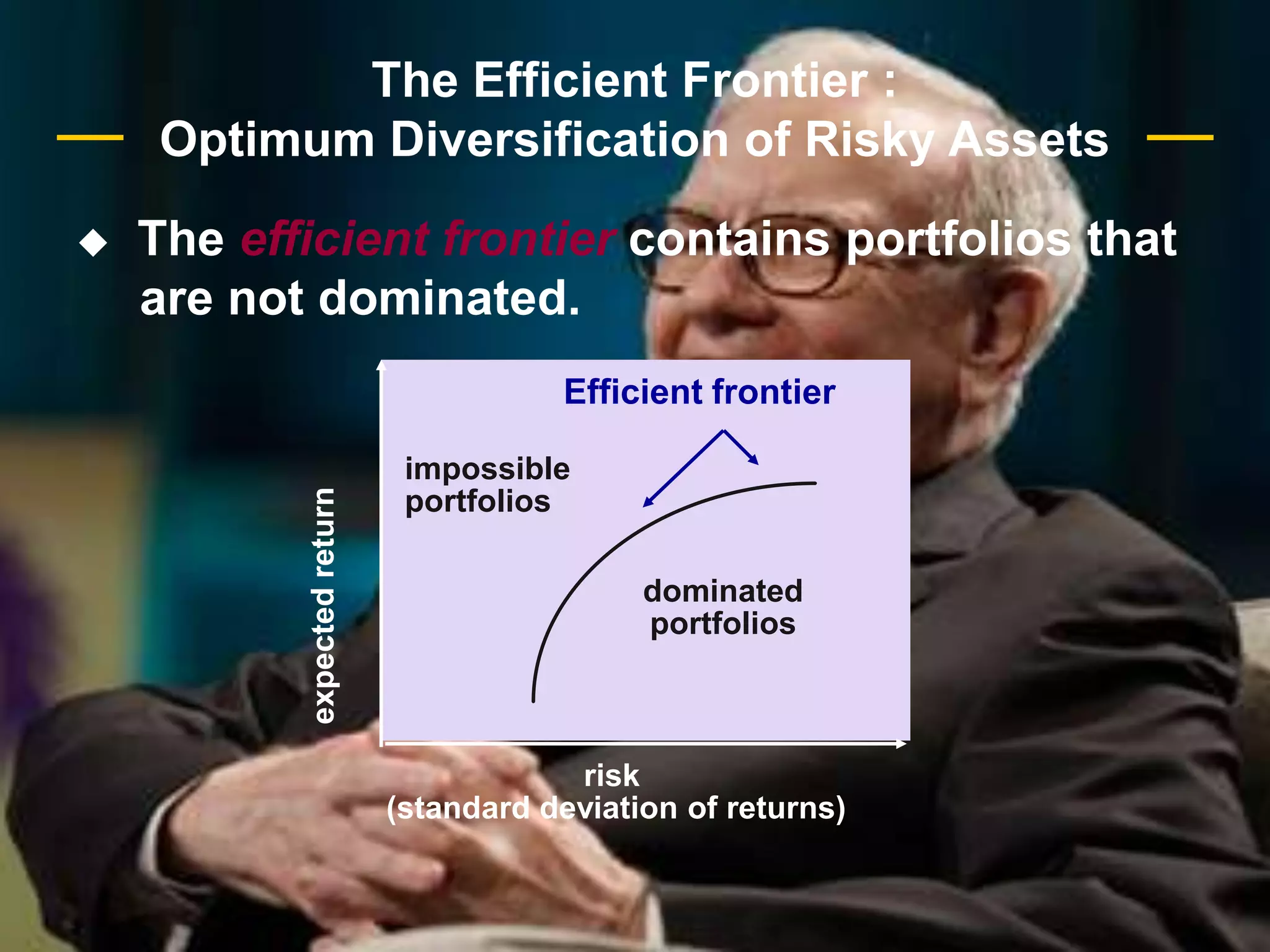
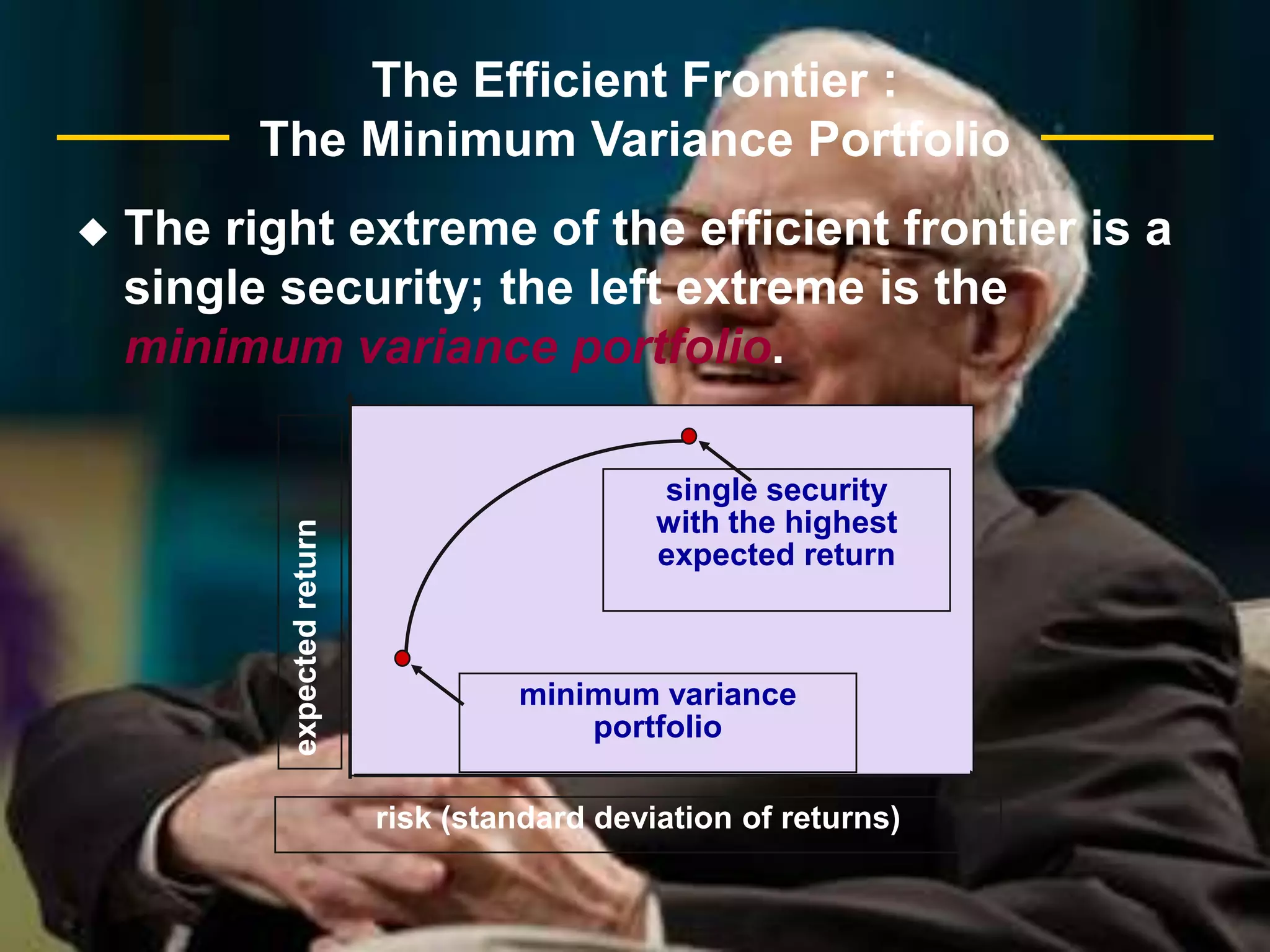
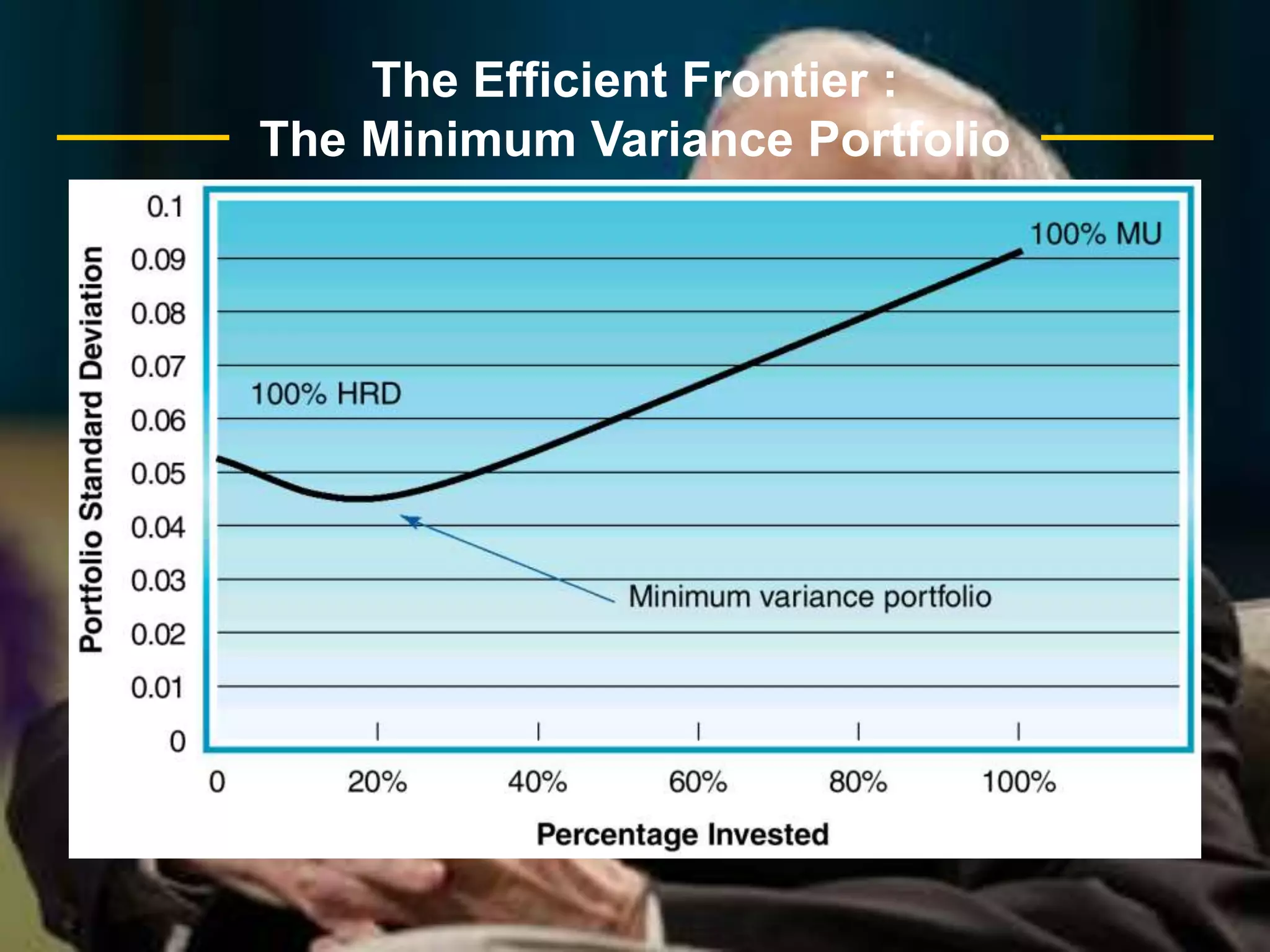
