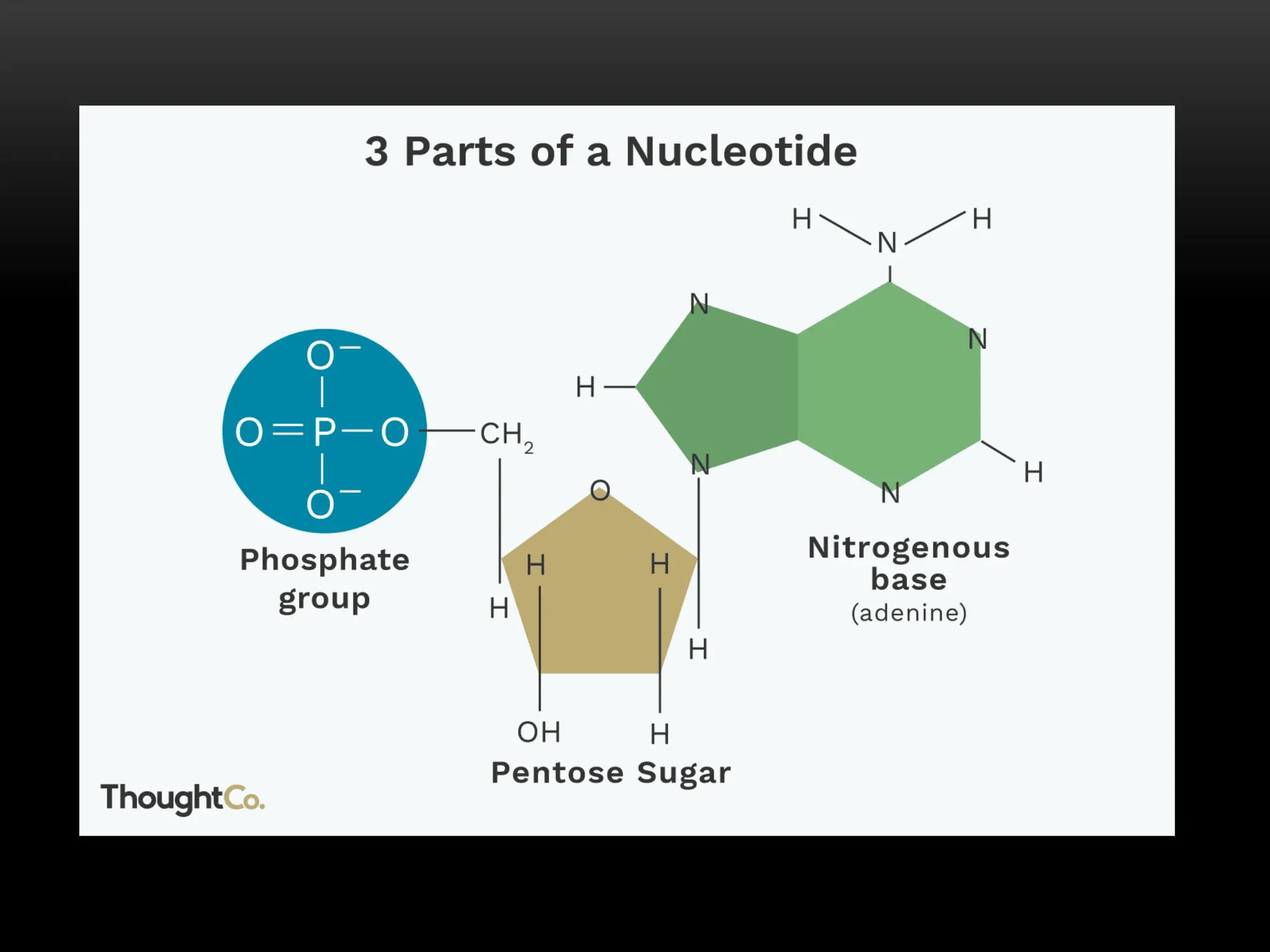
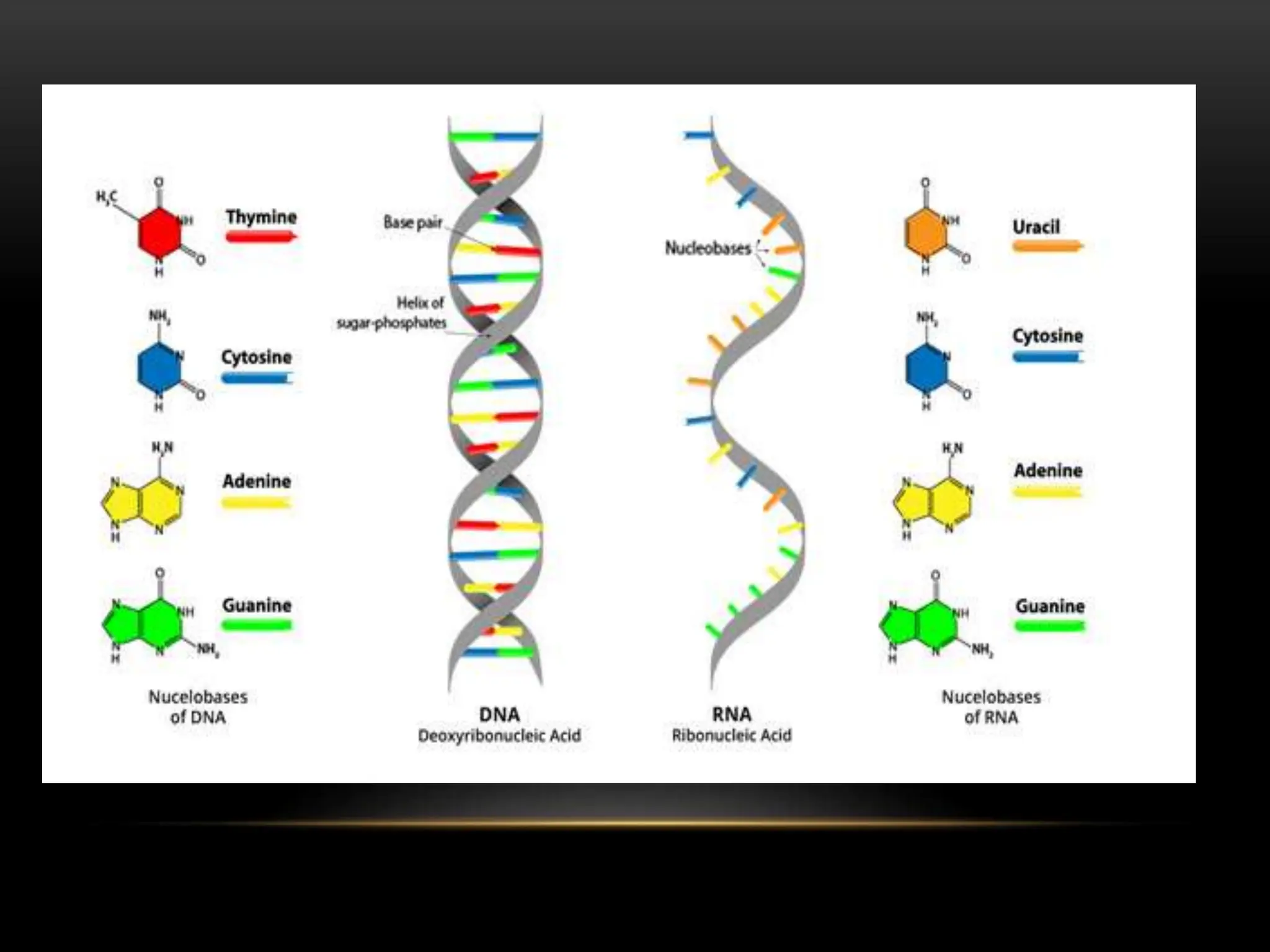
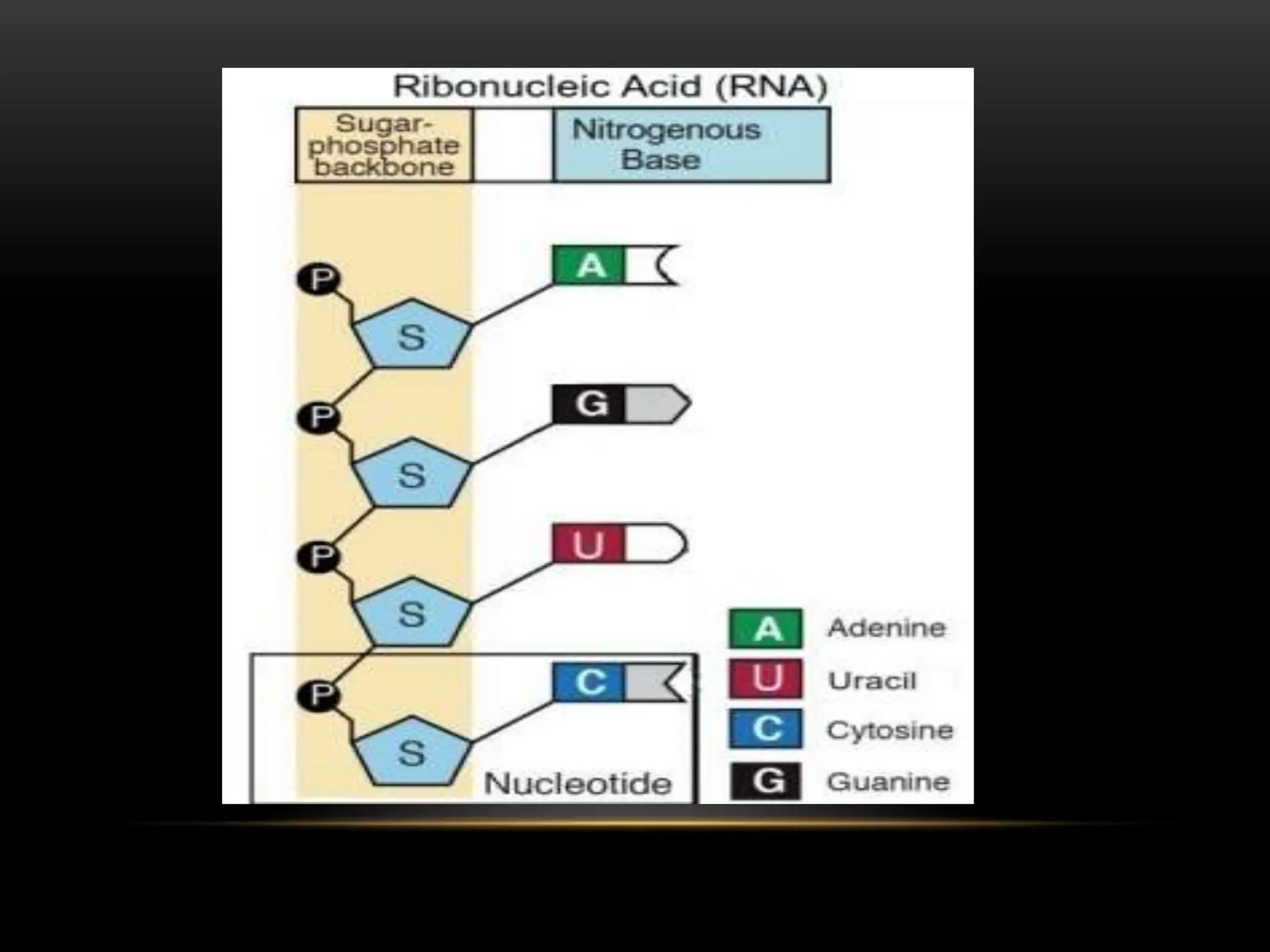
