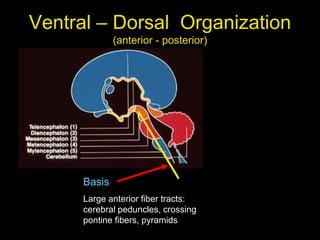
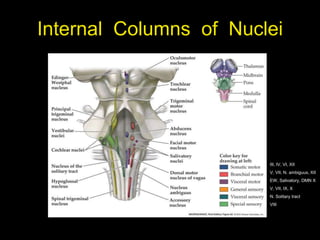
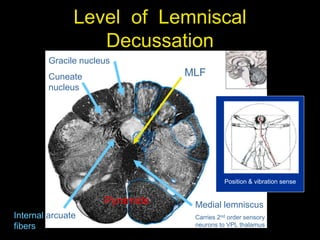
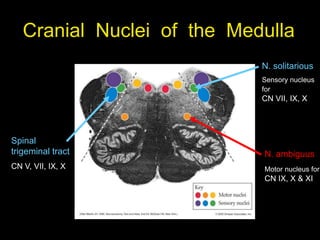
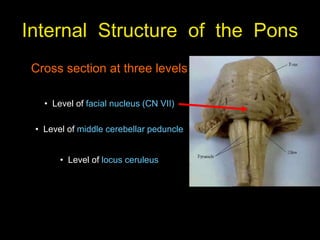
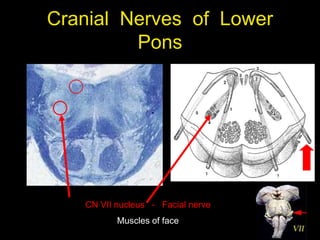
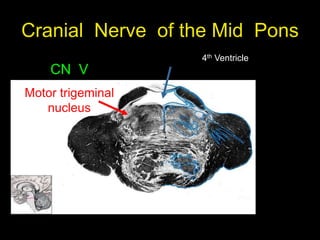
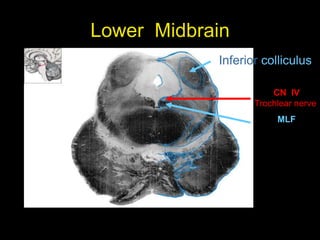
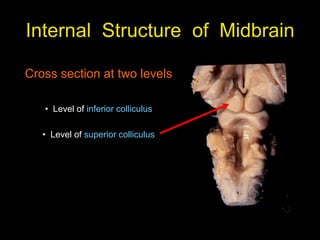
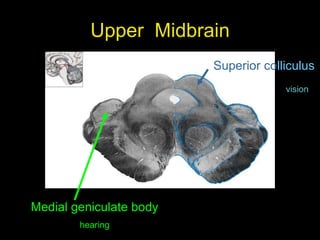
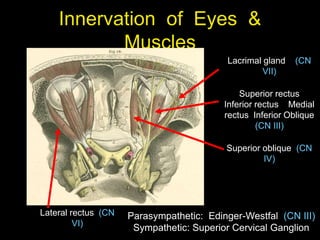
This document provides an overview of the anatomy of the brainstem, including the medulla, pons, and midbrain. It describes the internal structures and organization at different cross-sectional levels. Key structures discussed include cranial nerve nuclei, fiber tracts such as the medial lemniscus and pyramidal tract, and subcortical nuclei. The document also outlines the cranial nerves originating from each region and their functions.