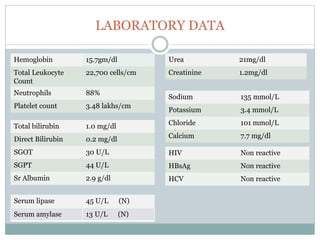
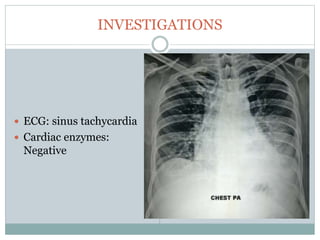
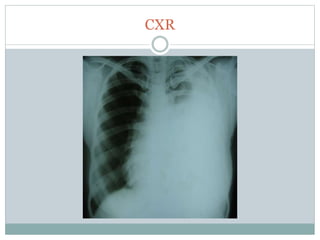
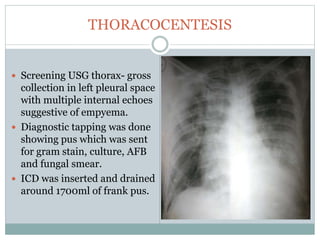
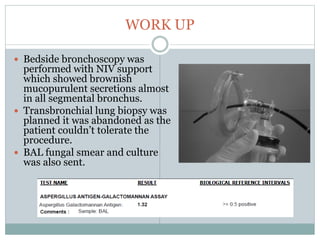
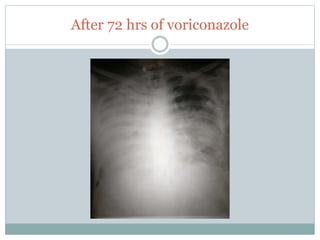
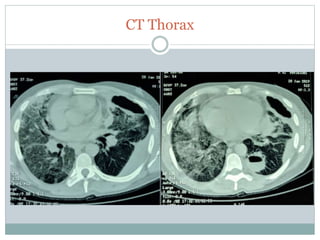
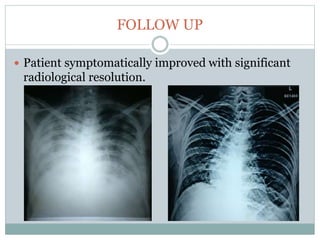
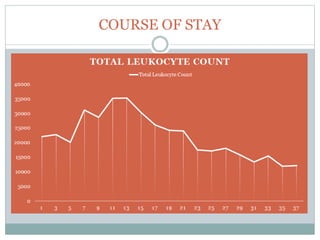
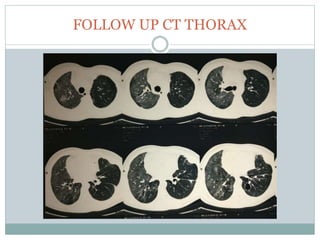
The document reports a clinical case of a 41-year-old male with chronic alcoholism who was initially suspected of having pancreatitis but later diagnosed with invasive pleuropulmonary aspergillosis after further examinations revealed a significant pleural effusion and positive fungal cultures. The patient's condition deteriorated despite treatment with voriconazole, leading to a regimen that included liposomal amphotericin B and capsofungin, resulting in clinical improvement and significant radiological resolution. Key takeaways highlight the atypical presentation of empyema, the role of combined antifungal therapy, and the challenges of diagnosis in immunocompetent patients.