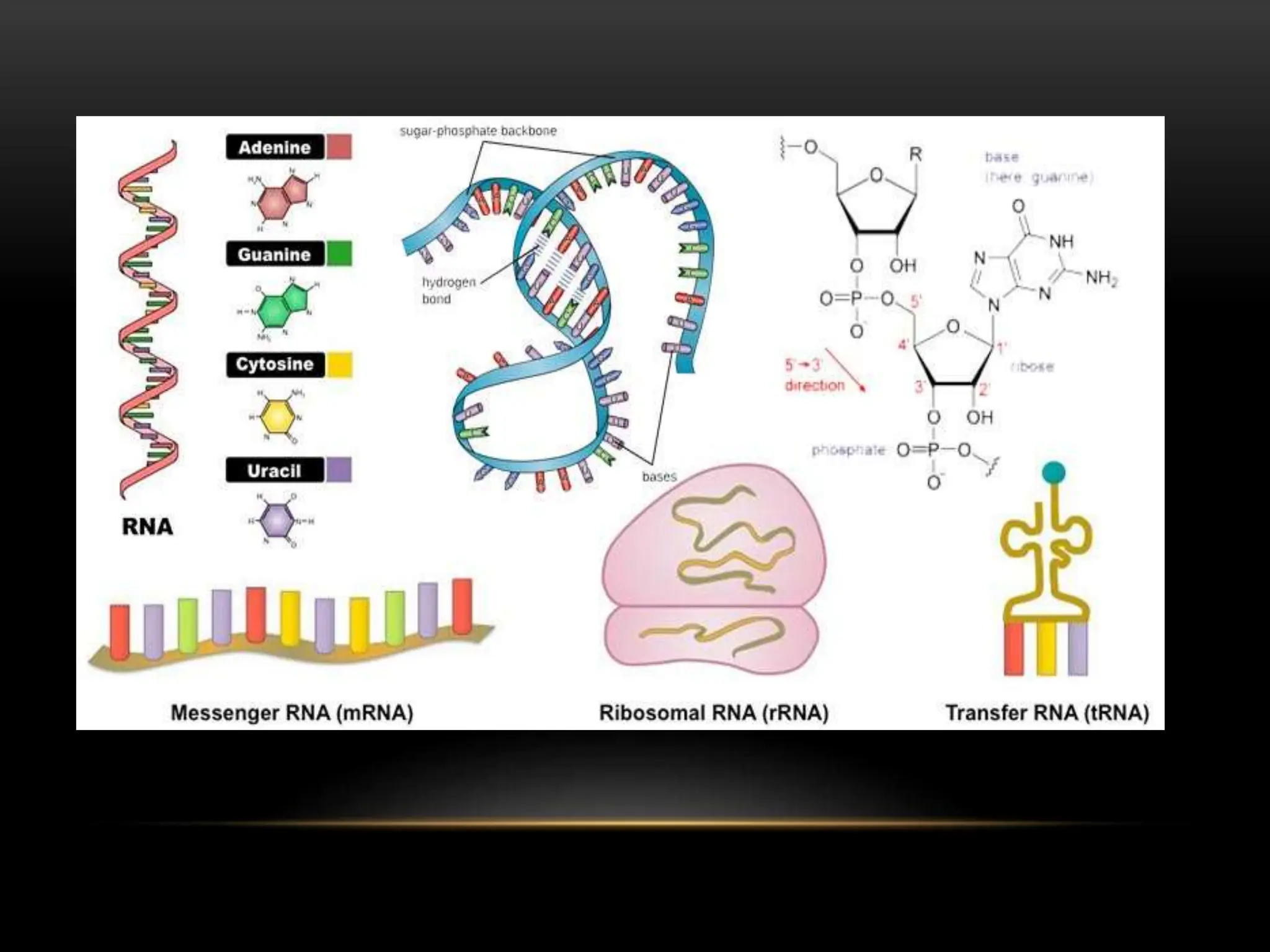
1. RNA is an important nucleic acid found in most prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in