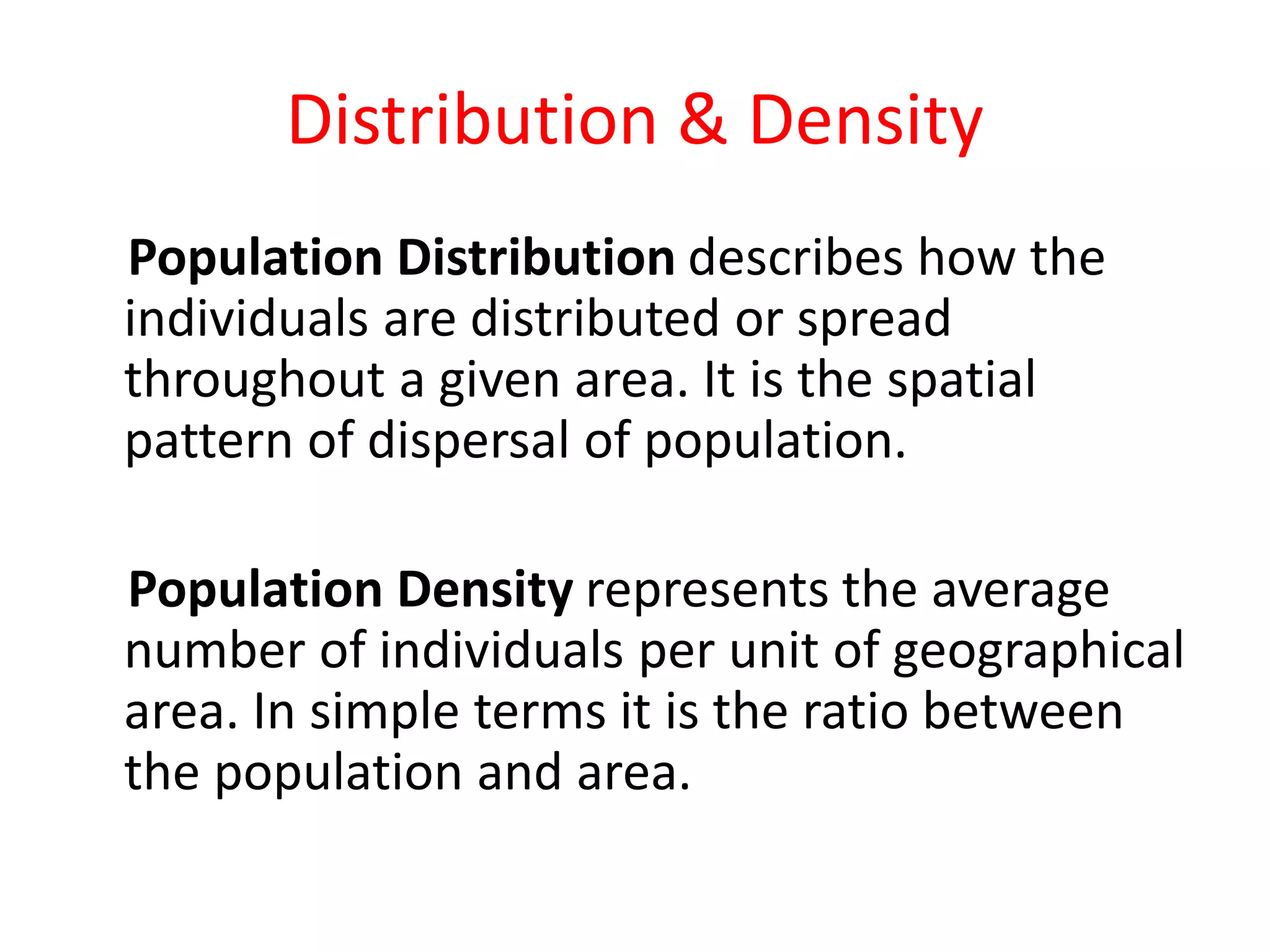
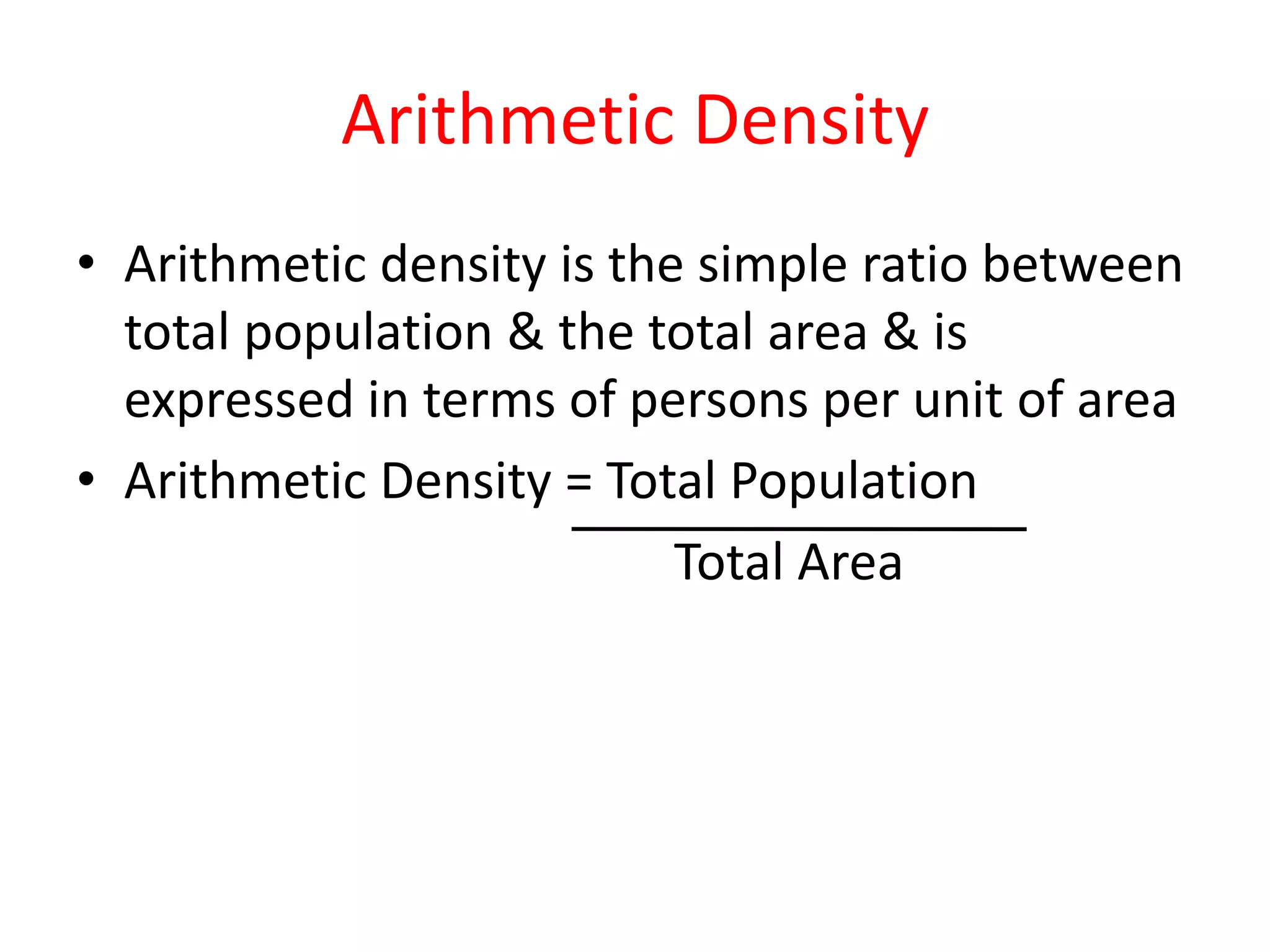
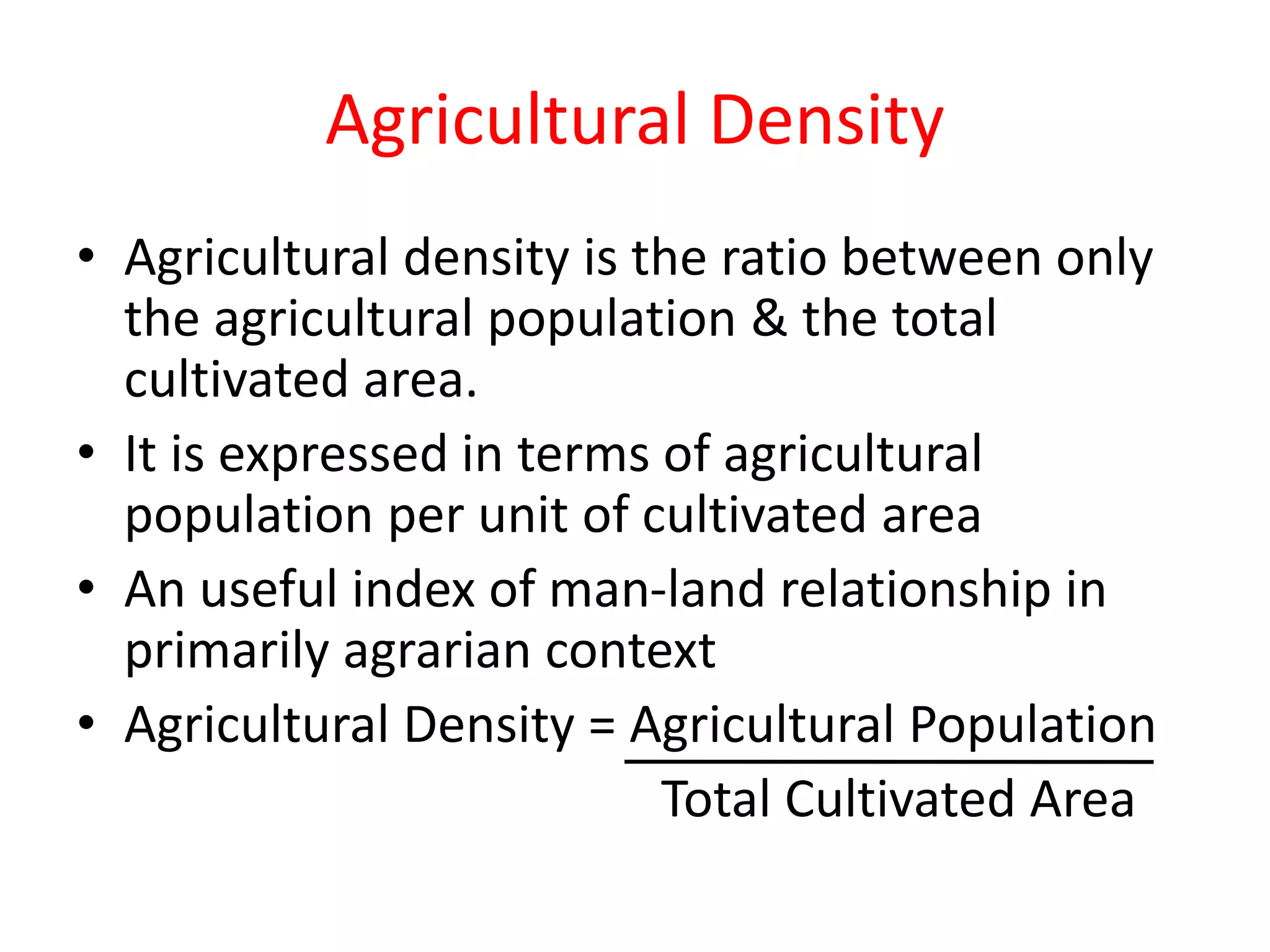
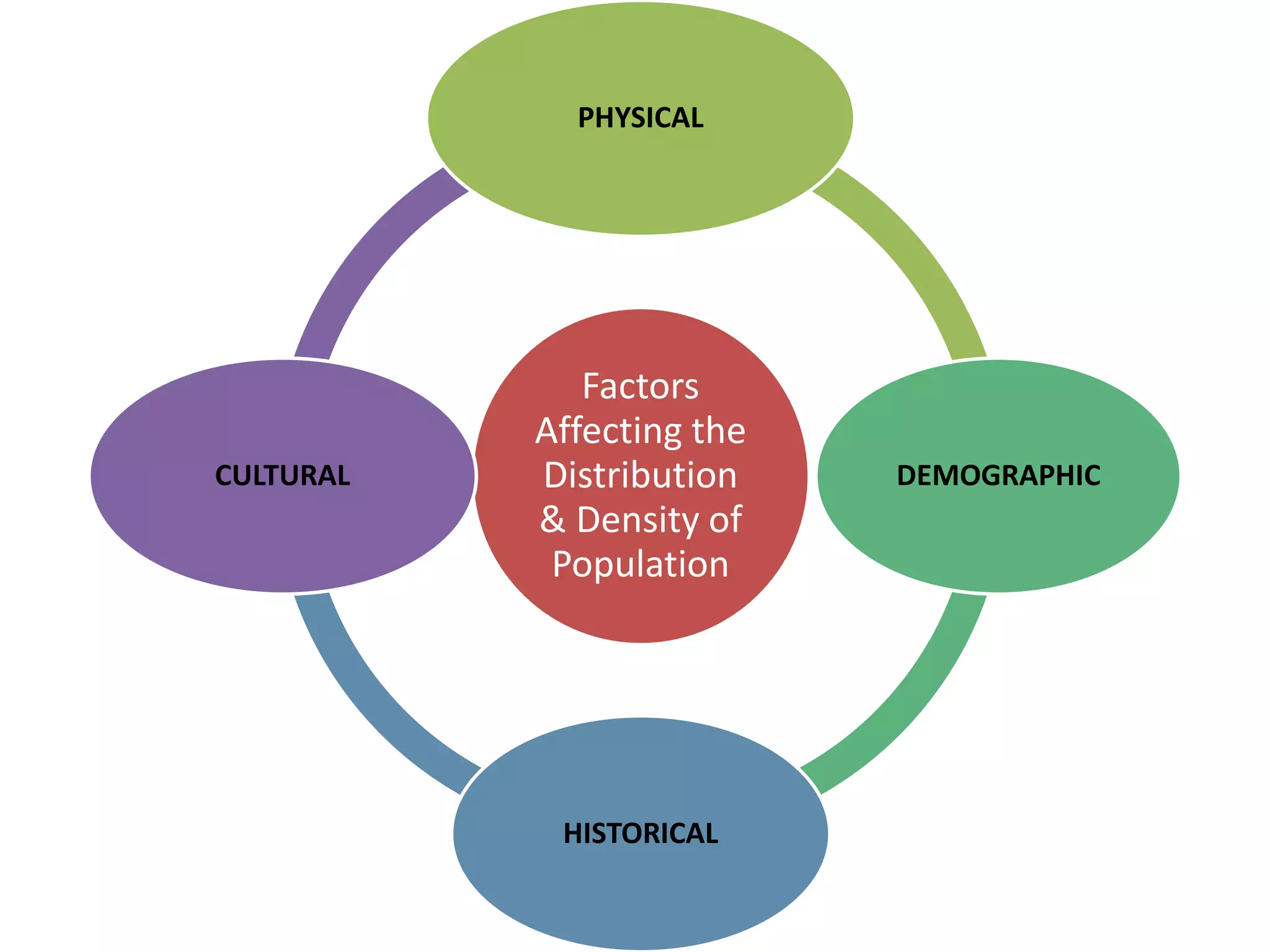
The document discusses population distribution and density, defining key concepts and types of population density, such as arithmetic, agricultural, and physiological density. It explores various factors influencing population distribution, including physical, cultural, and historical factors, emphasizing the significance of terrain, climate, resources, and government policies. Additionally, it highlights the demographic factors like fertility and migration that affect population concentration in different regions.