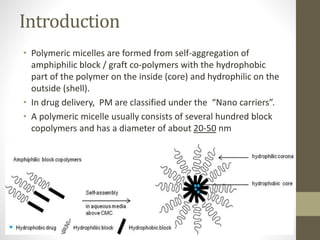
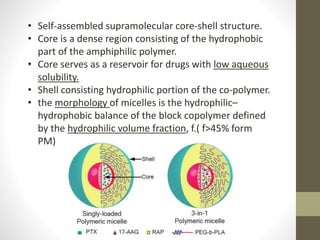
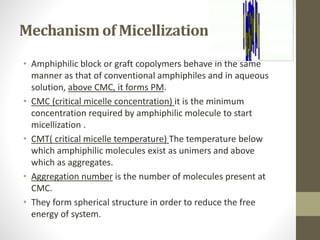
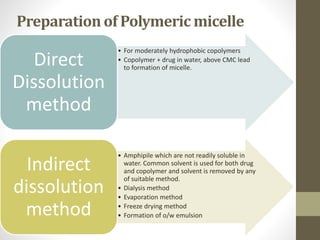
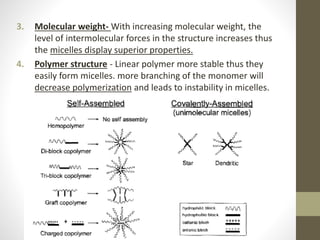
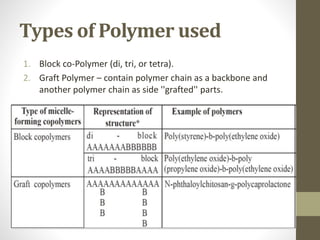
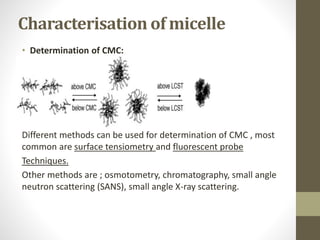
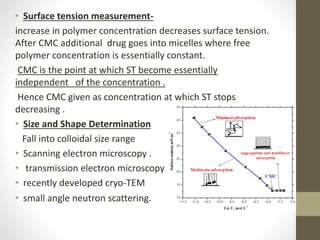
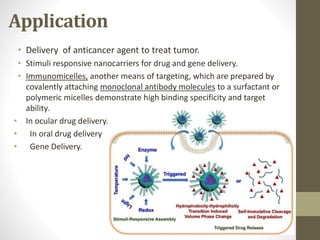
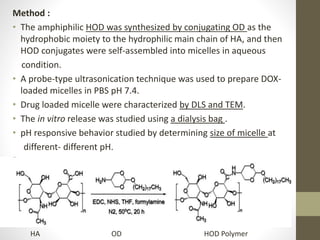
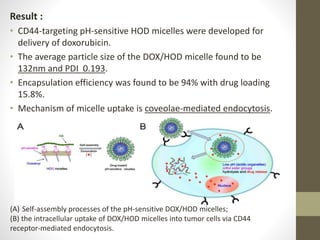
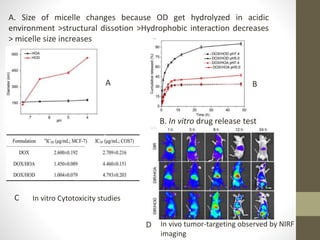
Polymeric micelles are self-assembled structures formed from amphiphilic block copolymers, utilized in drug delivery due to their core-shell morphology, which allows for encapsulation of hydrophobic drugs. Their stability and drug-loading capacity can be affected by several factors including chain length, molecular weight, and cross-linking. Applications include targeted delivery of anticancer agents and gene therapy, although challenges persist in their industrial production and stability upon intravenous administration.