addition to DNA. Some viruses contain only RNA, which acts as their genetic material.
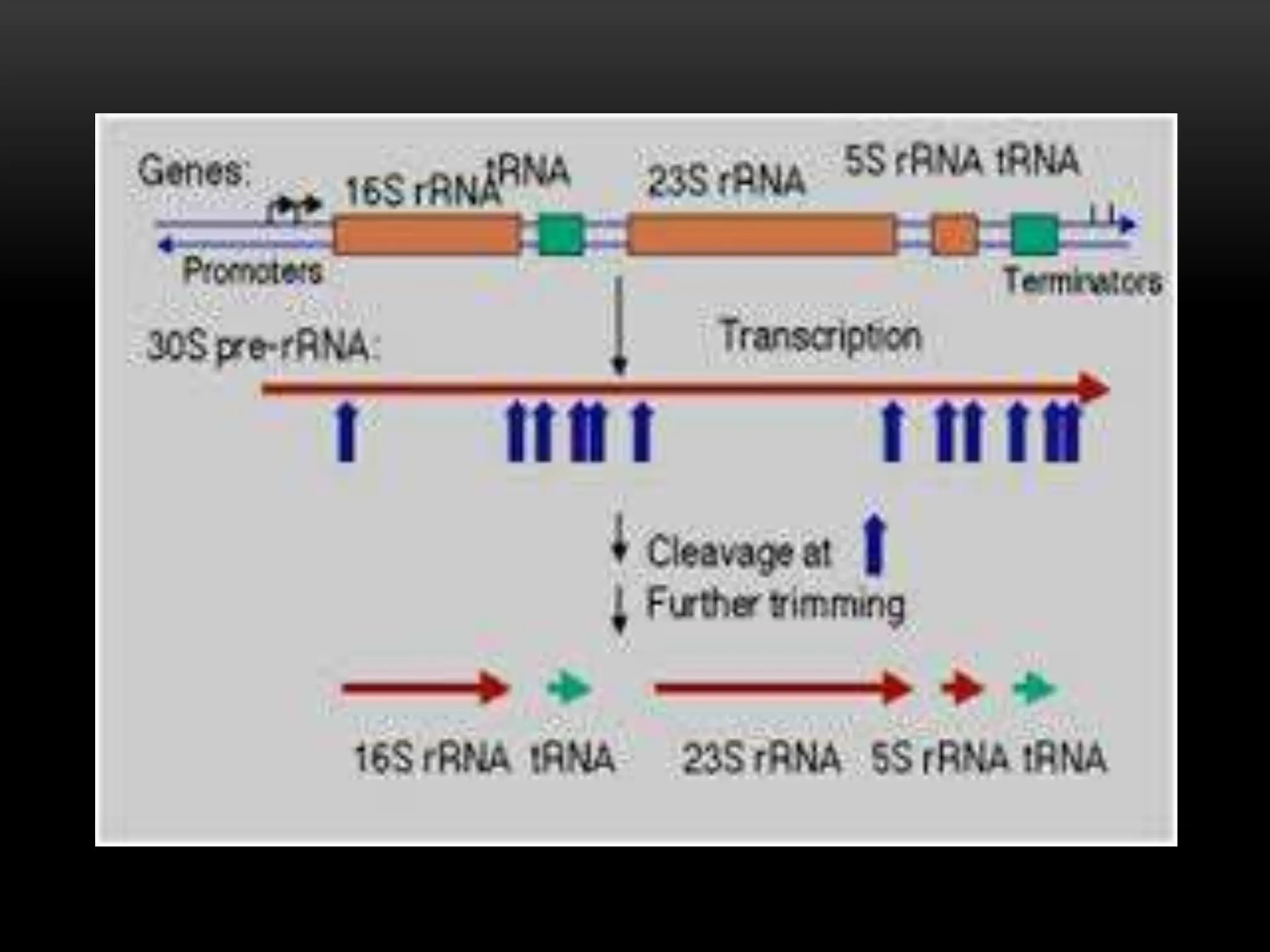
