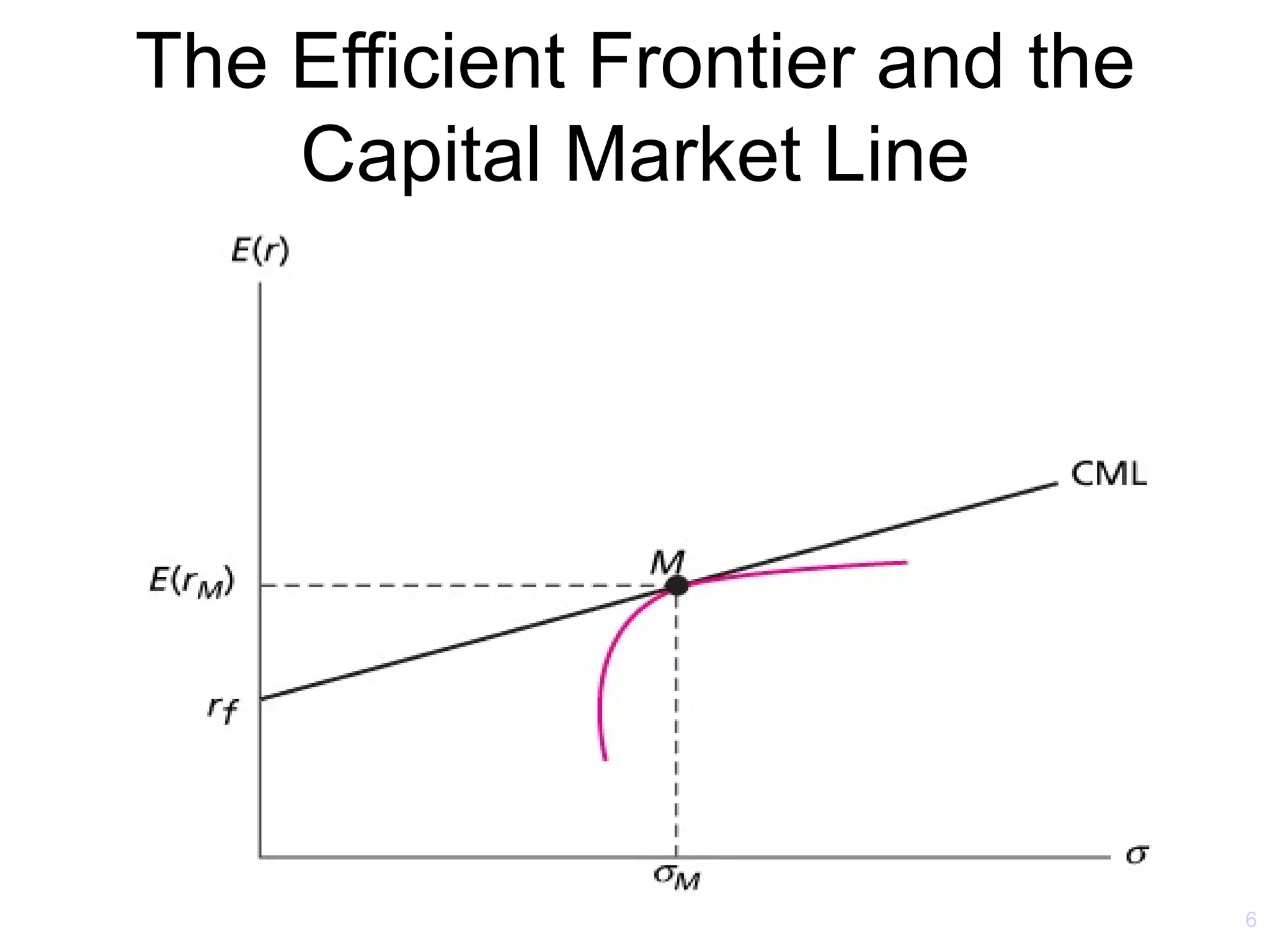
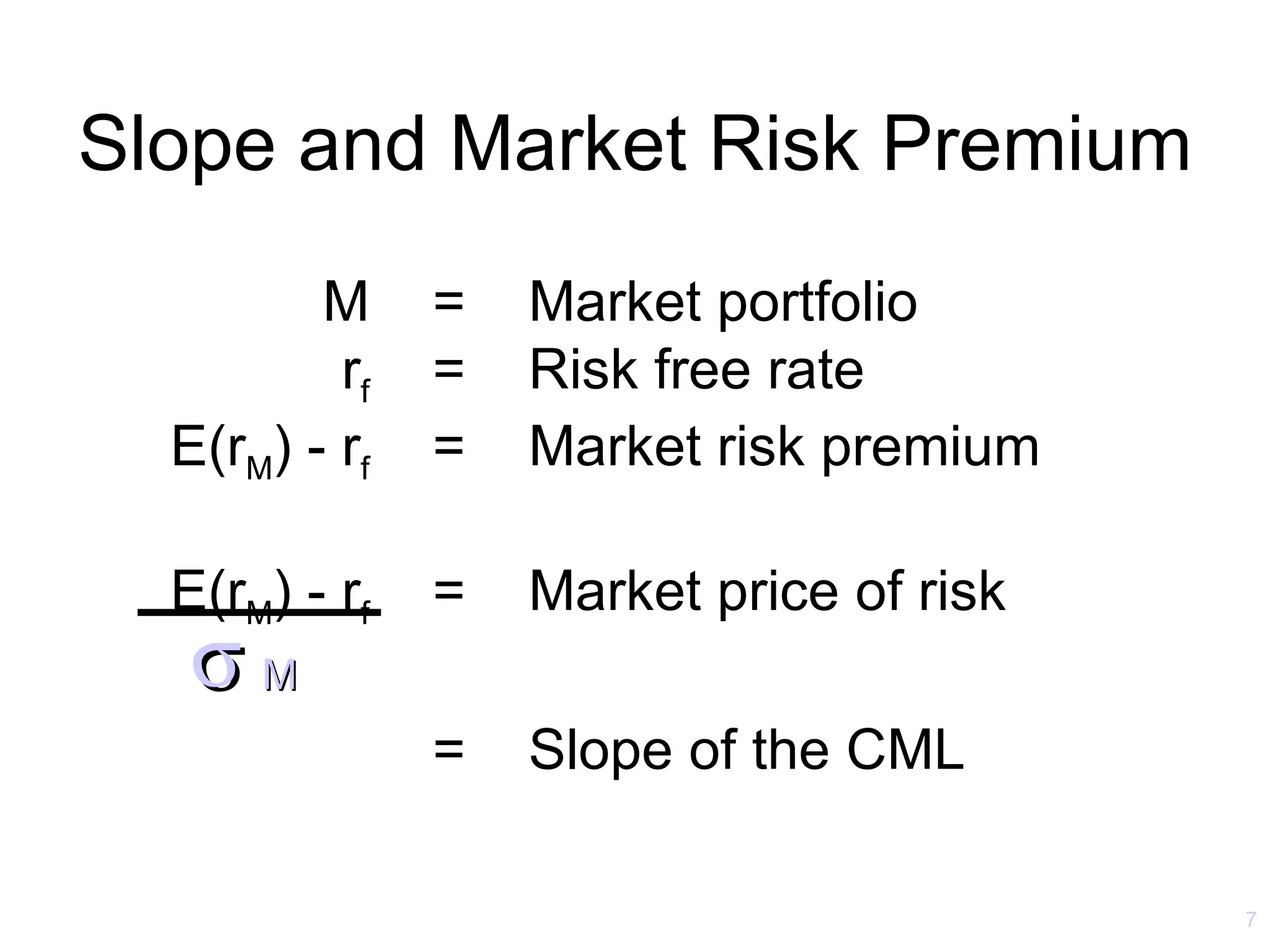
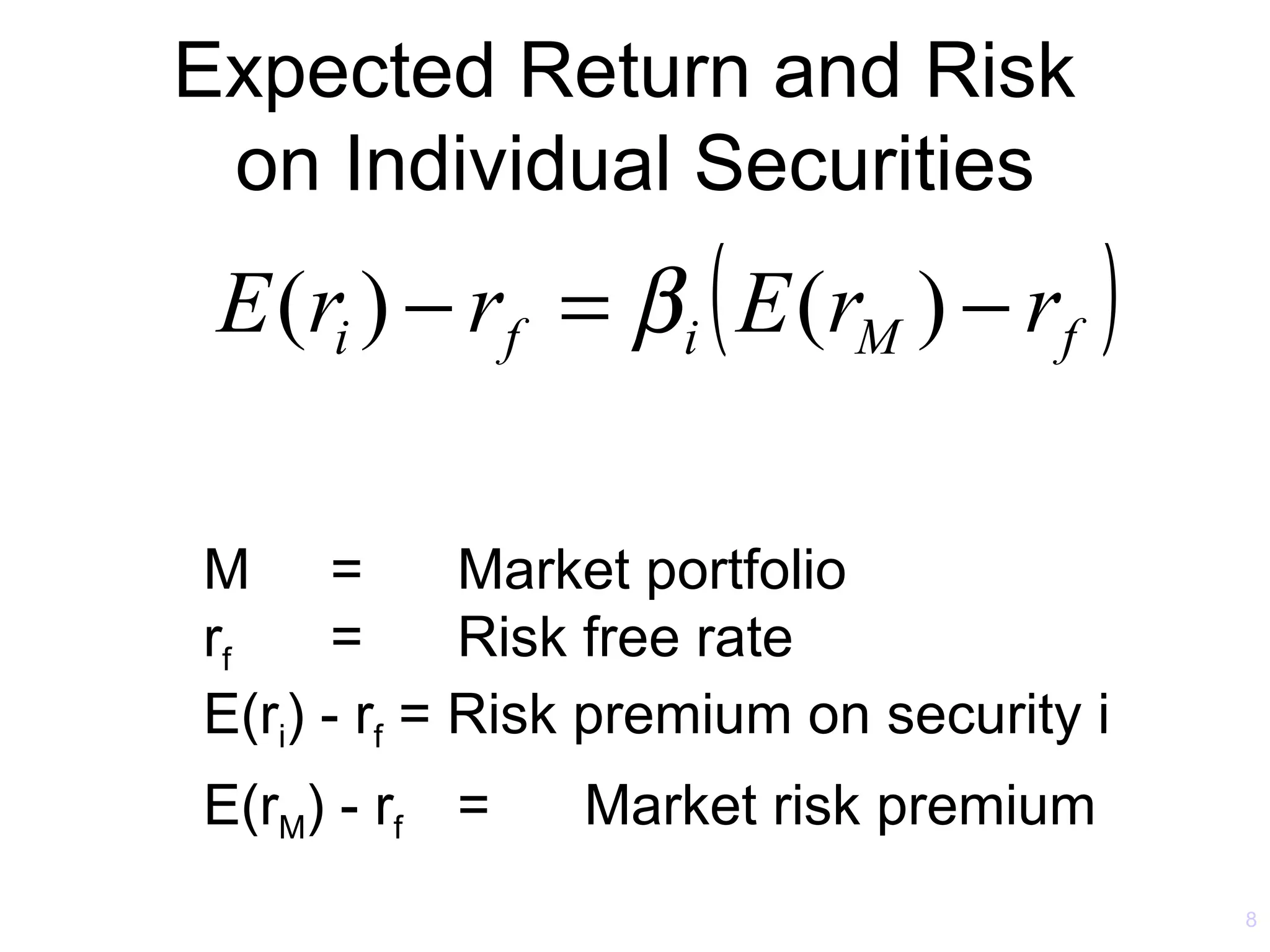
