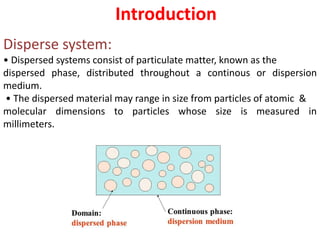
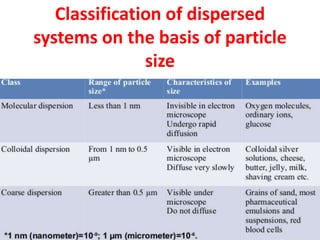
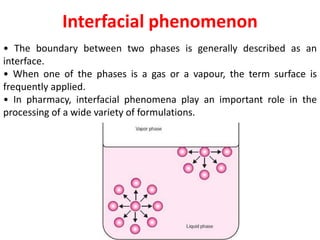
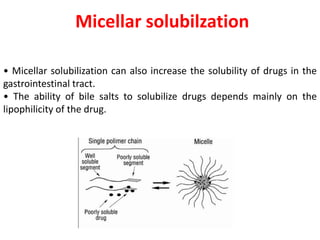
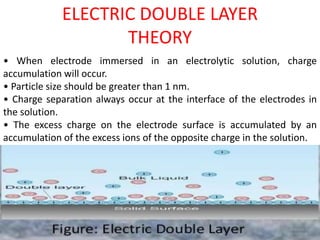
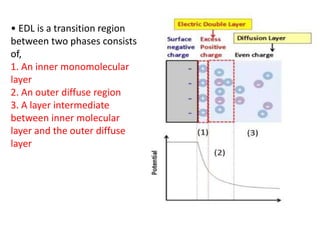
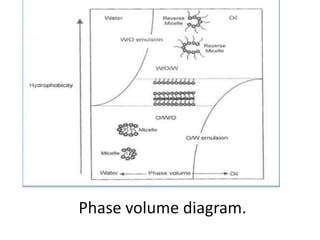
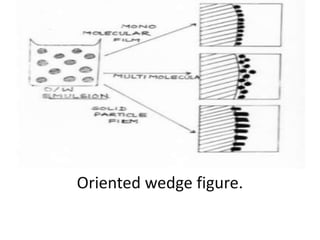
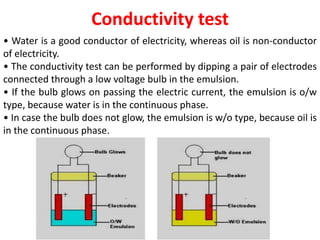
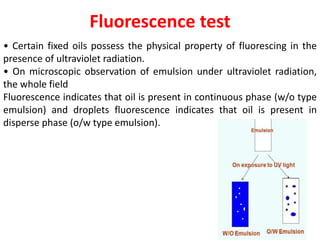
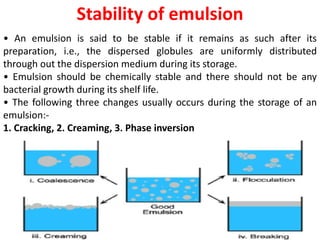
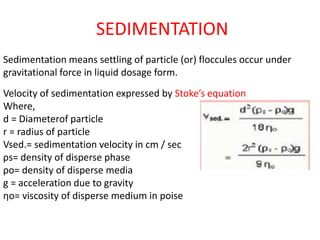
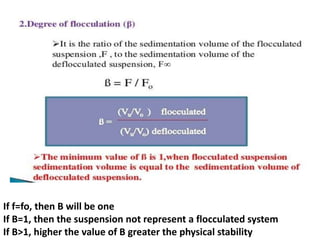
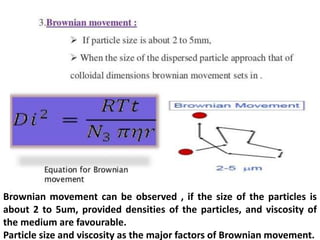
This document provides an overview of disperse systems, including emulsions and suspensions. It discusses key concepts such as interfacial phenomena, wetting, adsorption, surfactants, and micelle formation. Theories of emulsification including electric double layer, phase volume, oriented wedge, and surface tension are presented. Methods for determining emulsion type including dilution, dye, conductivity, and fluorescence tests are described. Emulsifying agents and factors influencing emulsion stability are also summarized. Suspensions are defined as biphasic systems with solid particles between 0.5-5 microns dispersed in a liquid. Particle size and sedimentation theories are briefly covered.