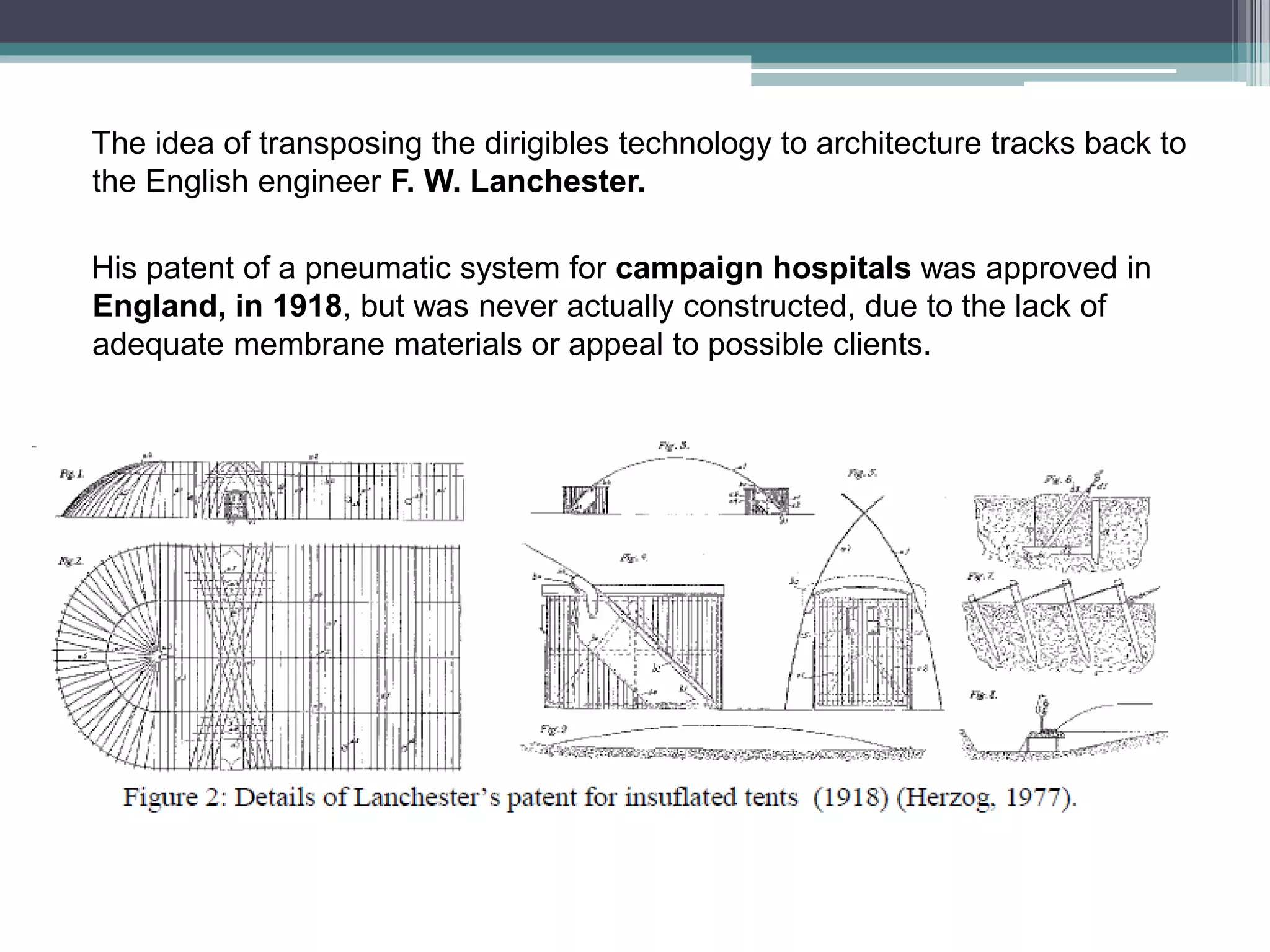
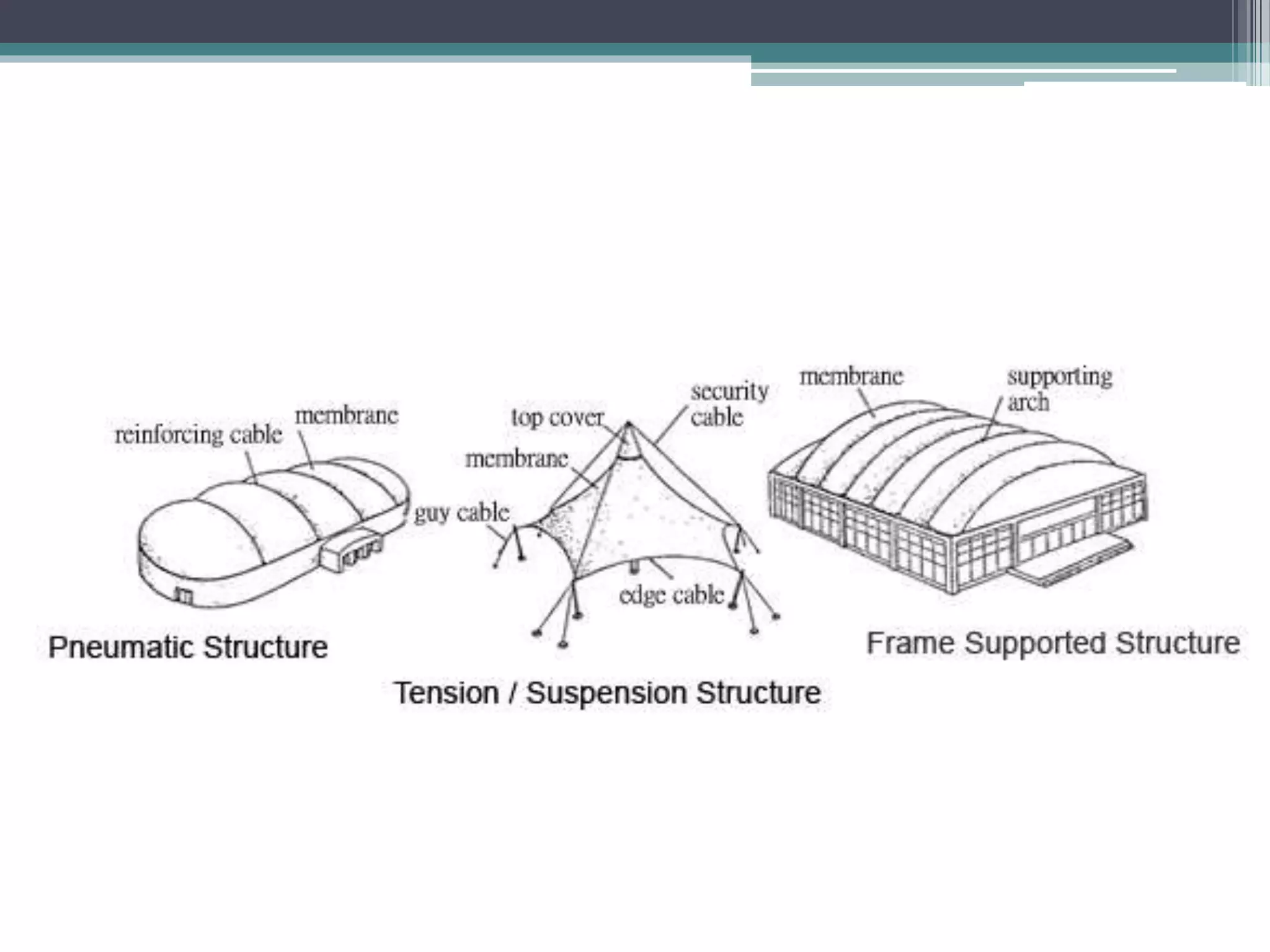
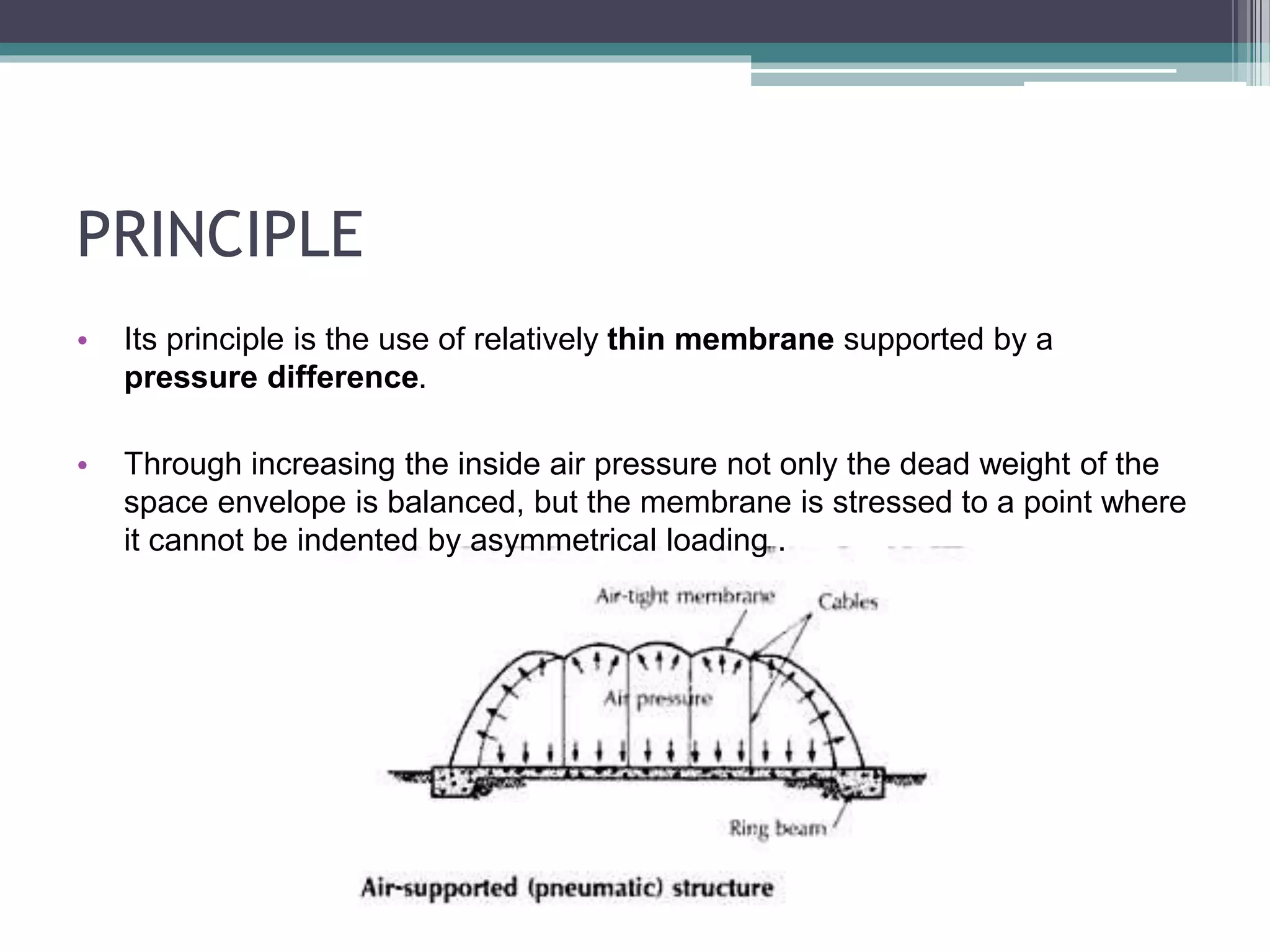
