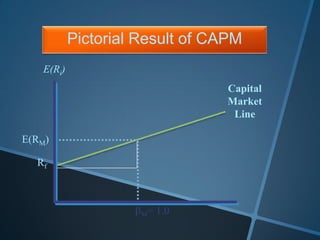
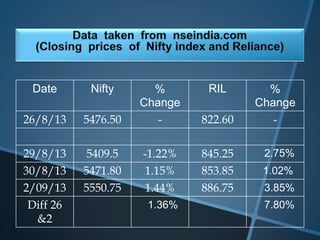
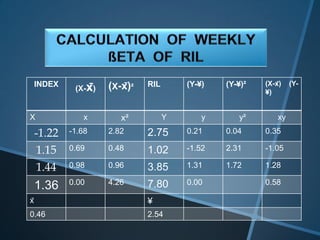
The document discusses the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which is a framework for understanding how securities are priced based on risk and return. It outlines key assumptions, such as the presence of a risk-free rate, homogeneous investor expectations, and the relationship between total risk and expected returns, illustrated through the Capital Market Line (CML) and Security Market Line (SML). Additionally, it addresses practical issues in estimating risk-free rates, market returns, and the application of beta and alpha in assessing investment performance.