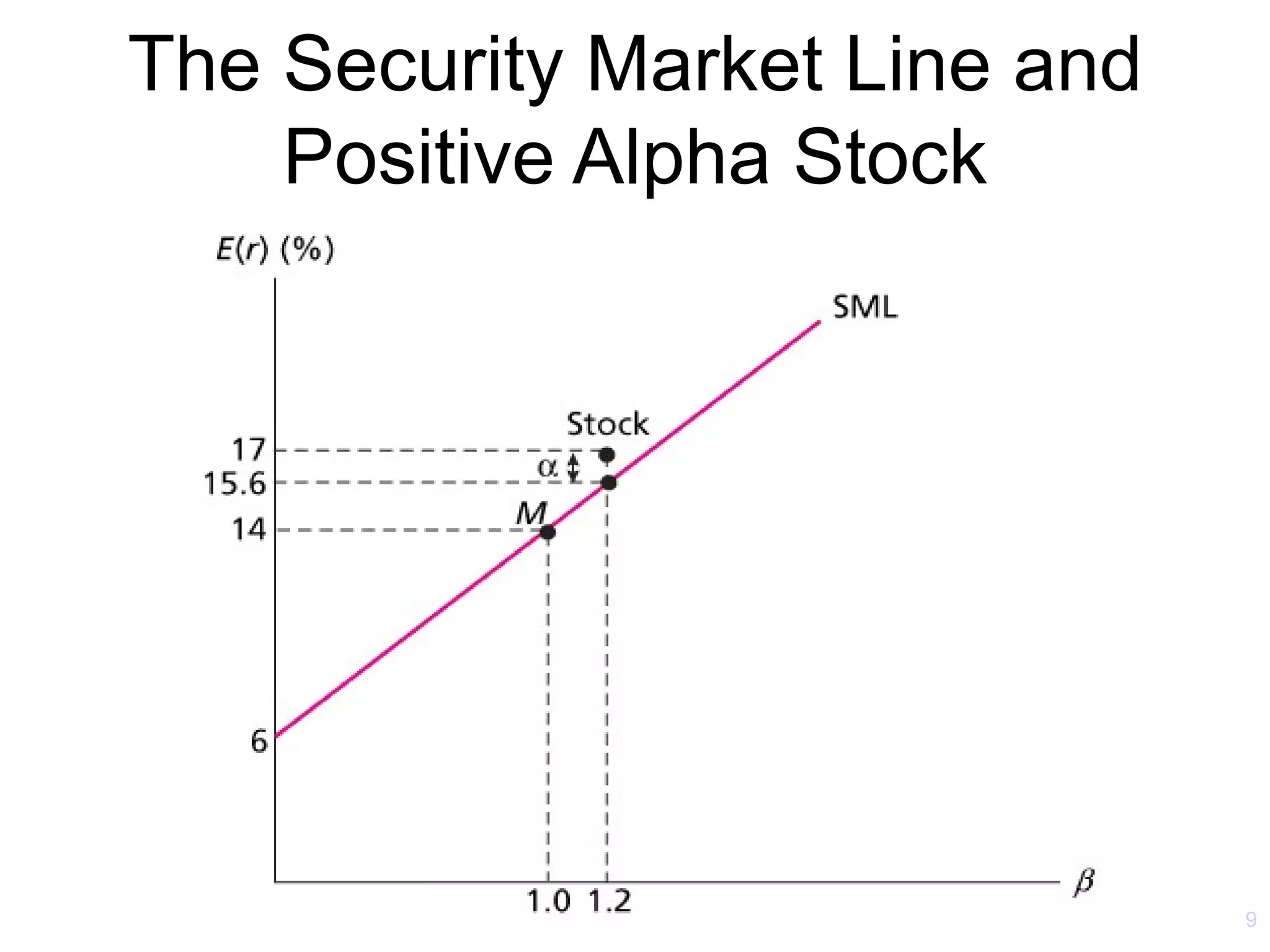
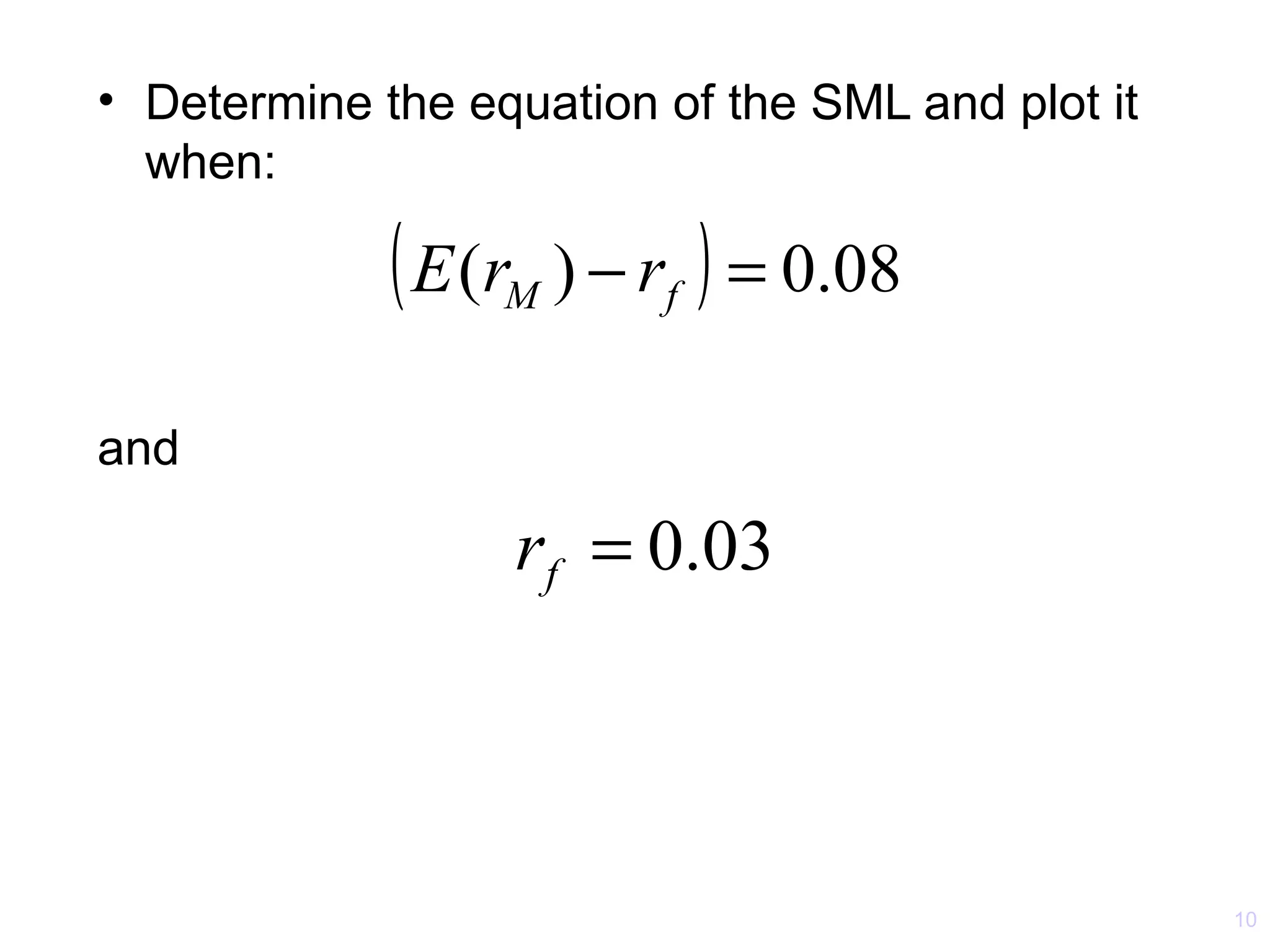
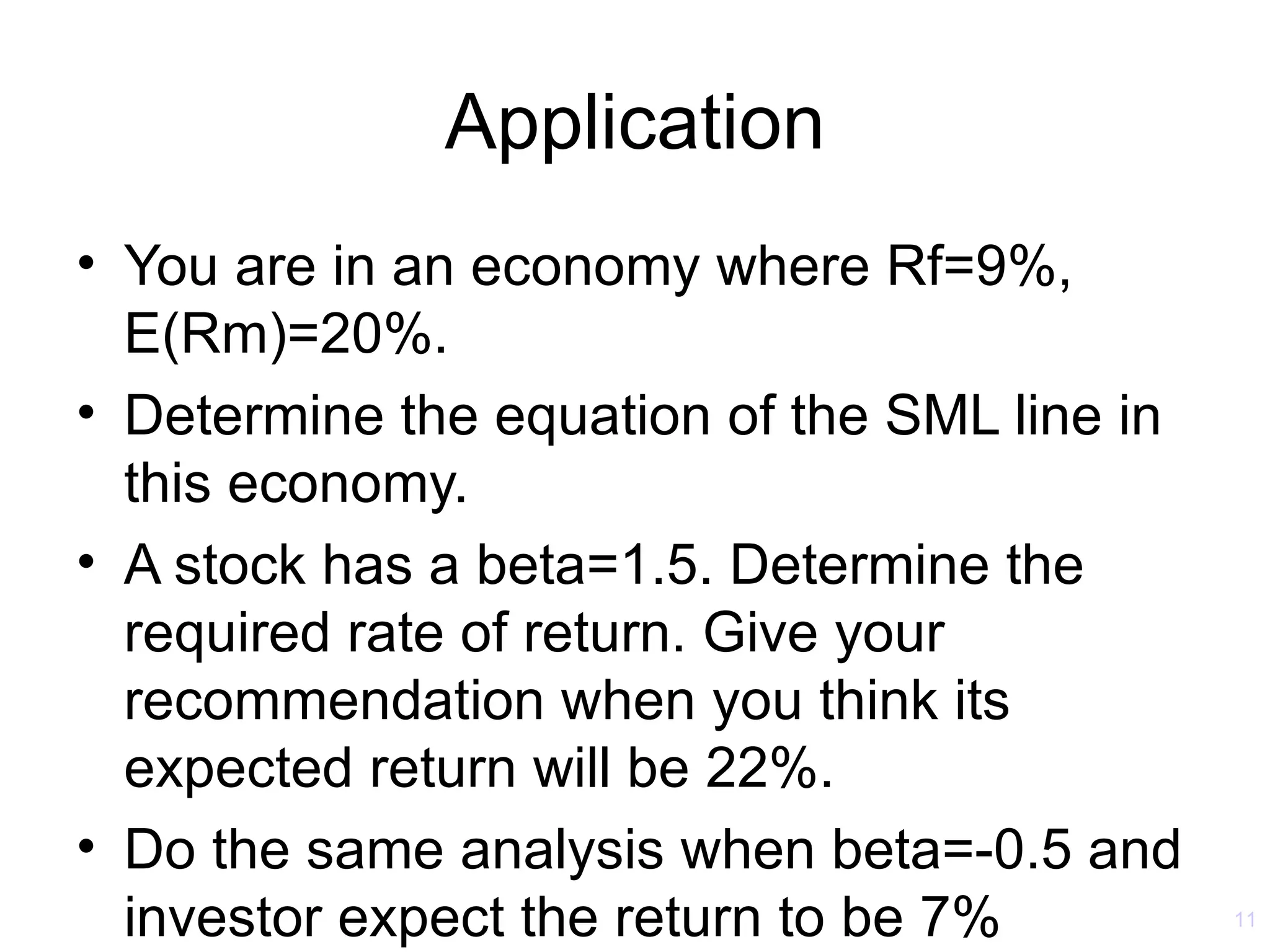
