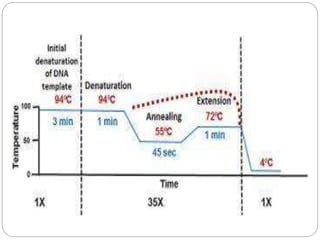
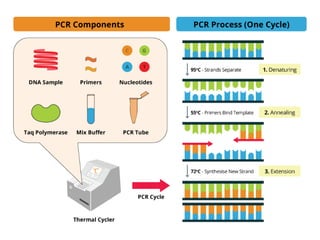
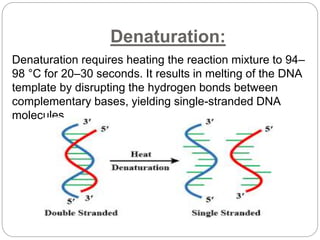
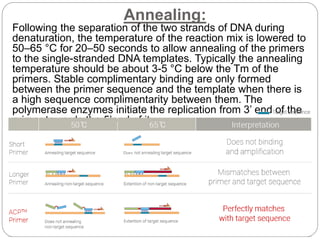
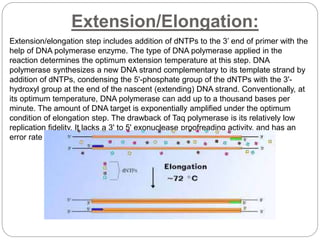
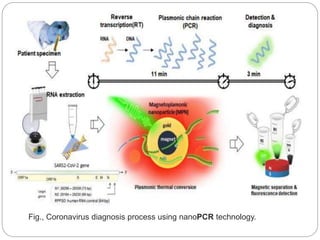
The document discusses polymerase chain reaction (PCR), including its basic components, procedure, and applications. PCR is a technique used to amplify DNA sequences. It involves repeated cycles of heating and cooling of the DNA sample to separate and copy the DNA strands. The key steps are initial denaturation, denaturation, annealing of primers, and extension of new strands by DNA polymerase. PCR can generate millions of copies of target DNA sequences and is widely used for applications like infectious disease diagnosis, genetic testing, forensics, and molecular biology research. Recent developments include using magneto-plasmonic nanoparticles to develop nanoPCR for faster COVID-19 diagnosis within 20 minutes at the point-of-care.