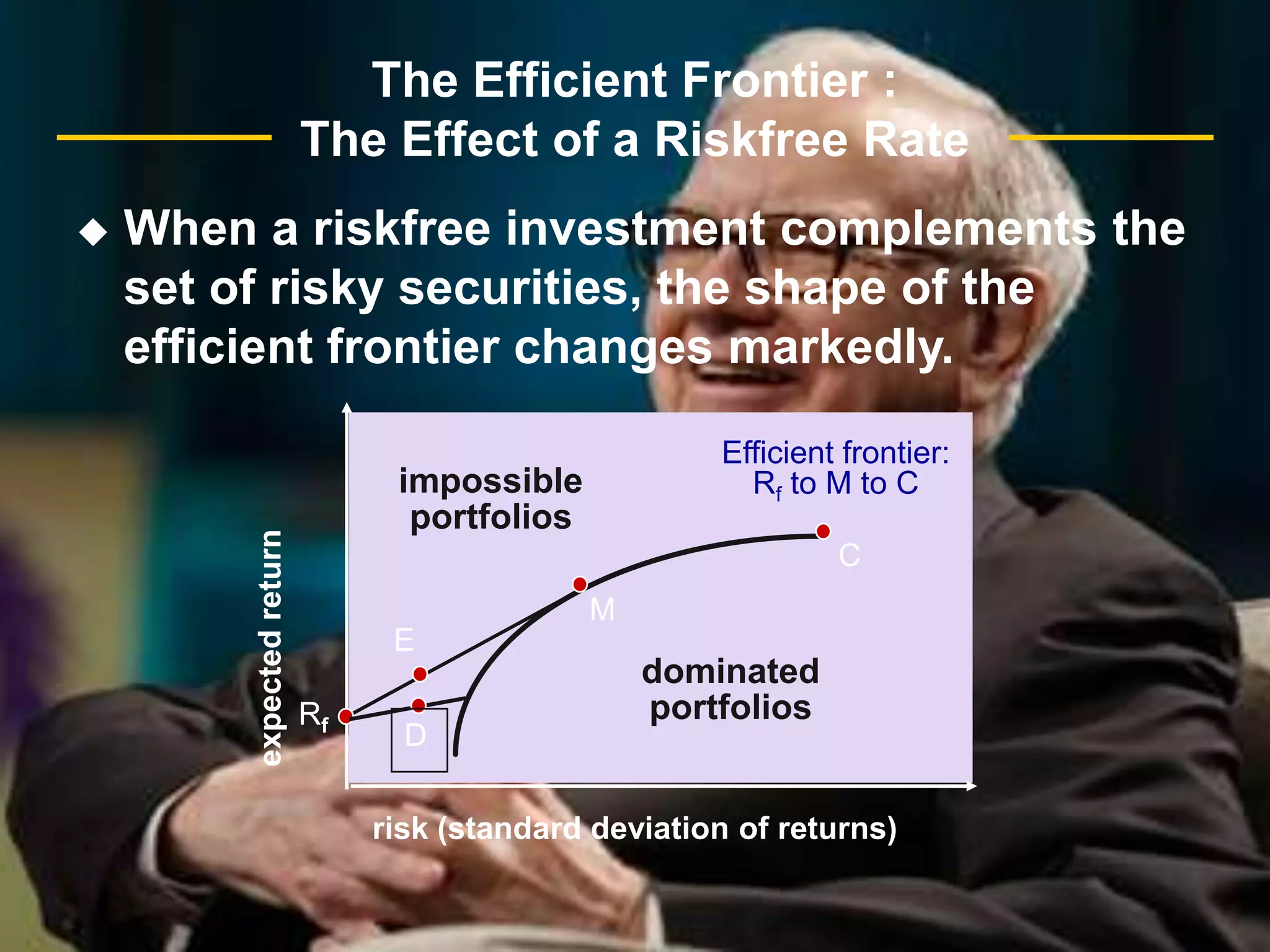
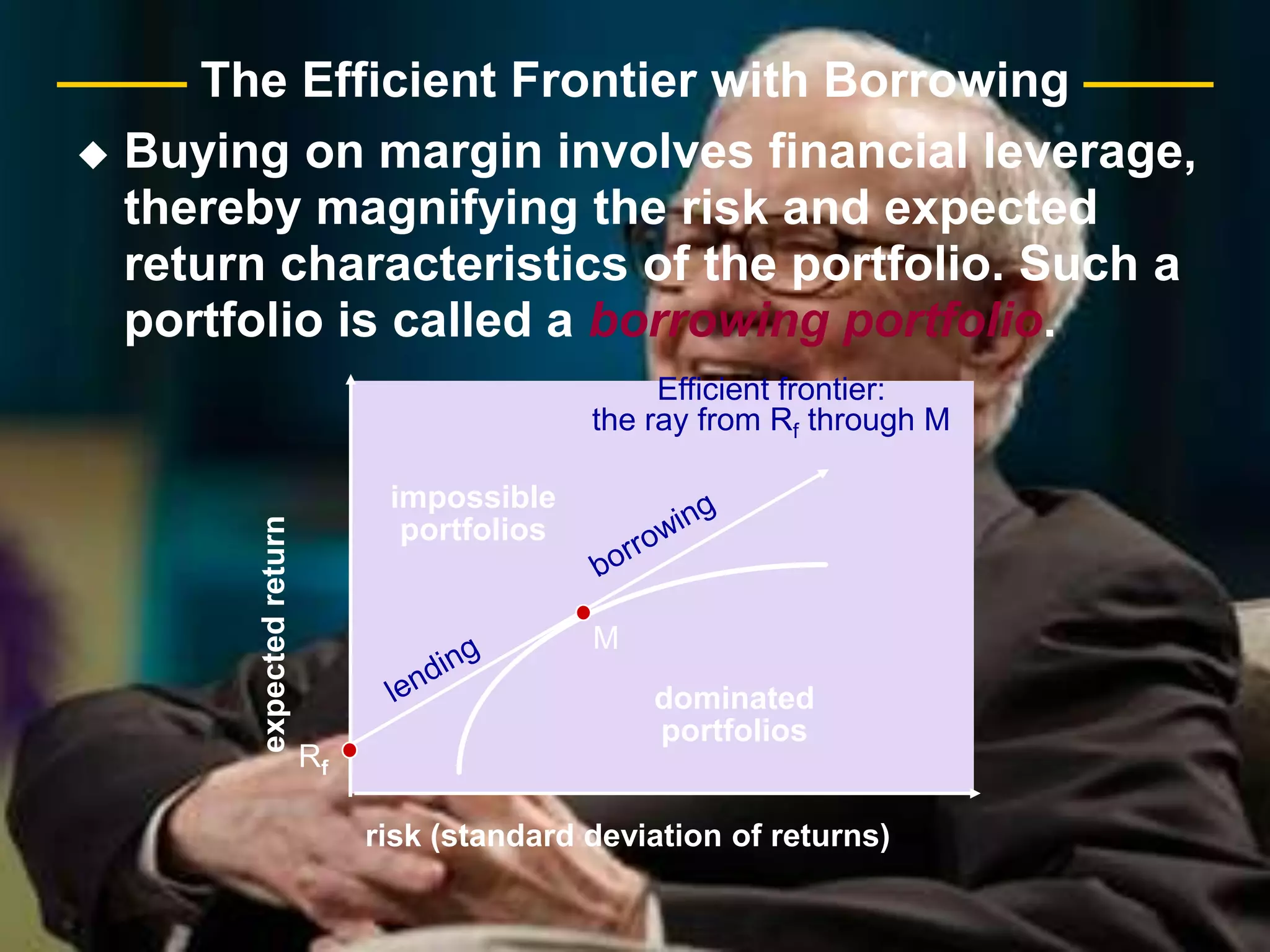
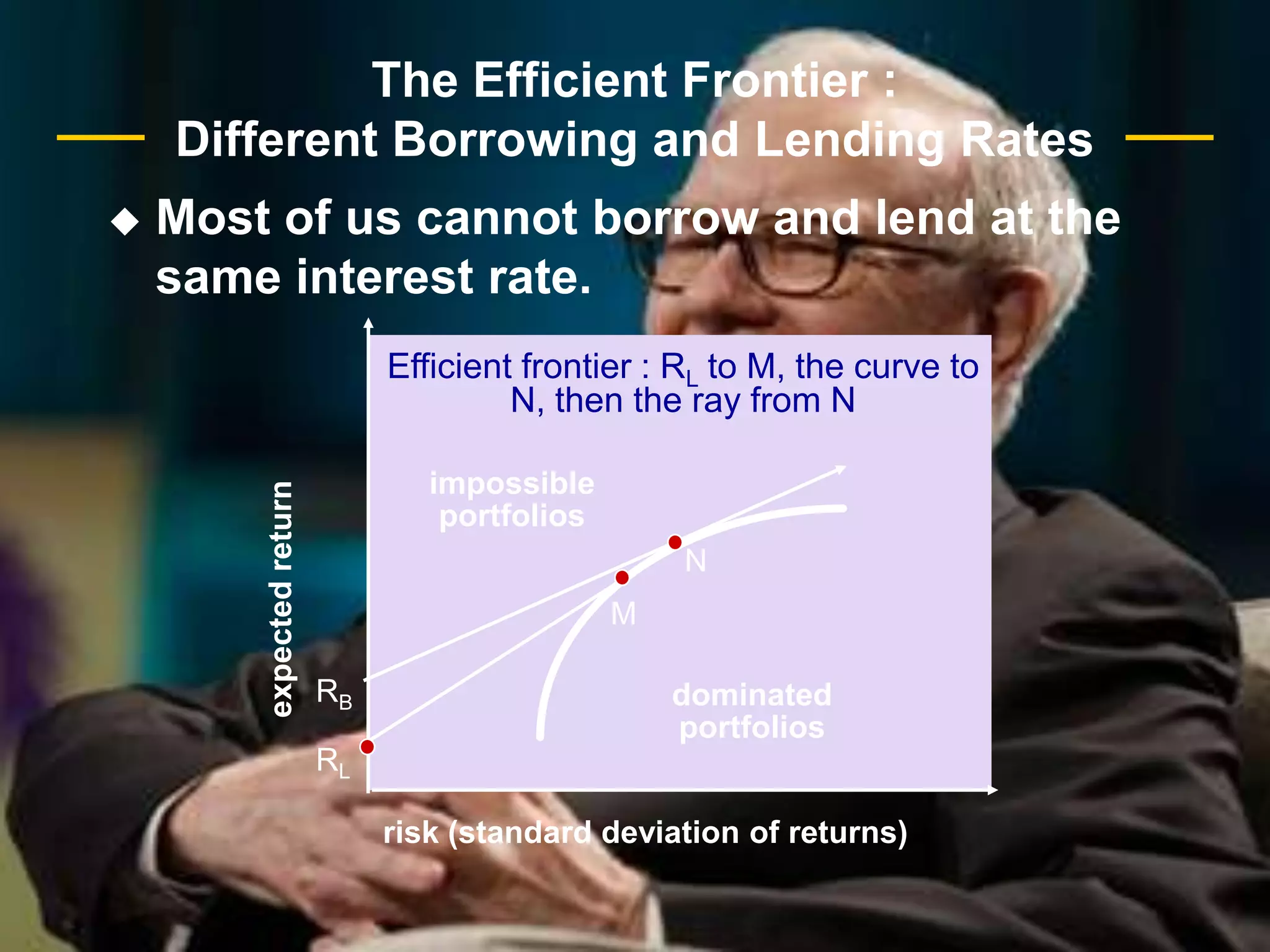
