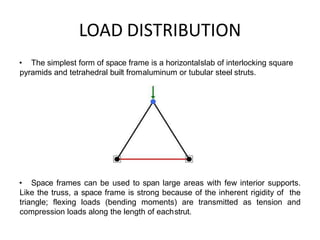
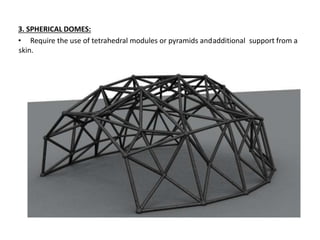
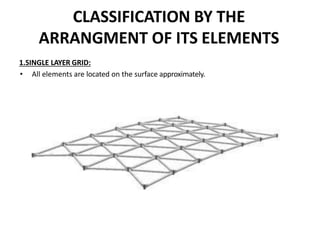
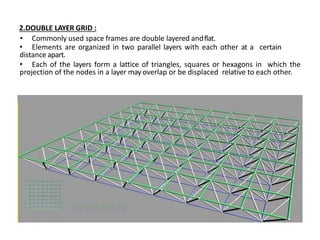
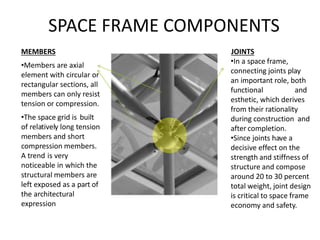
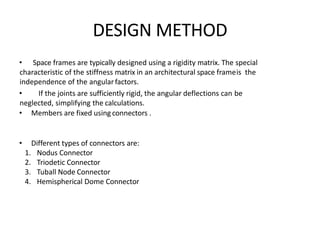
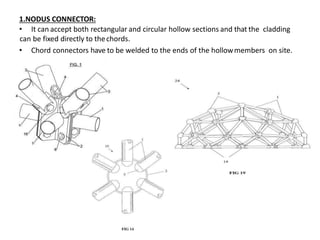
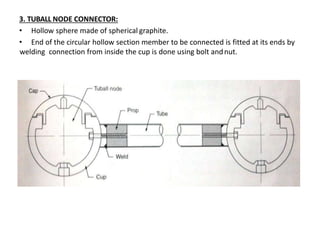
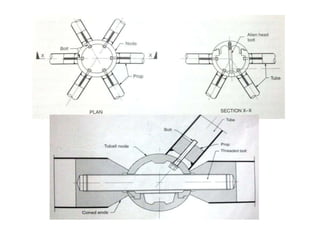
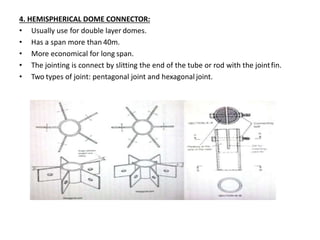
A space frame is a lightweight, rigid structure made of interlocking struts that can span large areas with minimal interior supports. Developed in the early 20th century, space frames utilize various materials, with steel and timber being prominent, and come in multiple configurations for different applications, such as barrel vaults and spherical domes. Their design emphasizes joint connection for structural integrity and aesthetic value, making space frames efficient and versatile in architectural design.