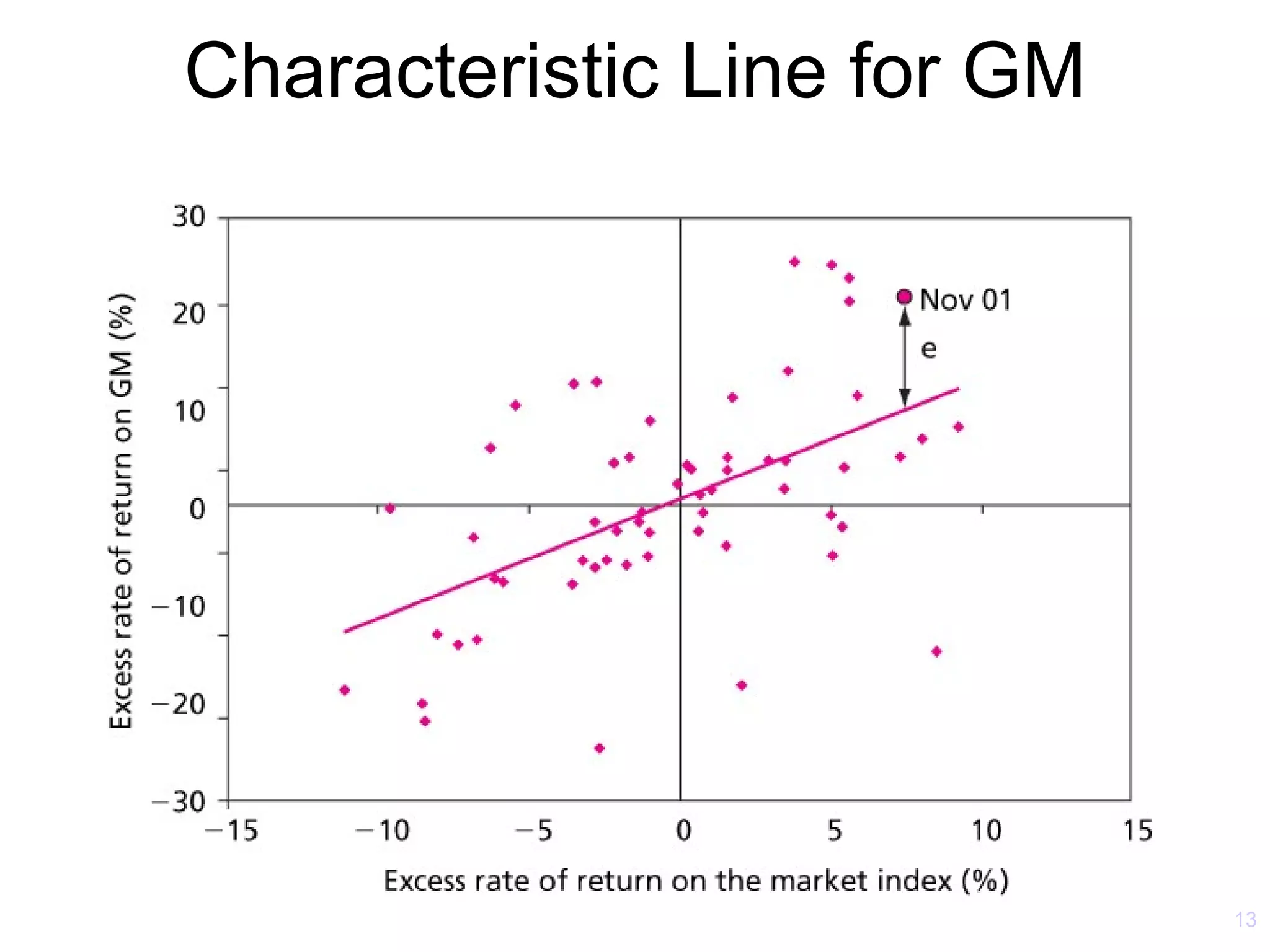
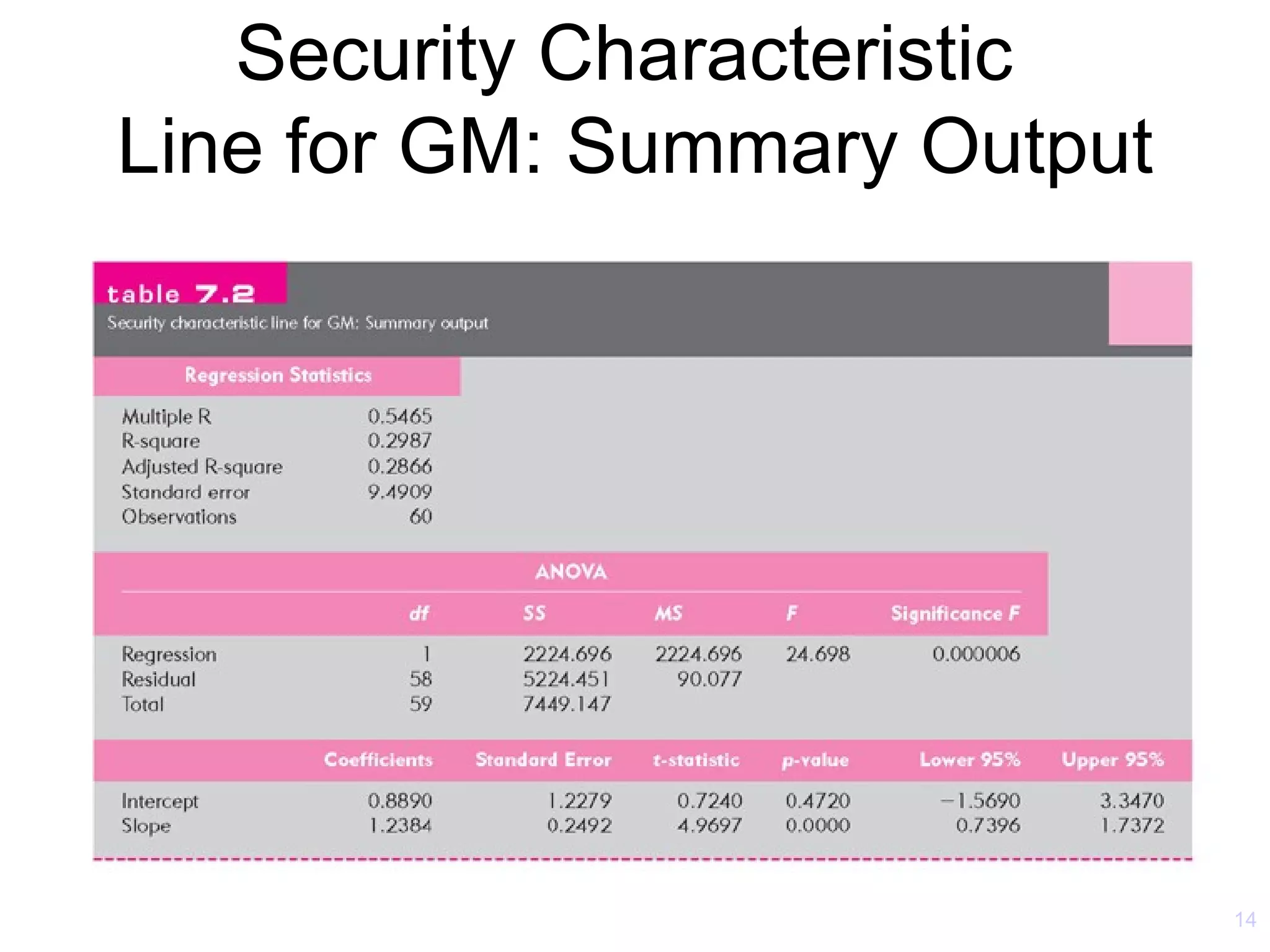
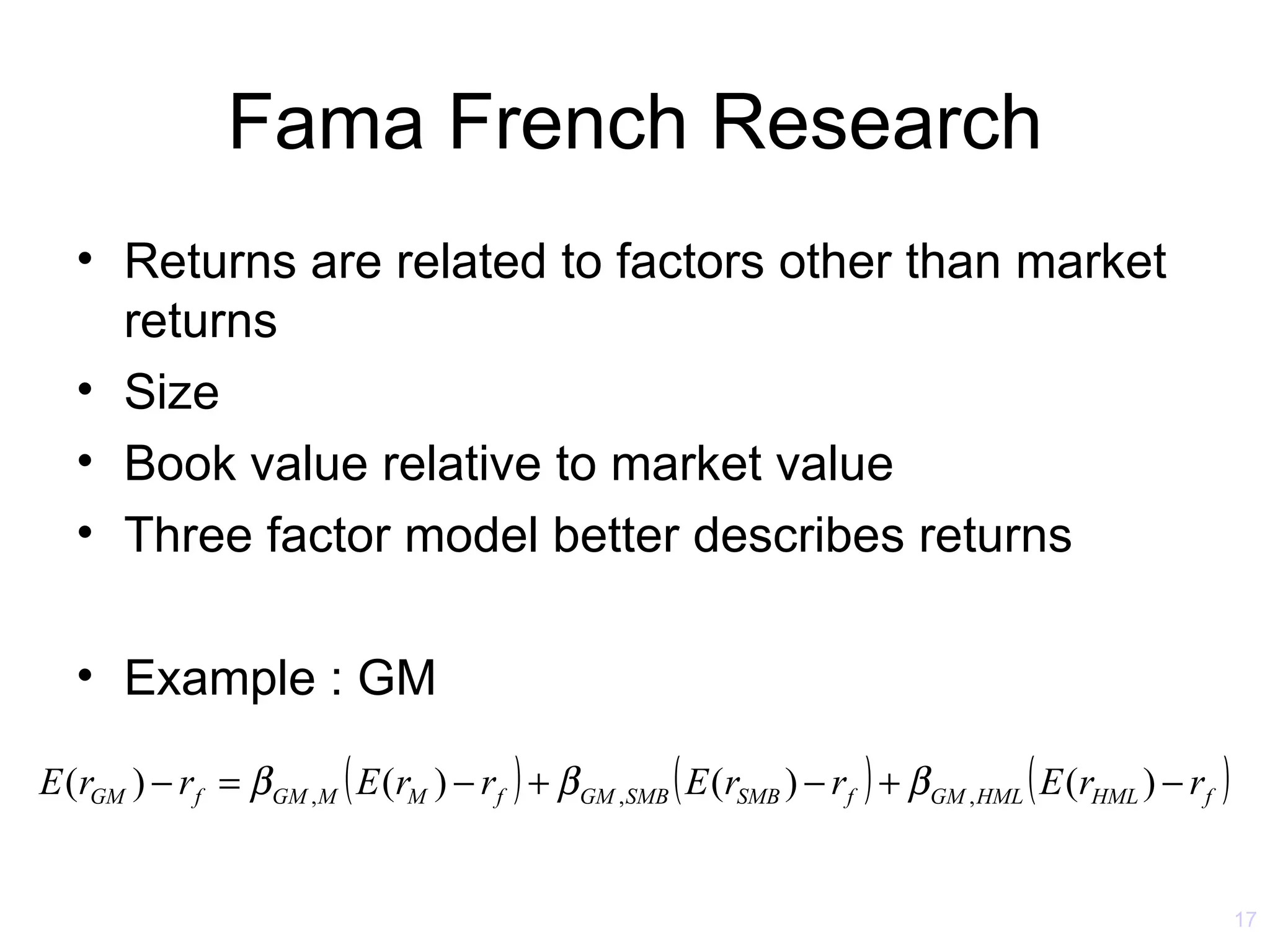
