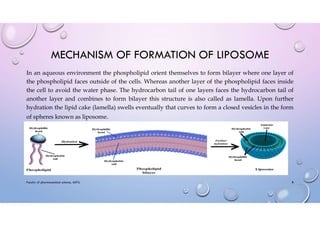
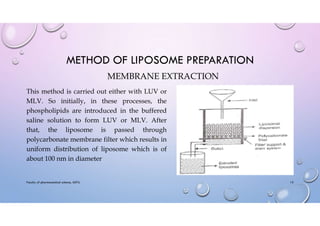
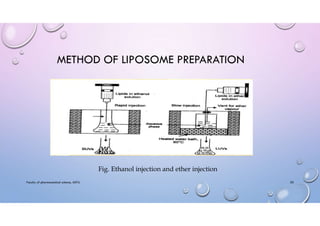
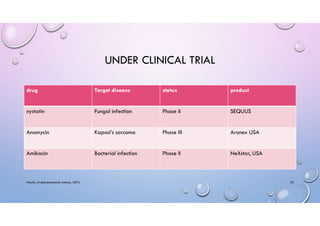
This document provides an overview of liposomes, including their composition, mechanisms of formation, advantages, classifications, preparation methods, applications, and examples of marketed products. Liposomes are spherical vesicles composed of phospholipid bilayers that can encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. They are classified based on structural parameters like lamellarity and size, as well as composition. Common preparation techniques include thin film hydration, ethanol injection, sonication, and microfluidization. Liposomes are useful for targeted drug delivery to treat conditions like cancer and fungal infections, and some commercial liposome products are used to deliver drugs like amphotericin B and daunorubicin.