2. There are two main types of RNA - genetic RNA found in viruses, and non-genetic RNA which depends on DNA for synthesis. Non-genetic RNA includes messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA.
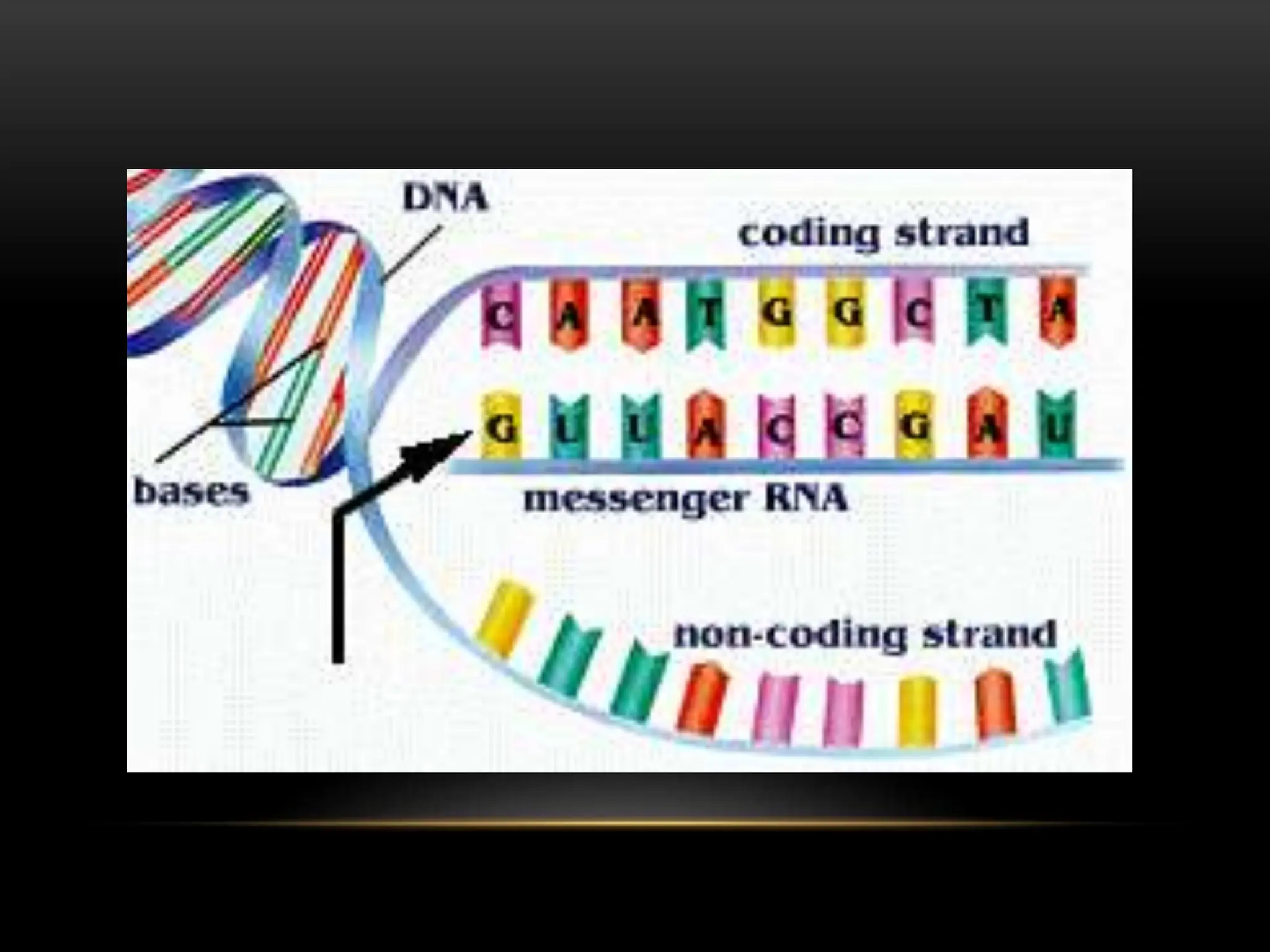