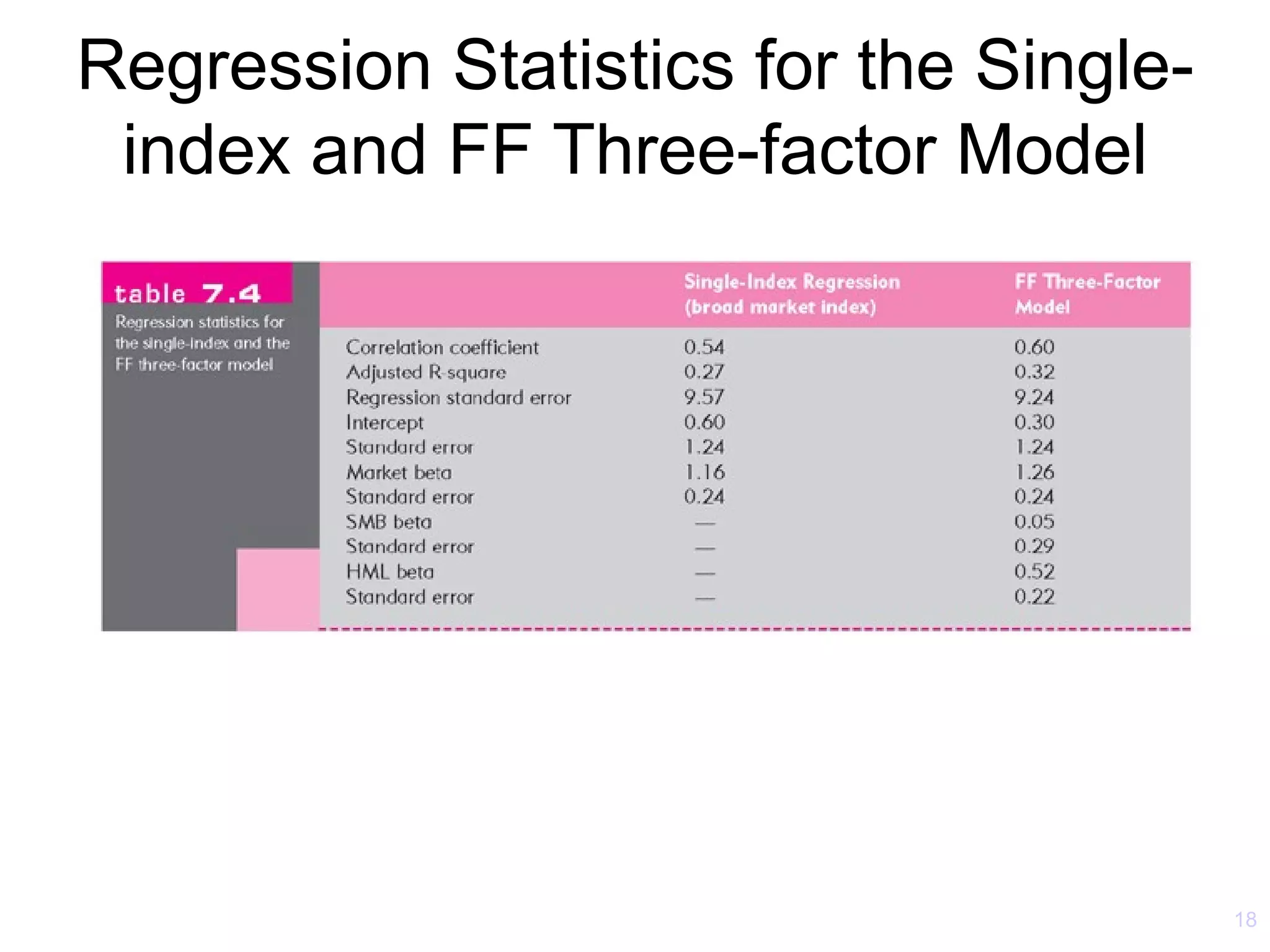
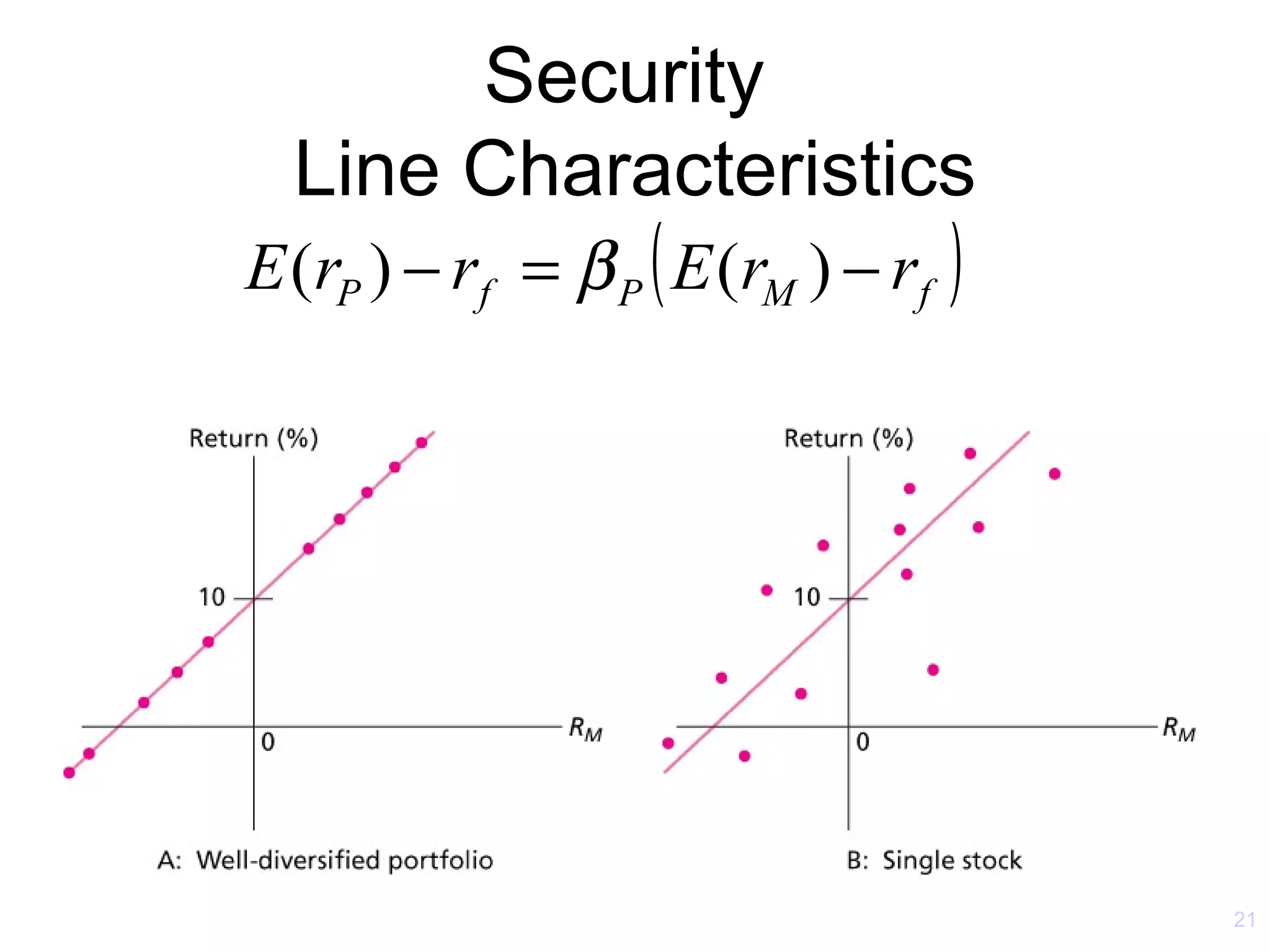
The document discusses the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) and Arbitrage Pricing Theory (APT). It outlines the key assumptions and results of CAPM, including that all investors hold the market portfolio and the security market line relates individual security risk premiums to market risk premiums through beta. It also discusses limitations of CAPM and how multifactor models like Fama-French can better describe returns. Finally, it explains how APT allows for arbitrage opportunities if mispriced portfolios exist and its relationship to CAPM.