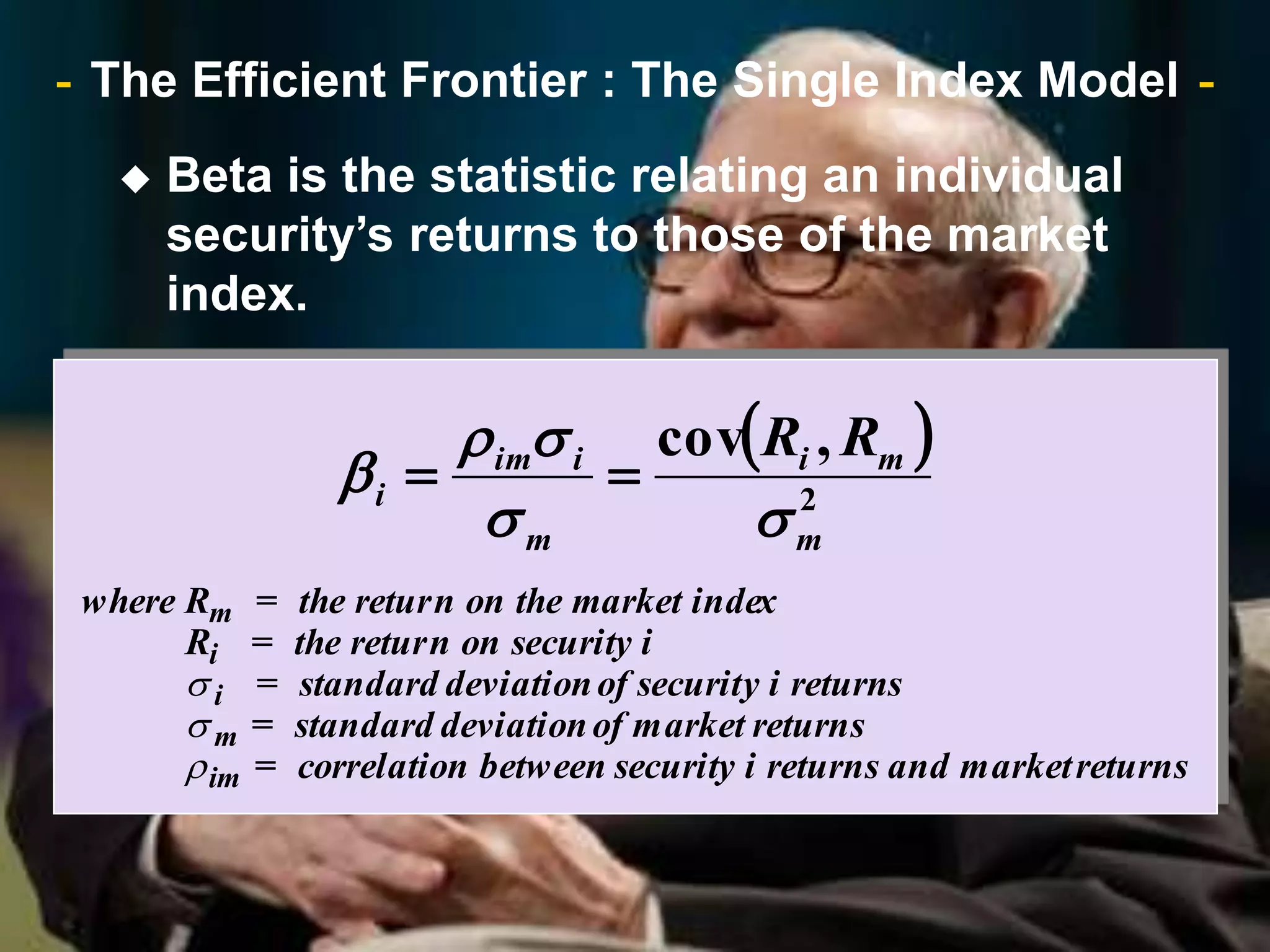
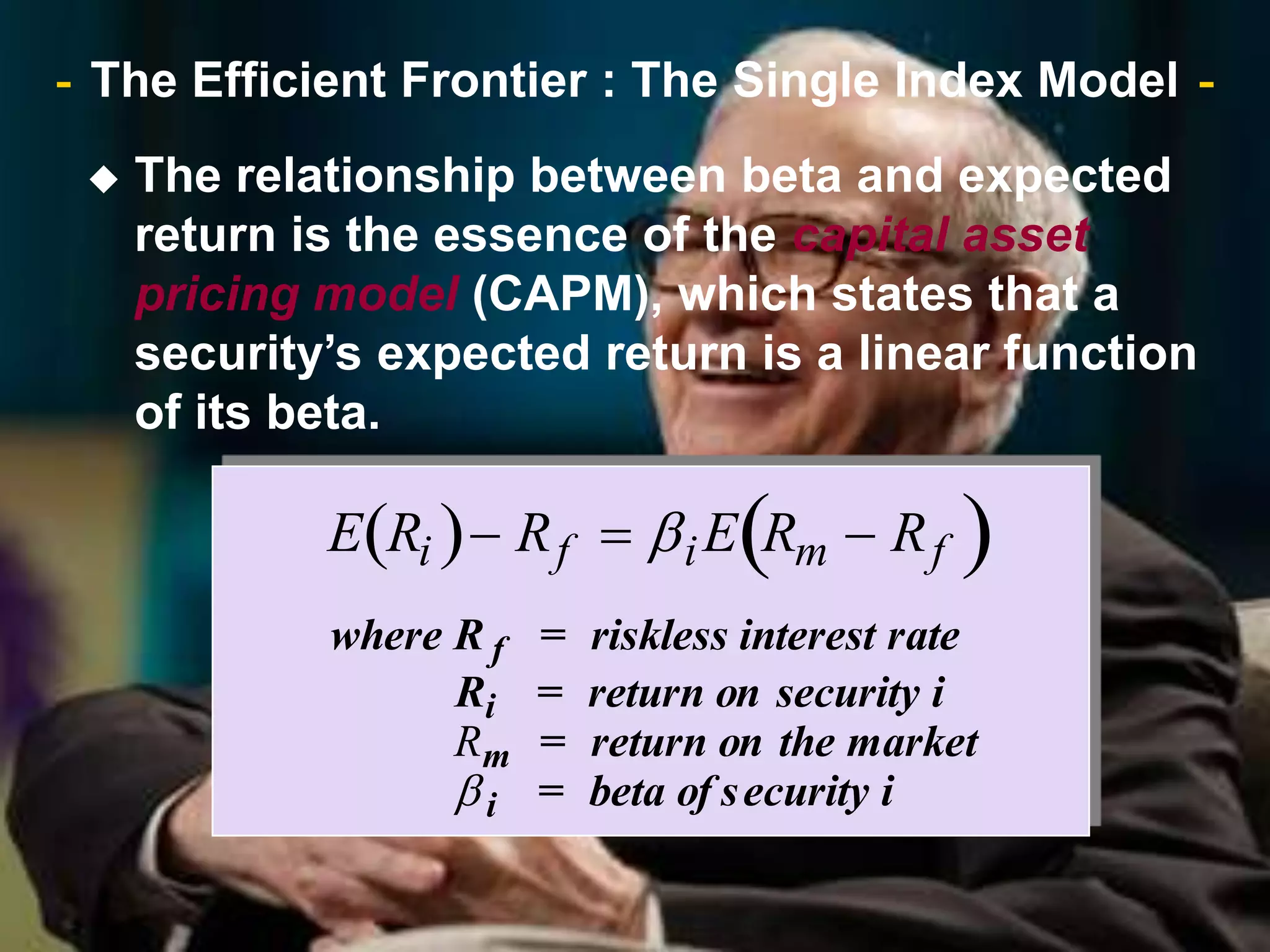
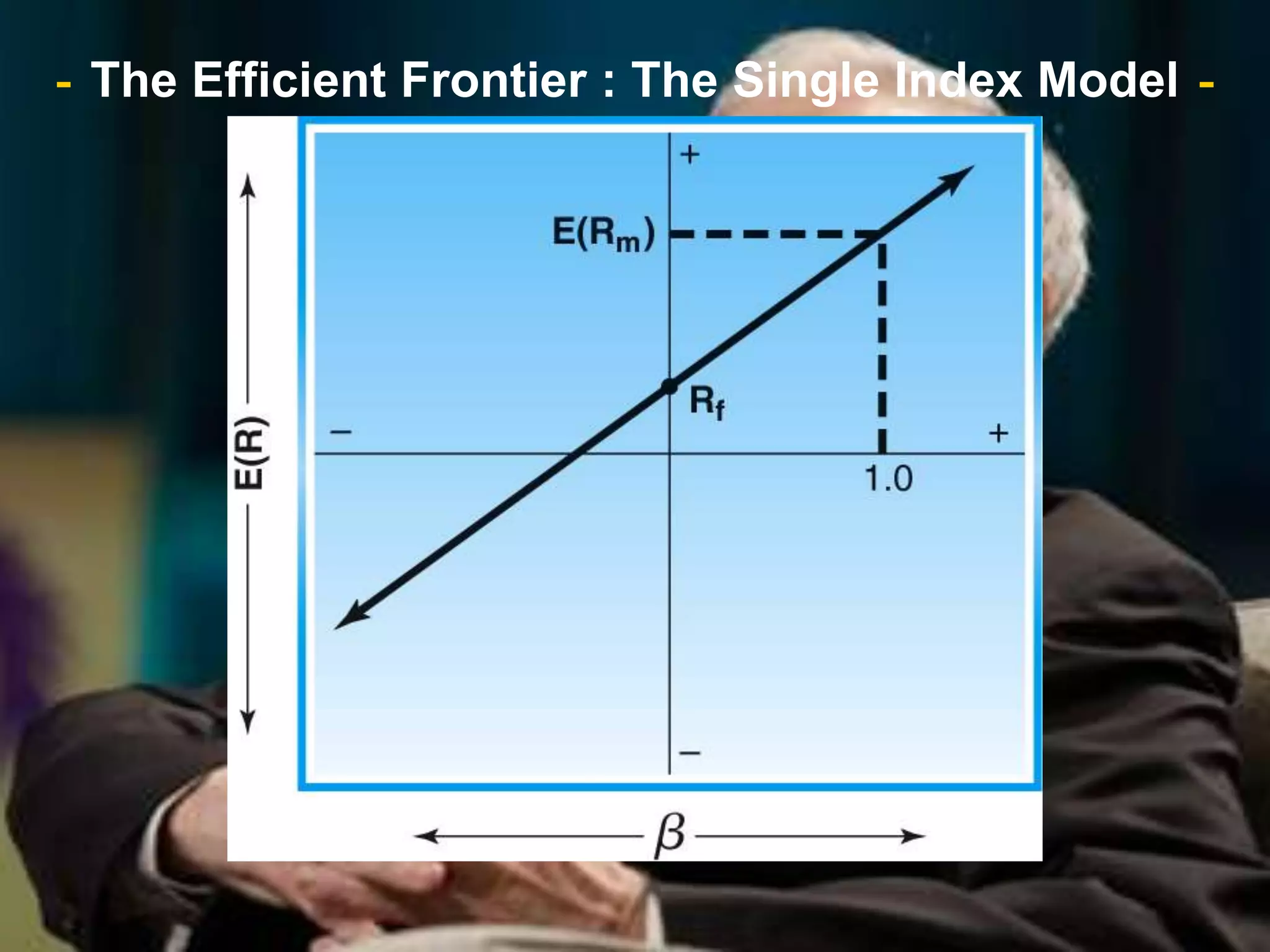
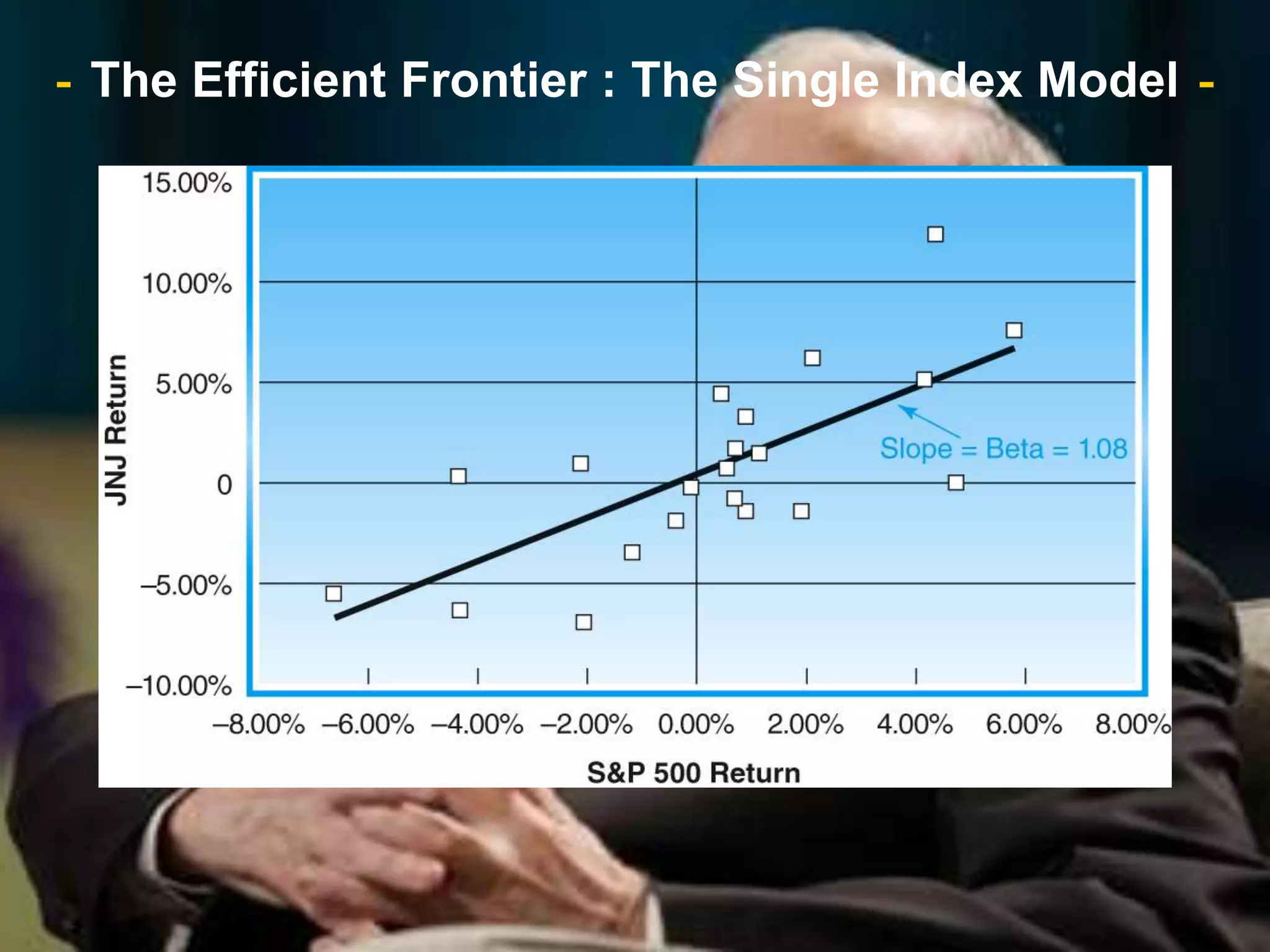