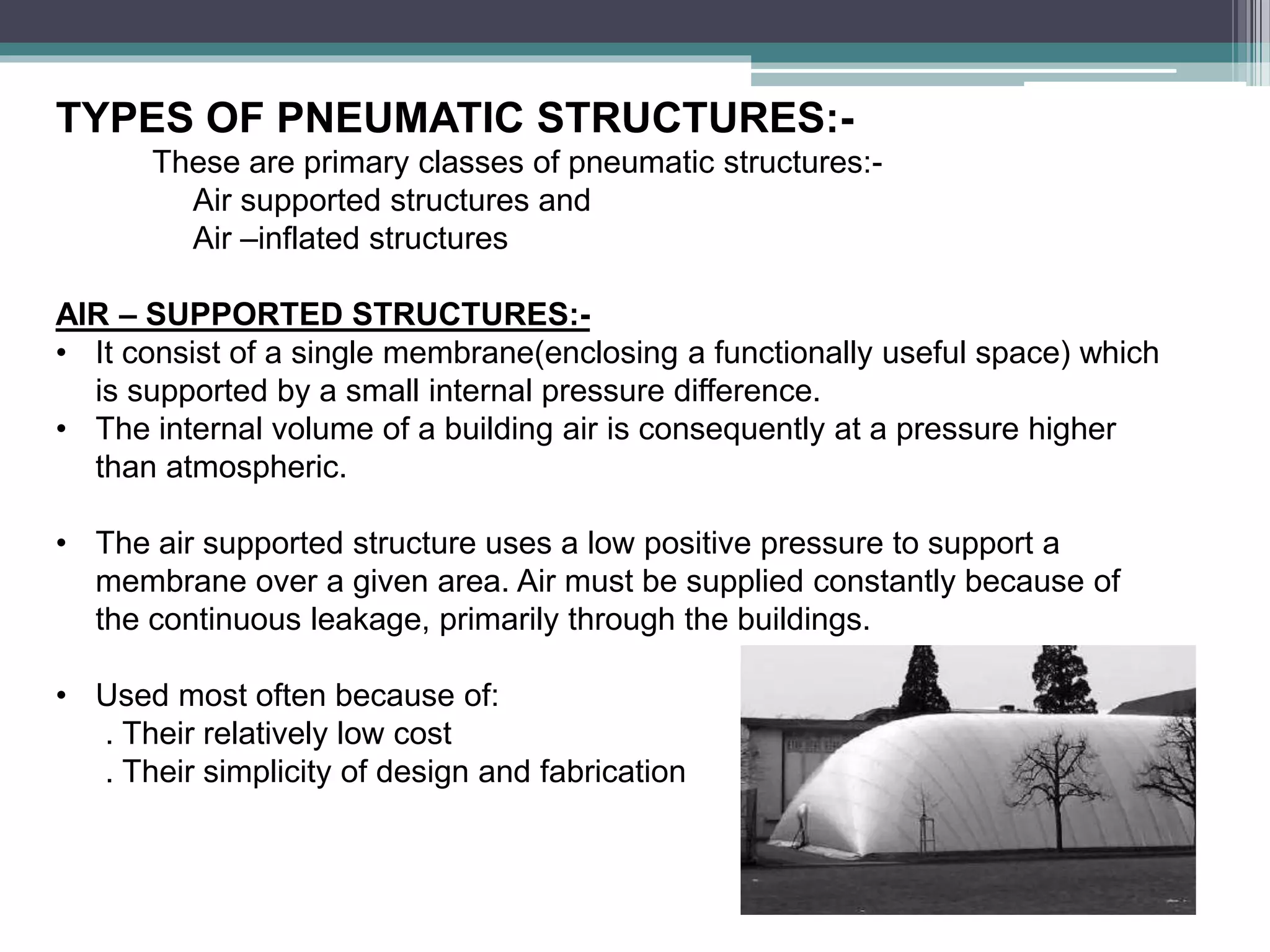
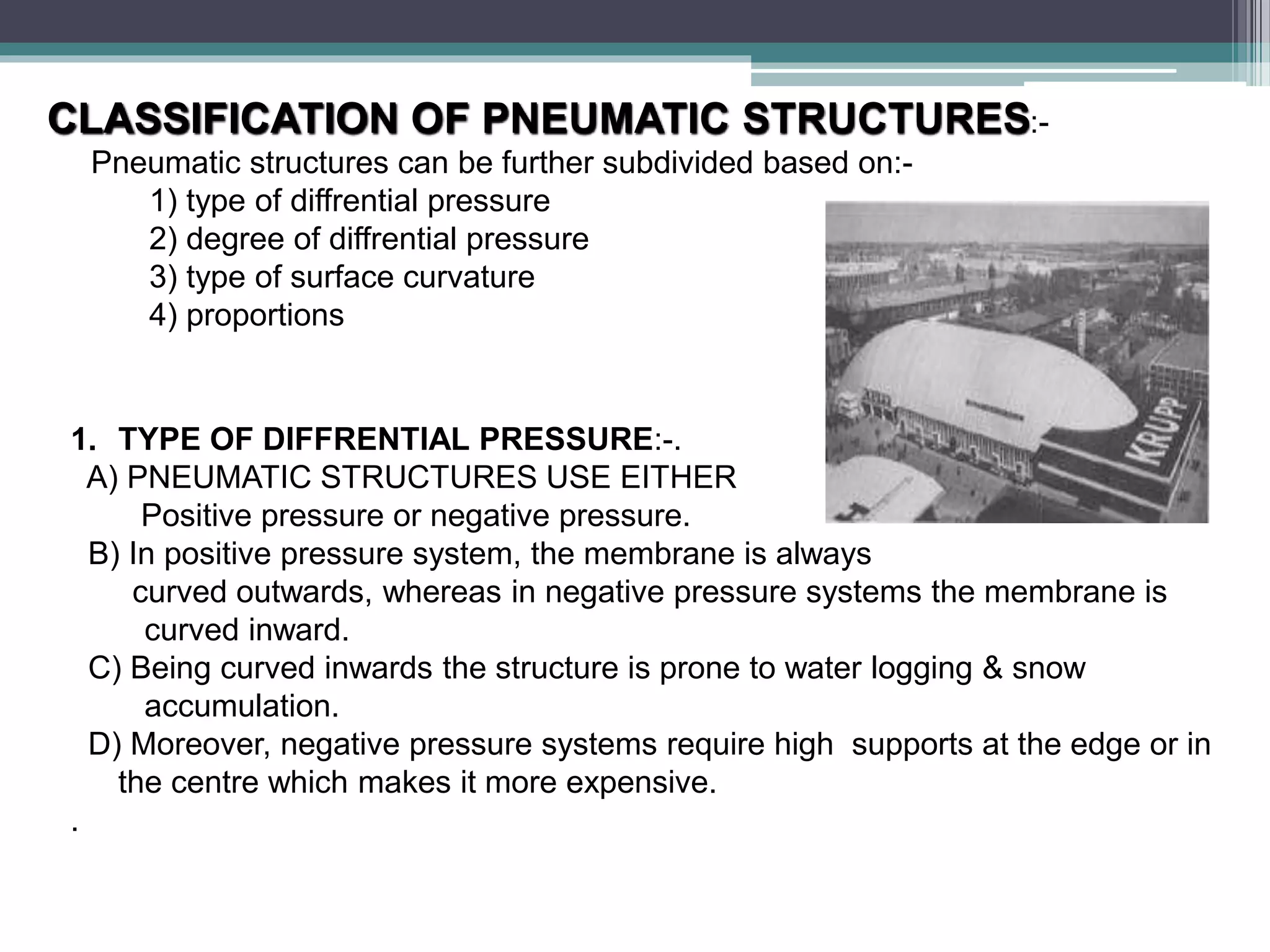
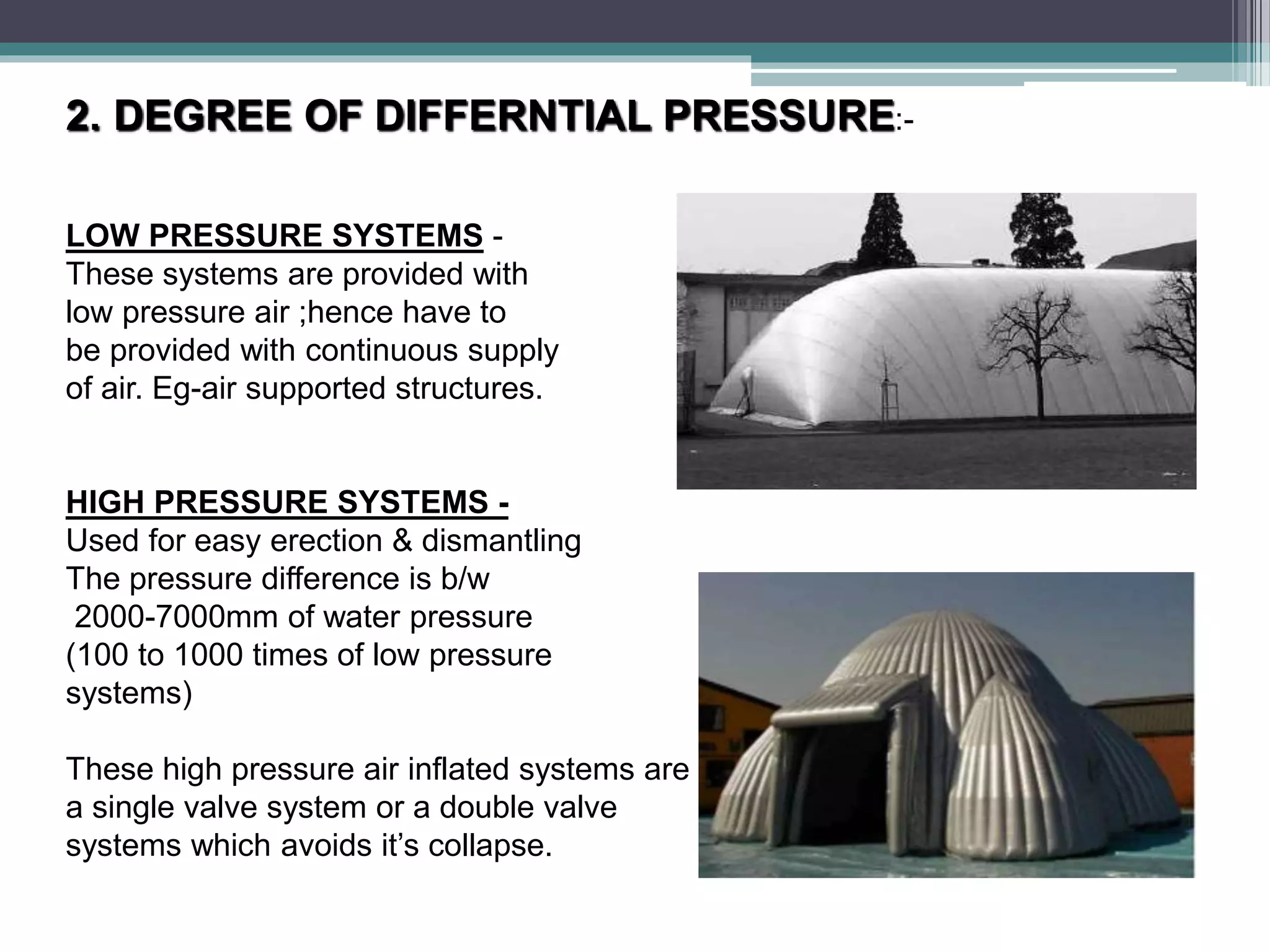
