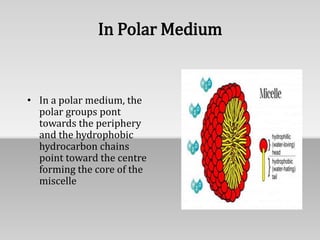
Miscelles are aggregates of surfactant molecules that form above the critical micelle concentration in a solution. The long hydrophilic tails of surfactant molecules coil to bind water molecules, while the hydrophobic tails cluster together at the core of the miscelle. In polar solvents, the hydrophilic heads point outward and hydrophobic tails inward. In nonpolar solvents, the arrangement is reversed. Miscelles allow insoluble compounds to dissolve within their cores and are important for nutrient absorption in the body. They are also used for targeted drug delivery and as emulsifiers in detergents.