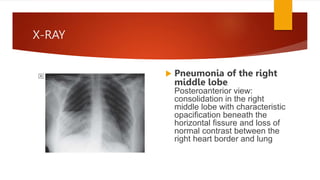
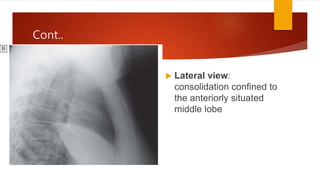
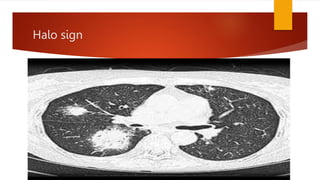
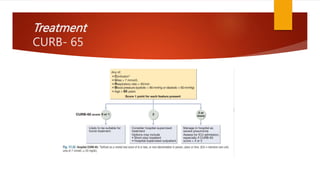
Bronchopneumonia is a type of pneumonia characterized by patchy lung inflammation and infection. It is often caused by aspiration of oropharyngeal bacteria. Community-acquired pneumonia is commonly seen in children and the elderly. Hospital-acquired pneumonia is a major complication for hospitalized patients, especially those on ventilators. Diagnosis involves clinical features, imaging, and microbiological testing of sputum or bronchial samples. Treatment focuses on oxygenation, fluid balance, and antibiotics tailored to likely causative organisms. Immunocompromised patients are at higher risk for opportunistic pathogens.