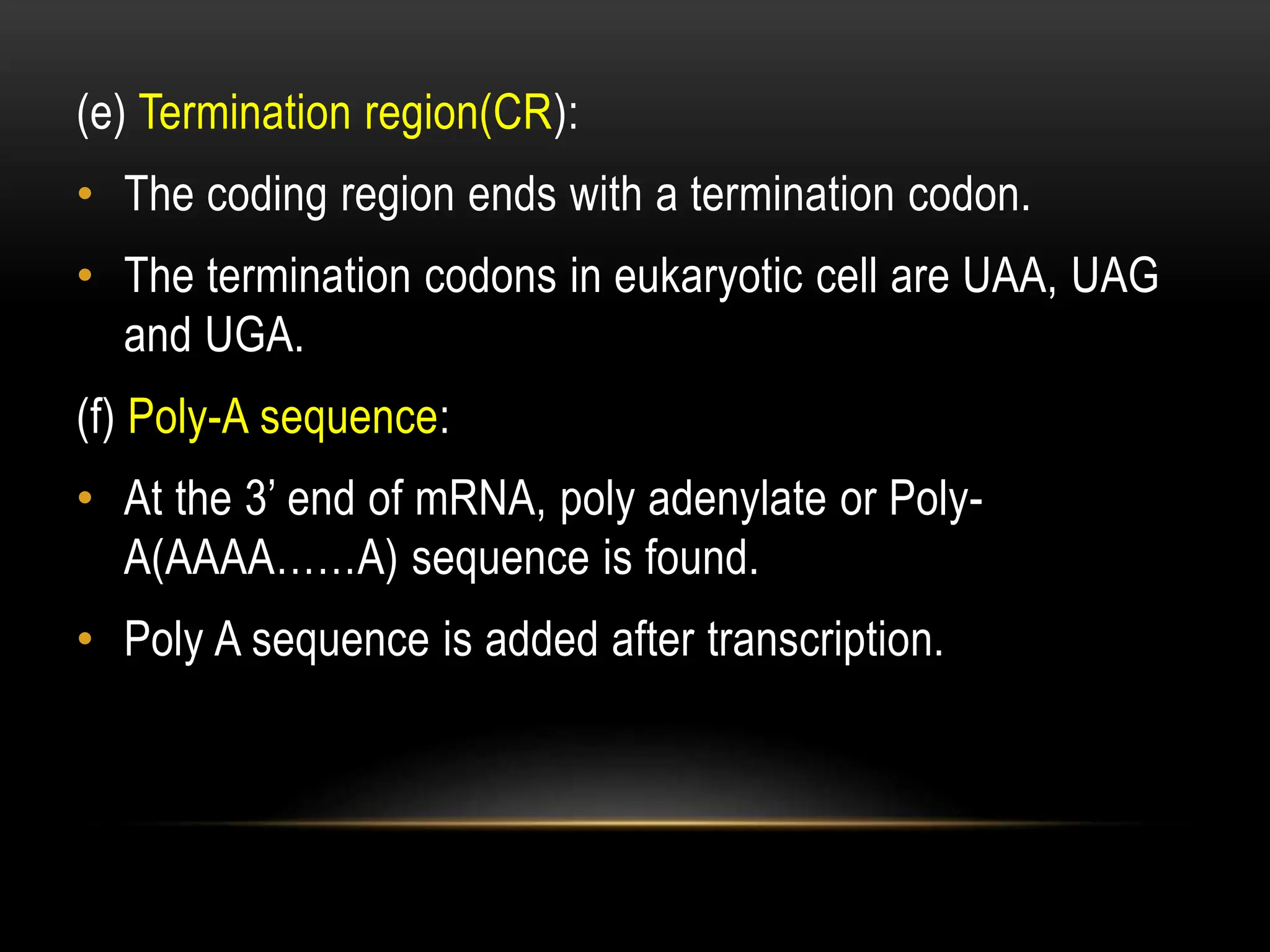
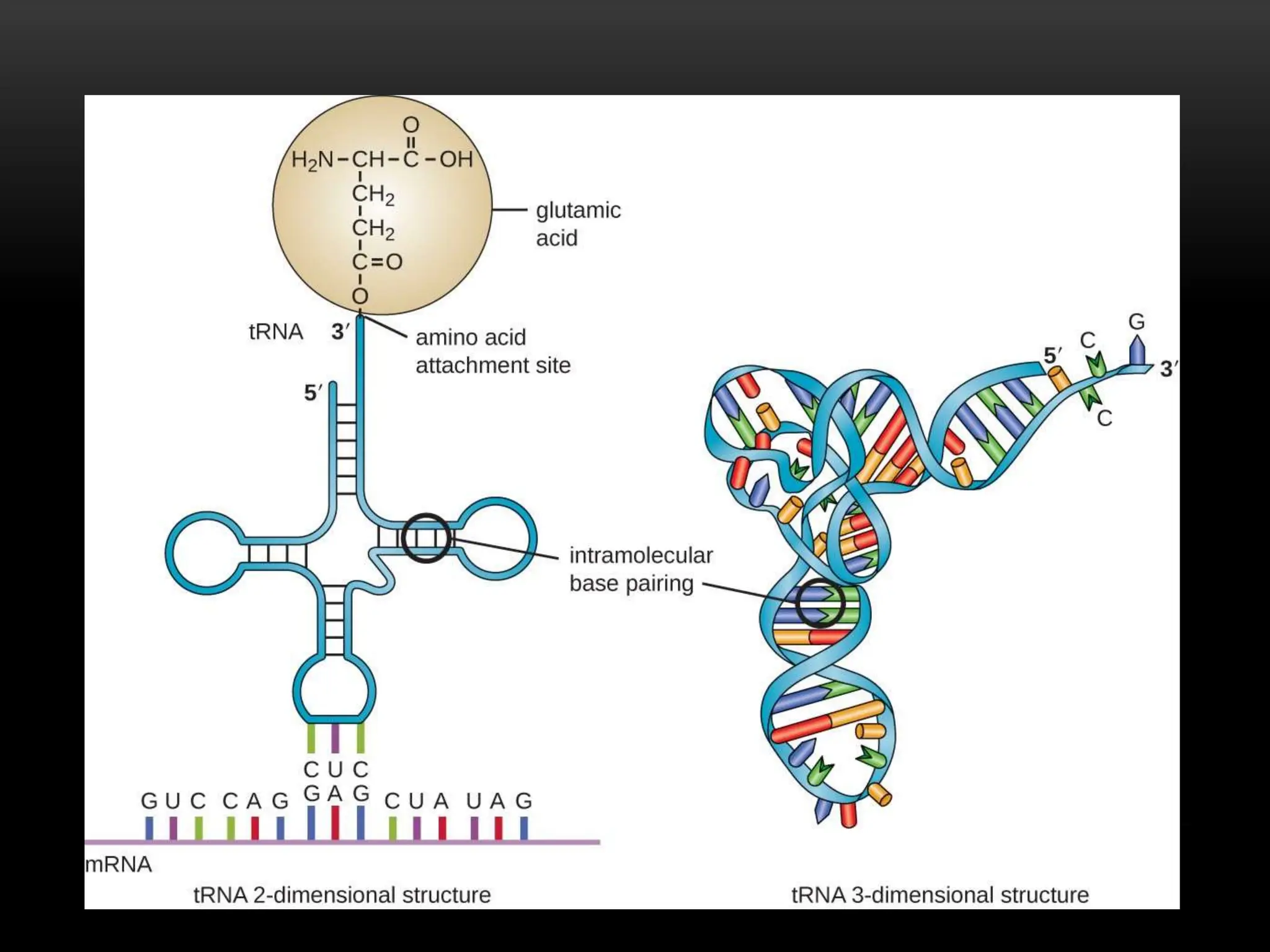
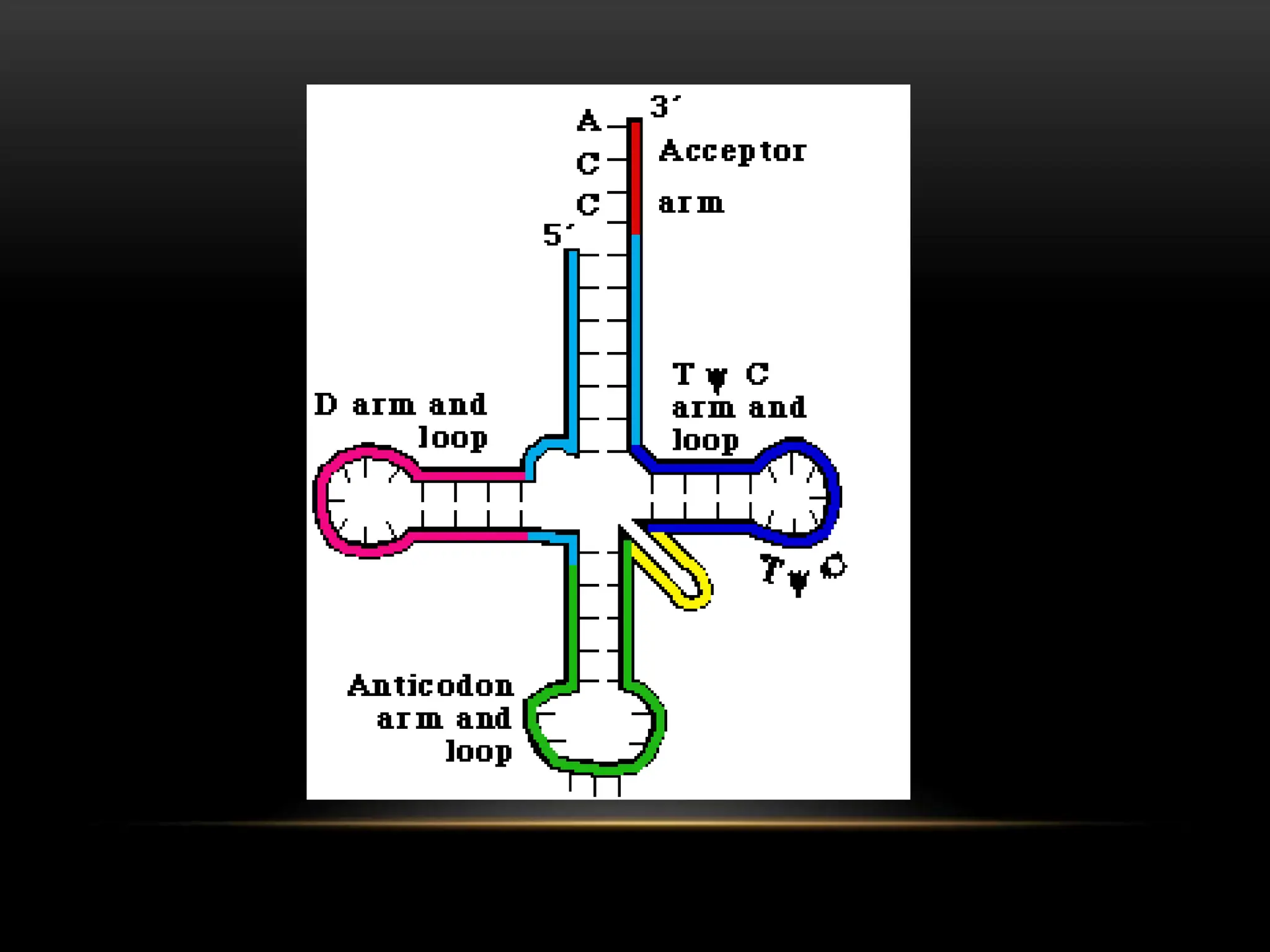
3. Messenger RNA carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis. It has a 5' cap, coding region, and 3' poly-A tail. Ribosomal RNA forms the major structural component of ribosomes. Transfer RNA transfers amino acids to the ribosome during protein