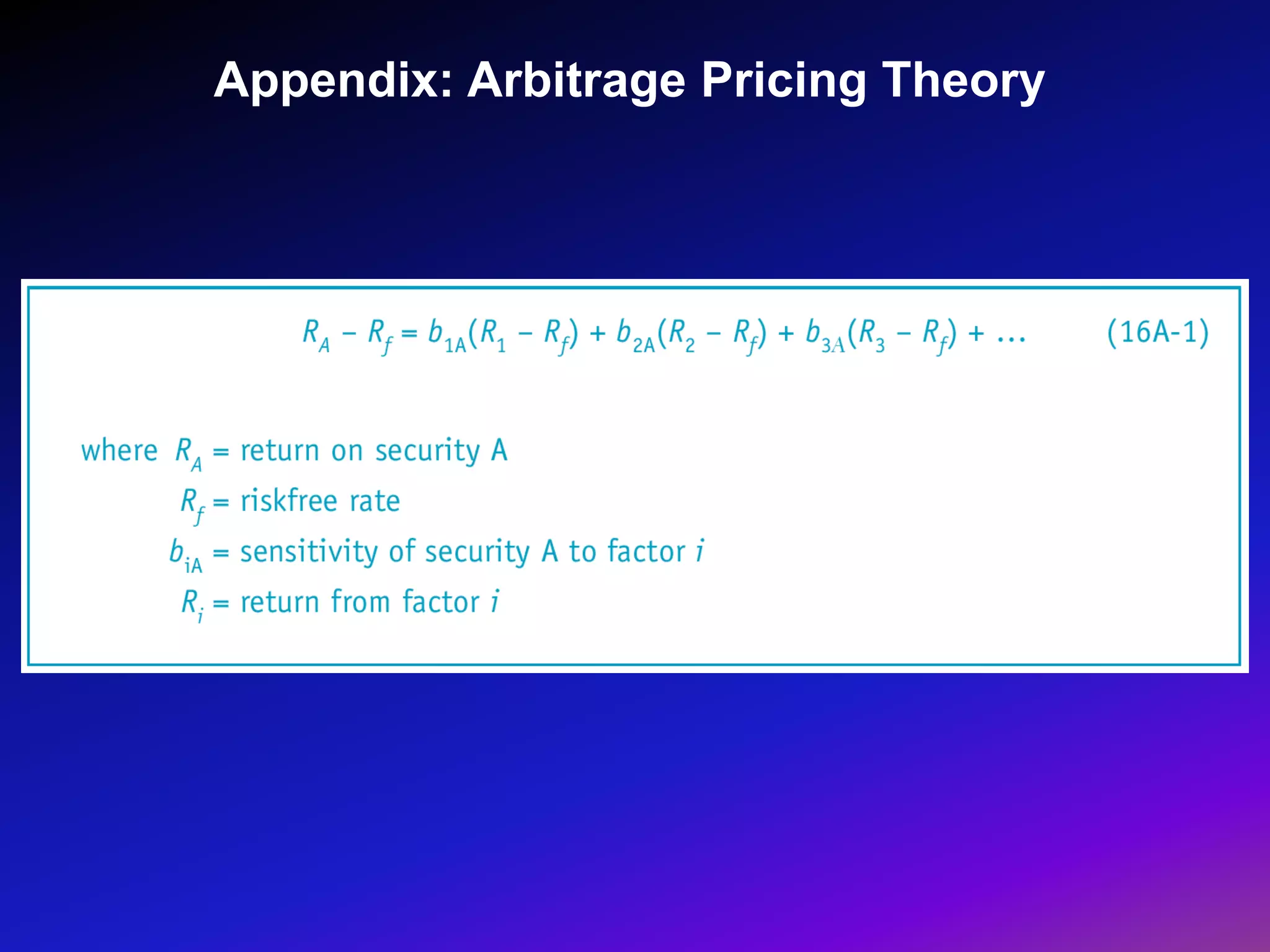
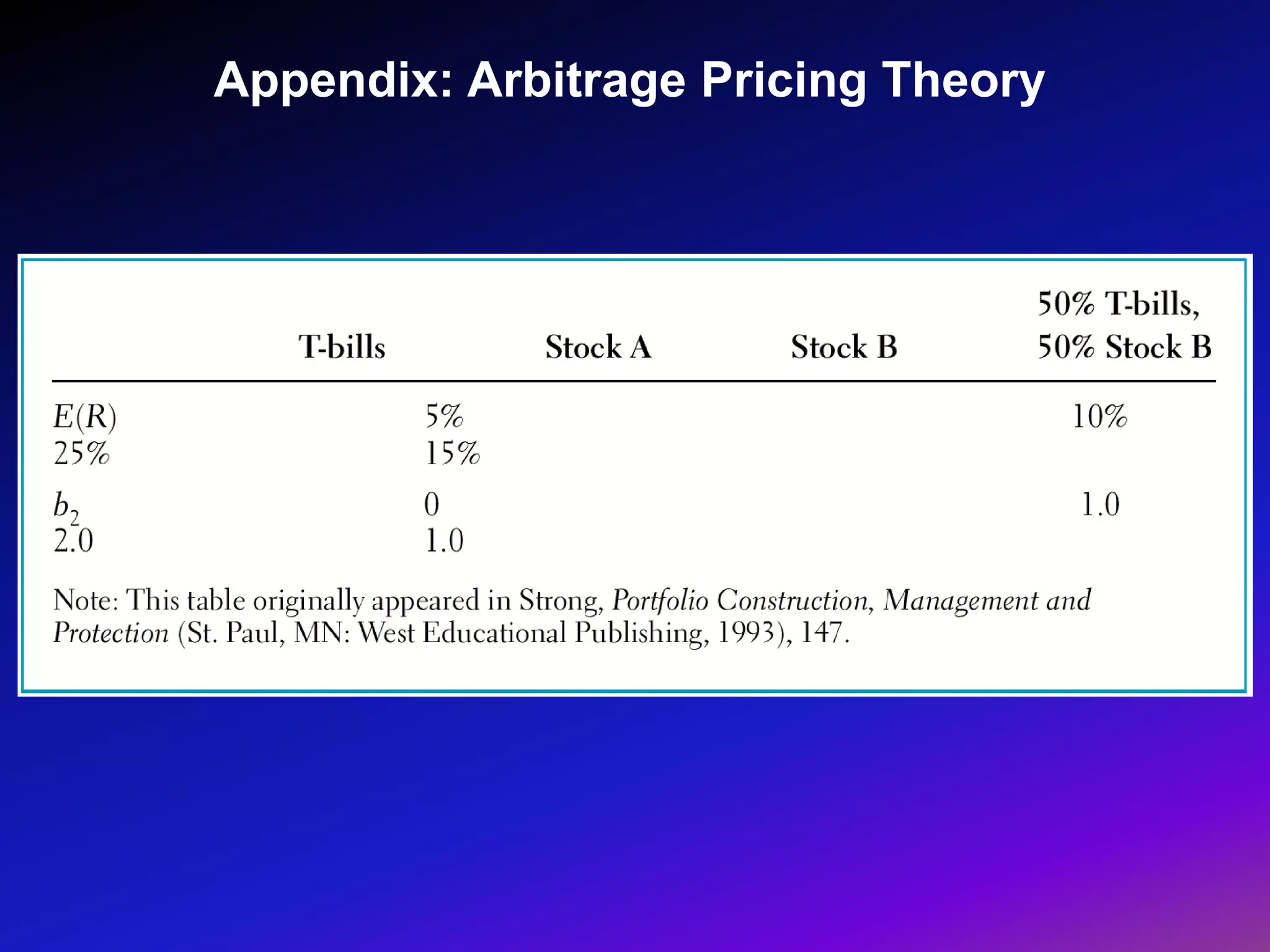
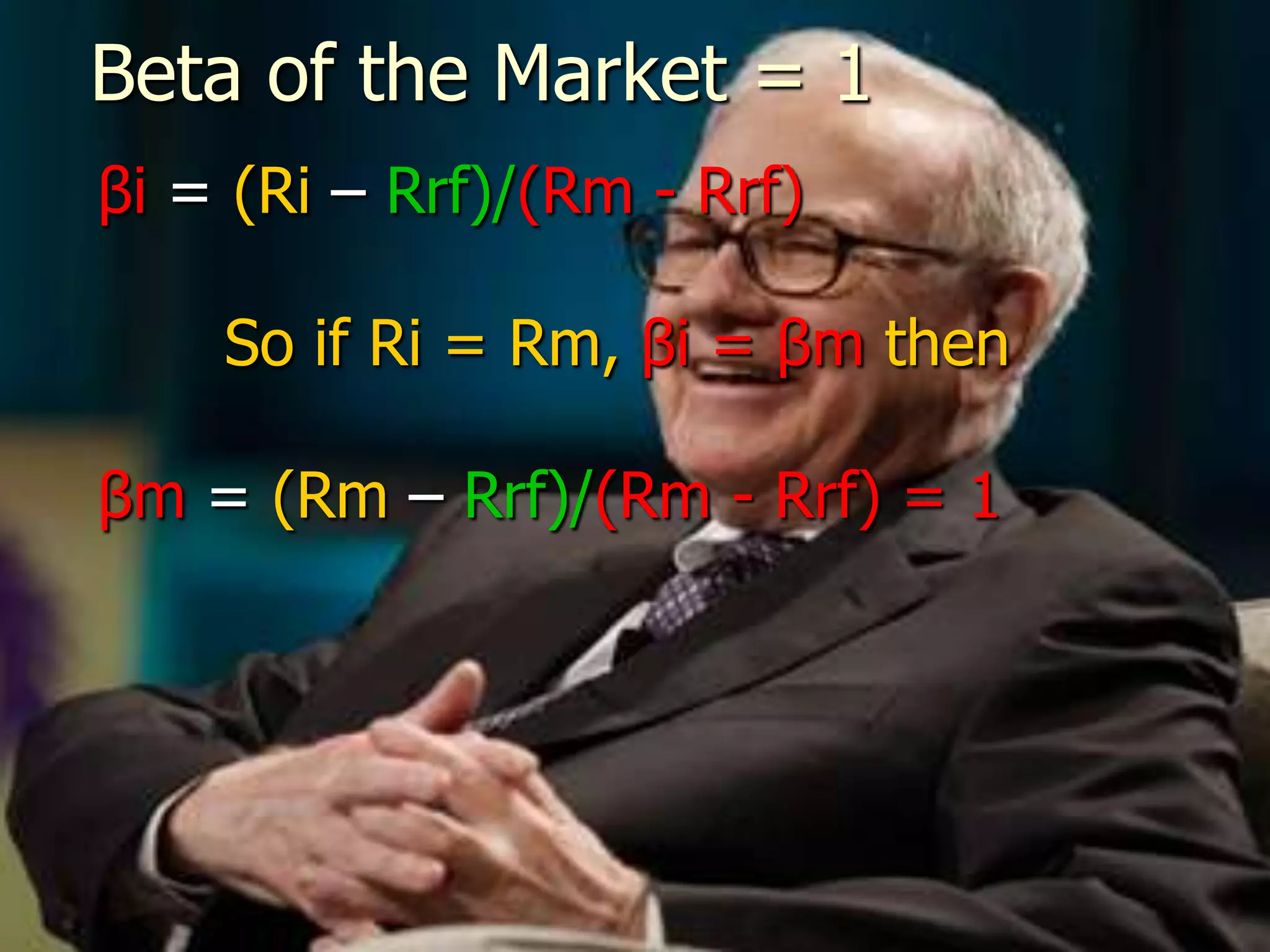The document discusses portfolio optimization and the efficient frontier. It explains that the efficient frontier shows the set of optimal portfolios that maximize return for a given level of risk. To find the efficient frontier, the risk and return of all potential investments must be analyzed to select a portfolio with minimum risk for its expected return level. Proper diversification across low-correlated assets is important to reduce non-systematic risk and move a portfolio toward the efficient frontier.