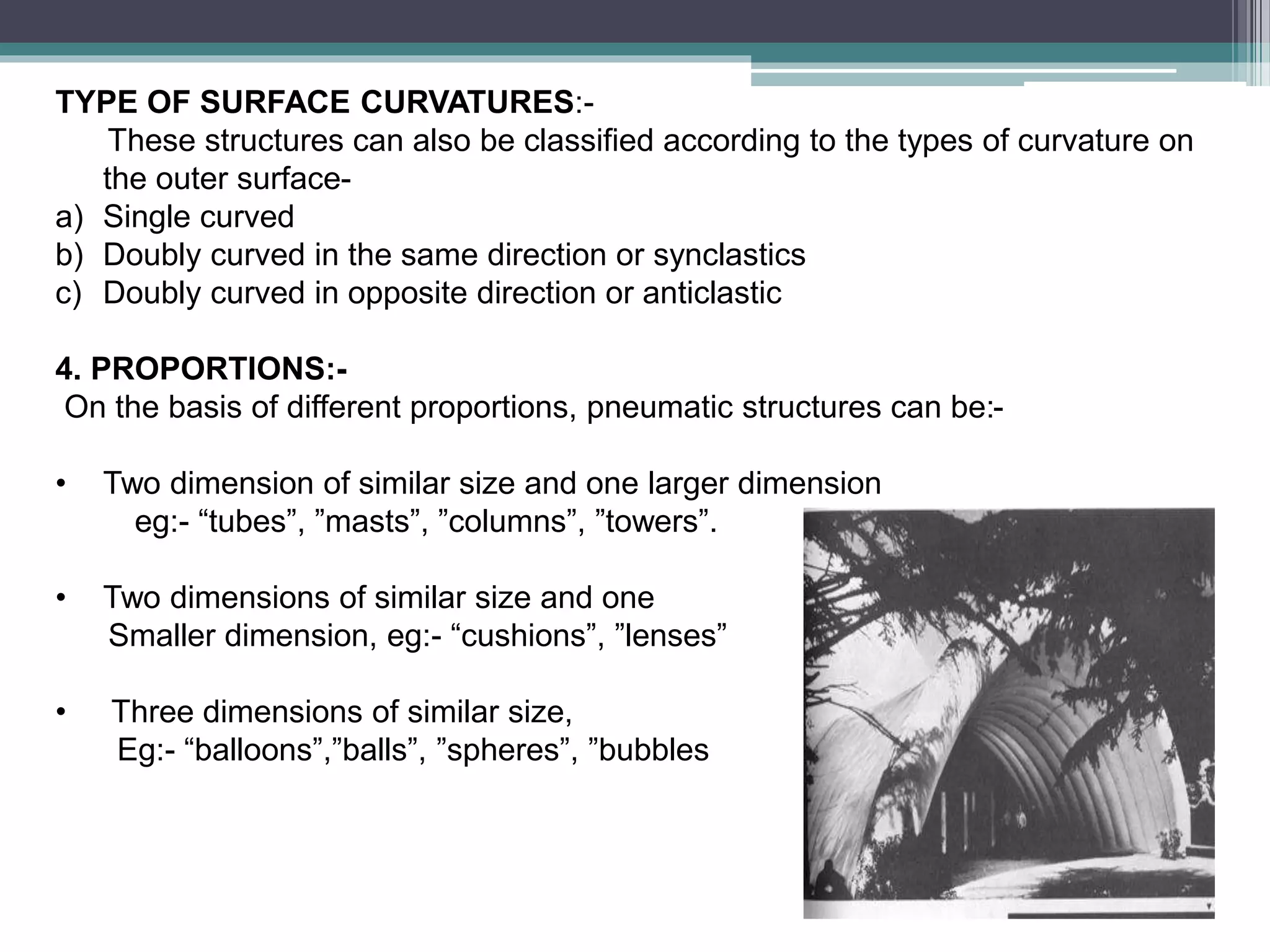
Pneumatic structures use thin, pressurized membranes to create enclosed spaces. Their key advantages are their light weight, ability to span large distances, quick assembly and disassembly times, and relatively low cost compared to permanent structures. There are two main types: air-supported structures, which use low internal pressure to support a single membrane, and air-inflated structures, which use pressurized air within building elements but keep the interior at atmospheric pressure. Materials used include plastics, fabrics, rubber, and metal foils.